Compare commits
No commits in common. "gh-pages" and "master" have entirely different histories.
@ -1,47 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
body {
|
|
||||||
font-family: questrial, sans-serif;
|
|
||||||
font-size:0.95em;
|
|
||||||
line-height: 1.5;
|
|
||||||
color: #f7f7f7;
|
|
||||||
background-color: #1744fa;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
a:link {color: #f7f7f7; text-decoration: underline; }
|
|
||||||
a:active {color: #f7f7f7; text-decoration: underline; }
|
|
||||||
a:visited {color: #f7f7f7; text-decoration: underline; }
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
content {
|
|
||||||
padding: 1.5em;
|
|
||||||
max-width: 45em;
|
|
||||||
display: block;
|
|
||||||
overflow:hidden;
|
|
||||||
text-align: justify;
|
|
||||||
margin: auto;
|
|
||||||
word-wrap: break-word;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
content img {
|
|
||||||
text-align: center;
|
|
||||||
display: block;
|
|
||||||
margin: 0 auto;
|
|
||||||
width: 100%;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
content #draw_canvas {
|
|
||||||
display: block;
|
|
||||||
margin: 0 auto;
|
|
||||||
width: 45em;
|
|
||||||
height: 13em;
|
|
||||||
border: 1px solid #aaaaaa;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.noir {
|
|
||||||
xborder: 1px solid black;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.rouge {
|
|
||||||
xborder: 1px solid red;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
1
.gitignore
vendored
1
.gitignore
vendored
@ -1,2 +1 @@
|
|||||||
_site
|
_site
|
||||||
.DS_Store
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
22
LICENSE
Normal file
22
LICENSE
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
|||||||
|
The MIT License (MIT)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Copyright (c) 2015 amsterdamcomics
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||||
|
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||||
|
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||||
|
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||||
|
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||||
|
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||||
|
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||||
|
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||||
|
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||||
|
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||||
|
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||||
|
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||||
|
SOFTWARE.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -1,38 +1,40 @@
|
|||||||
---
|
# Objects & Simulations
|
||||||
layout: index
|
|
||||||
title: Objects & Simulations
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#Objects & Simulations
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<canvas id="draw_canvas"></canvas>
|
<img src="https://le-club-des-sans-sujets.org/w/objects-and-simulations/img/objects-simulations.png" width="100%">
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
###Keywords
|
_Course taught in 2015_
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Keywords
|
||||||
object-oriented programming, graphical simulation, physics, behaviour modelling
|
object-oriented programming, graphical simulation, physics, behaviour modelling
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
##Introduction
|
## Introduction
|
||||||
This class investigates the use of software as ground for design observations, explorations and artistic expression. Using software one can formally describe objects and the types of relations these objects can have with each other and their environment. Simulations can be devised to perform such relational dynamics between objects and their environment. Emergent object-environment behaviours can thus be observed which would otherwise be impossible to even predict.
|
This class investigates the use of software as ground for design observations, explorations and artistic expression. Using software one can formally describe objects and the types of relations these objects can have with each other and their environment. Simulations can be devised to perform such relational dynamics between objects and their environment. Emergent object-environment behaviours can thus be observed which would otherwise be impossible to even predict.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This course focuses on basic concepts and techniques of object oriented programming and graphical computer simulations, that is, it introduces ways in which object oriented modelling may be used to create performative contexts where complex graphical artefacts may emerge from.
|
This course focuses on basic concepts and techniques of object oriented programming and graphical computer simulations, that is, it introduces ways in which object oriented modelling may be used to create performative contexts where complex graphical artefacts may emerge from.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Participants will have a chance to derive a practical “hands-on” understanding of computational and graphical programming with an emphasis on object and behaviour modelling.
|
Participants will have a chance to derive a practical “hands-on” understanding of computational and graphical programming with an emphasis on object and behaviour modelling.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
##Content
|
## Content
|
||||||
Five areas of exploration will be covered during this course: (1) Object-Oriented Programming, (2) Affine Transformation, (3) Oscillations, (4) Physics Simulation, and (5) (Basic) Behaviour Modelling.
|
Five areas of exploration will be covered during this course: (1) Object-Oriented Programming, (2) Affine Transformation, (3) Oscillations, (4) Physics Simulation, and (5) (Basic) Behaviour Modelling.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Each area is composed of various small exercises where participants are expected to program computational artefacts reflecting their learning as they go along. Participants will be presented various ways of quickly and easily composing programs incorporating a mix of the above subjects, leading them to conceptualise and implement a final exploration of their own.
|
Each area is composed of various small exercises where participants are expected to program computational artefacts reflecting their learning as they go along. Participants will be presented various ways of quickly and easily composing programs incorporating a mix of the above subjects, leading them to conceptualise and implement a final exploration of their own.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This course not only focuses on tools, but on how these tools can become a part of the ways participants work and think, enabling them to prototype, experiment and explore emerging ideas more quickly and more effectively using software.
|
This course not only focuses on tools, but on how these tools can become a part of the ways participants work and think, enabling them to prototype, experiment and explore emerging ideas more quickly and more effectively using software.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
##Syllabus
|
## Programming environment
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Objects](objects.html)
|
[Processing](https://processing.org/)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Environment - [Affine Transformation](affine.html) and [Oscillators](/)
|
## Basic Notions
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Simulation](/)
|
[Objects](https://le-club-des-sans-sujets.org/w/objects-and-simulations/objects.html)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
##Learnings Expectations
|
[Affine Transformation](https://le-club-des-sans-sujets.org/w/objects-and-simulations/affine.html)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[Oscillators](https://le-club-des-sans-sujets.org/w/objects-and-simulations/oscillations.html)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Learnings Expectations
|
||||||
__Discourse:__
|
__Discourse:__
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- develop an appreciation of the field of generative design.
|
- develop an appreciation of the field of generative design.
|
||||||
@ -45,7 +47,7 @@ __Skills:__
|
|||||||
- learn how to develop expressive and interactive graphical artefacts and representations.
|
- learn how to develop expressive and interactive graphical artefacts and representations.
|
||||||
- learn how to develop social interactions using software.
|
- learn how to develop social interactions using software.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
##Evaluation Criteria
|
## Evaluation Criteria
|
||||||
__Evaluation Criteria (course)__
|
__Evaluation Criteria (course)__
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The course will be a success if ...
|
The course will be a success if ...
|
||||||
@ -63,7 +65,7 @@ On which basis will the students and their work be evaluated?
|
|||||||
- commitment: how much energy did the student invest over the course of the workshop.
|
- commitment: how much energy did the student invest over the course of the workshop.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
##Reading List
|
## Reading List
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[DeLanda, Manuel. _Philosophy and Simulation: The Emergence of Synthetic Reason_. London ; New York, NY: Continuum, 2011.](http://www.amazon.com/Philosophy-Simulation-Emergence-Synthetic-Reason/dp/1441170286/ref=sr_1_1?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1425221232&sr=1-1&keywords=Philosophy+and+Simulation%3A)
|
[DeLanda, Manuel. _Philosophy and Simulation: The Emergence of Synthetic Reason_. London ; New York, NY: Continuum, 2011.](http://www.amazon.com/Philosophy-Simulation-Emergence-Synthetic-Reason/dp/1441170286/ref=sr_1_1?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1425221232&sr=1-1&keywords=Philosophy+and+Simulation%3A)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -71,11 +73,4 @@ On which basis will the students and their work be evaluated?
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
[Braitenberg, Valentino. _Vehicles: Experiments in Synthetic Psychology_. Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press, 1986.](http://www.amazon.com/Vehicles-Experiments-Psychology-Valentino-Braitenberg/dp/0262521121/ref=sr_1_1?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1425221365&sr=1-1&keywords=Vehicles%3A+Experiments+in+Synthetic+Psychology)
|
[Braitenberg, Valentino. _Vehicles: Experiments in Synthetic Psychology_. Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press, 1986.](http://www.amazon.com/Vehicles-Experiments-Psychology-Valentino-Braitenberg/dp/0262521121/ref=sr_1_1?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1425221365&sr=1-1&keywords=Vehicles%3A+Experiments+in+Synthetic+Psychology)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Gamma, Erich, ed. _Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software_. Reading, Mass: Addison-Wesley, 1995.](http://www.amazon.com/Design-Patterns-Elements-Reusable-Object-Oriented/dp/0201633612/ref=sr_1_1?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1425221395&sr=1-1&keywords=Design+Patterns%3A+Elements+of+Reusable+Object-Oriented+Software)
|
[Gamma, Erich, ed. _Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software_. Reading, Mass: Addison-Wesley, 1995.](http://www.amazon.com/Design-Patterns-Elements-Reusable-Object-Oriented/dp/0201633612/ref=sr_1_1?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1425221395&sr=1-1&keywords=Design+Patterns%3A+Elements+of+Reusable+Object-Oriented+Software)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<!-- Notes -->
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<!-- Jacob von Uexkull -->
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<!-- http://www.gliffy.com/uses/uml-software/ -->
|
|
||||||
13
_config.yml
13
_config.yml
@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
# Site settings
|
|
||||||
title: Objects & Simulations
|
|
||||||
email: d@gauthiier.info
|
|
||||||
description: Course focusing on basic concepts and techniques of object oriented programming and graphical computer simulations.
|
|
||||||
baseurl: ""
|
|
||||||
url: "http://gauthiier.github.io/objects-and-simulations" # the base hostname & protocol for your site
|
|
||||||
github_username: gauthiier
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Build settings
|
|
||||||
markdown: kramdown
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Custom Variables
|
|
||||||
#navigation: true
|
|
||||||
@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
|
||||||
<html>
|
|
||||||
<head>
|
|
||||||
<meta charset="utf-8">
|
|
||||||
<title>Objects & Simulations</title>
|
|
||||||
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="{{ site.url }}/+++/le_style.css" media="screen"/>
|
|
||||||
<script src="//use.edgefonts.net/questrial.js"></script>
|
|
||||||
</head>
|
|
||||||
<body>
|
|
||||||
<content>
|
|
||||||
<div id="main" class="section">
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
{{ content }}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
</div>
|
|
||||||
</content>
|
|
||||||
</body>
|
|
||||||
</html>
|
|
||||||
@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
|
||||||
<html>
|
|
||||||
<head>
|
|
||||||
<meta charset="utf-8">
|
|
||||||
<title>Objects & Simulations</title>
|
|
||||||
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="{{ site.url }}/+++/le_style.css" media="screen"/>
|
|
||||||
<script src="//use.edgefonts.net/questrial.js"></script>
|
|
||||||
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/paper.js"></script>
|
|
||||||
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/paper-error.js"></script>
|
|
||||||
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/paper-agents.js"></script>
|
|
||||||
<script type="text/paperscript" canvas="draw_canvas">
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
var randomAgent = new Agent(view.center);
|
|
||||||
randomAgent.addBehaviour(new Behaviour.RandomWalk());
|
|
||||||
randomAgent.addBehaviour(new Behaviour.Trace())
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
var creepyAgent = new Agent(view.center);
|
|
||||||
creepyAgent.addBehaviour(new Behaviour.FollowPoint(randomAgent.position));
|
|
||||||
creepyAgent.shape.fillColor = "#f7f7f7";
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
function onFrame() {
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
</script>
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
</head>
|
|
||||||
<body>
|
|
||||||
<content>
|
|
||||||
<div id="main" class="section">
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
{{ content }}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
</div>
|
|
||||||
</content>
|
|
||||||
</body>
|
|
||||||
</html>
|
|
||||||
@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
|
||||||
<html>
|
|
||||||
<head>
|
|
||||||
<meta charset="utf-8">
|
|
||||||
<title>Objects & Simulations</title>
|
|
||||||
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="{{ site.url }}/+++/le_style.css" media="screen"/>
|
|
||||||
<script src="//use.edgefonts.net/questrial.js"></script>
|
|
||||||
<!-- mathjax config similar to math.stackexchange -->
|
|
||||||
<script type="text/x-mathjax-config">
|
|
||||||
MathJax.Hub.Config({
|
|
||||||
asciimath2jax: {
|
|
||||||
delimiters: [['$','$'], ['`','`']],
|
|
||||||
skipTags: ["script","noscript","style","textarea","pre","code"]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
});
|
|
||||||
</script>
|
|
||||||
<script src="http://cdn.mathjax.org/mathjax/latest/MathJax.js?config=AM_HTMLorMML-full" type="text/javascript"></script>
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
</head>
|
|
||||||
<body>
|
|
||||||
<content>
|
|
||||||
<div id="main" class="section">
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
{{ content }}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
</div>
|
|
||||||
</content>
|
|
||||||
</body>
|
|
||||||
</html>
|
|
||||||
@ -1,4 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
---
|
|
||||||
layout: default
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
{{ content }}
|
|
||||||
104
affine.md
104
affine.md
@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
---
|
|
||||||
layout: math
|
|
||||||
title: Environment
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Affine Transforms & Vector Math
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class Transformable {
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// attaributes
|
|
||||||
PVector _position;
|
|
||||||
float _rotation;
|
|
||||||
float _scale;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
...
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public void display() {
|
|
||||||
pushMatrix();
|
|
||||||
translate(_position.x, _position.y);
|
|
||||||
rotate(_rotation);
|
|
||||||
scale(_scale);
|
|
||||||
draw_shape();
|
|
||||||
popMatrix();
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
...
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
};
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
What is a geometry / shape?
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
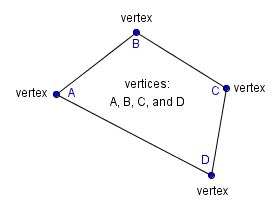
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
What types of (2D / 3D) transformations can we apply to geometries / shapes?
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<!-- ASCIImath -->
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
What is a matrix Matrix?
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
[[a, b, c], [d, e, f], [g, h, i]]
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Matrix [3 x 3] multiplication with a Vector [1 x 3]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
[[a, b, c], [d, e, f], [g, h, i]] [[x], [y], [z]] = [[ax + by + cz], [dx + ey + fz], [gx + hy + iz]]
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
What types of geometrical transformations (vertices transformation) can we perform using a Matrix?
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Translation
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
[[1, 0, tx], [0, 1, ty], [0, 0, 1]] [[x], [y], [1]] = [[dot x], [dot y], [1]]
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Scaling
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
[[sx, 0, 0], [0, sy, 0], [0, 0, 1]] [[x], [y], [1]] = [[dot x], [dot y], [1]]
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Rotation $theta$
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
[[cos theta, -sin theta, 0], [sin theta, cos theta, 0], [0, 0, 1]] [[x], [y], [1]] = [[dot x], [dot y], [1]]
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Shearing
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
[[1, shx, 0], [shy, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]] [[x], [y], [1]] = [[dot x], [dot y], [1]]
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
What is an Affine Transform?
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Affine Transform Matrix comprises a Translation, Scaling, Rotation and Shearing
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
[[sx * cos theta, -sin theta * shx, tx], [sin theta * shy, sy * cos theta, ty], [0, 0, 1]] [[x], [y], [1]] = [[dot x], [dot y], [1]]
|
|
||||||
$
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Yes, but what other types of transformations exists?
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
56
brief.md
56
brief.md
@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
---
|
|
||||||
layout: default
|
|
||||||
title: Project Brief
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#Micrographia der (digitalen) Mikrowelt
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
During the course of this class, we have discovered a novel method to observe digital native microcreatures living in a multitude of digital devices. These creatures have been vaguely reported in scientific litterature over the last 20 years, yet our method is the first able to graphicaly identify and catalogue them accurately.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The brief is thus to develop a "digital micrographia" of these creatures, that is, reporting on your novel observations, formalising the knowledge you acquired about these microwelt creatures.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You are asked to create __two__ micrographical reports of __two__ different creatures observed in the digital wild.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A Report consists of four sections:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- Image of the microcreature
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. __Name:__ - Microcreature Name
|
|
||||||
2. __Occurence:__ - Date of first observation
|
|
||||||
3. __Where:__ - Where was the creature first observed
|
|
||||||
4. __Characteristics:__ - What are the creature's specific features / behaviours
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Teams of 2 (scientists).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Bacteroid Base64
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. Name: Bacteroid Base64
|
|
||||||
2. Occurence: 1992
|
|
||||||
3. Where: Bacteroid Base64 was first observed in a defunct laptop found on train DSB D2344-B connecting Hamburg to Copenhagen.
|
|
||||||
4. Characteristics: Bacteroid Base64 displays traits of an tribe nurturing itself in herds comprising up to hundreds of creatures. Its main nutriment is 16-bits memory sectors found in defunct Seagate Hard Disk Drives (HDD).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Constraints
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. All micrographical element __must__ extend the class Creature to be drawn in the mikrowelt.
|
|
||||||
2. All creatures of a specific type are drawn with a single color stroke and without fill (noFill) or a fill of the same color with maximium of 30 alpha.
|
|
||||||
3. The background color of your sketch is - background(23, 68, 250);
|
|
||||||
3. Creature animations can be performed using __Oscillators__, __Physics__ or __Behaviors__.
|
|
||||||
4. There will be _no_ gravity in the mikrowelt.
|
|
||||||
5. All advanced Behaviors __must__ implement the interface __CreatureBehavior__.
|
|
||||||
6. The canvas size has to be of dimension 650 width X 650 height.
|
|
||||||
7. The name of your creature class has to be the same in you report.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## References
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Micrographia by Robert Hooke](http://www.gutenberg.org/files/15491/15491-h/15491-h.htm)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<!-- notes -->
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
54
day1/sketch_things_and_surfaces/Cup.pde
Normal file
54
day1/sketch_things_and_surfaces/Cup.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Cup extends Thing {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int _temperature;
|
||||||
|
boolean _empty;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Cup(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
|
||||||
|
super(x, y, w, h);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void filled() {
|
||||||
|
_empty = false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void drink() {
|
||||||
|
_empty = true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void display() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
super.display();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if(_empty) {
|
||||||
|
fill(255);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
fill(0,0,255);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ellipse(_position.x, _position.y, _width, _height);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void mousePressed(int mx, int my) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float d = dist( _position.x, _position.y, mx, my);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
println("mouse");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if(d < _width) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
println("touched!");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if(_empty) {
|
||||||
|
filled();
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
drink();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
15
day1/sketch_things_and_surfaces/Desk.pde
Normal file
15
day1/sketch_things_and_surfaces/Desk.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Desk extends Surface {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int nbr_legs;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void display() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
fill(0,255,0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
rect(20, 20, 20 + _width, 20 + _height);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
super.display();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
31
day1/sketch_things_and_surfaces/Surface.pde
Normal file
31
day1/sketch_things_and_surfaces/Surface.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Surface {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ArrayList<Thing> array = new ArrayList<Thing>();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int _width;
|
||||||
|
int _height;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void addItem(Thing item) {
|
||||||
|
array.add(item);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void display() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for(int i = 0; i < array.size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
Thing t = array.get(i);
|
||||||
|
t.display();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void mousePressed(int mx, int my) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for(int i = 0; i < array.size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
Thing t = array.get(i);
|
||||||
|
t.mousePressed(mx, my);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
27
day1/sketch_things_and_surfaces/Thing.pde
Normal file
27
day1/sketch_things_and_surfaces/Thing.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Thing {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
PVector _position;
|
||||||
|
int _weight;
|
||||||
|
color _color;
|
||||||
|
int _width;
|
||||||
|
int _height;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Thing(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
|
||||||
|
_position = new PVector();
|
||||||
|
_position.x = x;
|
||||||
|
_position.y = y;
|
||||||
|
_width = w;
|
||||||
|
_height = h;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void move(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
_position.x = x;
|
||||||
|
_position.y = y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void display() {}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void mousePressed(int mx, int my) {}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
2
day1/sketch_things_and_surfaces/sketch.properties
Normal file
2
day1/sketch_things_and_surfaces/sketch.properties
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||||||
|
mode.id=processing.mode.java.JavaMode
|
||||||
|
mode=Java
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Desk desk = new Desk();
|
||||||
|
int NBR_CUPS = 5;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
size(500, 500);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
desk._width = 450;
|
||||||
|
desk._height = 450;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for(int i = 0; i < NBR_CUPS; i++) {
|
||||||
|
Cup c = new Cup(i * 100, i * 100, 20, 20);
|
||||||
|
desk.addItem(c);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
desk.display();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void mousePressed() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
desk.mousePressed(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
21
day2/sketch_transformable/Circle.pde
Normal file
21
day2/sketch_transformable/Circle.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Circle extends Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Circle(int x, int y, int r) {
|
||||||
|
super(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_radius = r;
|
||||||
|
ellipseMode(RADIUS);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){
|
||||||
|
ellipse(0, 0, _radius, _radius);
|
||||||
|
line(0, 0, _radius, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my) {
|
||||||
|
if(dist(mx, my, _position.x, _position.y) < _radius) return true;
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
22
day2/sketch_transformable/Square.pde
Normal file
22
day2/sketch_transformable/Square.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Square extends Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int _width;
|
||||||
|
int _height;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Square(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
|
||||||
|
super(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_width = w;
|
||||||
|
_height = h;
|
||||||
|
rectMode(CENTER);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){
|
||||||
|
rect(0, 0, _width, _height);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my) {
|
||||||
|
if(dist(mx, my, _position.x, _position.y) < _width /2) return true;
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
86
day2/sketch_transformable/Transformable.pde
Normal file
86
day2/sketch_transformable/Transformable.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// attaributes
|
||||||
|
PVector _position;
|
||||||
|
float _rotation;
|
||||||
|
float _scale;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// constructor (without arguments)
|
||||||
|
public Transformable() {
|
||||||
|
_position = new PVector(0, 0);
|
||||||
|
_rotation = 0;
|
||||||
|
_scale = 1.0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// constructor (with arguments)
|
||||||
|
public Transformable(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
_position = new PVector(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_rotation = 0;
|
||||||
|
_scale = 1.0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// (absolute) transforms
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void rotate_to(float r) {
|
||||||
|
_rotation = r;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void translate_to(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
_position.x = x;
|
||||||
|
_position.y = y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void scale_to(float s) {
|
||||||
|
_scale = s;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// (incremental) transforms
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void rotate_increment(float r) {
|
||||||
|
_rotation += r;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void translate_increment(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
_position.x += x;
|
||||||
|
_position.y += y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void scale_increment(float s) {
|
||||||
|
_scale += s;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// display method
|
||||||
|
// + applies transformations
|
||||||
|
// + draws shape of the subclass
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void display() {
|
||||||
|
pushMatrix();
|
||||||
|
translate(_position.x, _position.y);
|
||||||
|
rotate(_rotation);
|
||||||
|
scale(_scale);
|
||||||
|
draw_shape();
|
||||||
|
popMatrix();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// helper method - distance_from
|
||||||
|
// + computes distance from other position
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float distance_from(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
return dist(_position.x, _position.y, x, y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// ** METHODS FOR SUBCLASSES **
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// draws a (subclass) shape (in own coordinates)
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// evaluates if mx and my are inside the (subclass) shape
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my){return false;}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
37
day2/sketch_transformable/Triangle.pde
Normal file
37
day2/sketch_transformable/Triangle.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Triangle extends Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int _radius;
|
||||||
|
PVector A, B, C;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Triangle(int x, int y, int r) {
|
||||||
|
super(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_radius = r;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A = new PVector();
|
||||||
|
B = new PVector();
|
||||||
|
C = new PVector();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float theta = TWO_PI/3;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A.x = cos(0 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
A.y = sin(0 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
B.x = cos(1 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
B.y = sin(1 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
C.x = cos(2 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
C.y = sin(2 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){
|
||||||
|
triangle(A.x, A.y, B.x, B.y, C.x, C.y);
|
||||||
|
line(0, 0, A.x, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my) {
|
||||||
|
if(dist(mx, my, _position.x, _position.y) < _radius) return true;
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
2
day2/sketch_transformable/sketch.properties
Normal file
2
day2/sketch_transformable/sketch.properties
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||||||
|
mode.id=processing.mode.java.JavaMode
|
||||||
|
mode=Java
|
||||||
15
day2/sketch_transformable/sketch_transformable.pde
Normal file
15
day2/sketch_transformable/sketch_transformable.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
|||||||
|
final int CANVAS_WIDTH = 500;
|
||||||
|
final int CANVAS_HEIGHT = 500;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(CANVAS_WIDTH, CANVAS_HEIGHT);
|
||||||
|
background(23, 68, 250);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
background(23, 68, 250);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void mousePressed() {
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
21
day2/sketch_transformable_click_create/Circle.pde
Normal file
21
day2/sketch_transformable_click_create/Circle.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Circle extends Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Circle(int x, int y, int r) {
|
||||||
|
super(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_radius = r;
|
||||||
|
ellipseMode(RADIUS);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){
|
||||||
|
ellipse(0, 0, _radius, _radius);
|
||||||
|
line(0, 0, _radius, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my) {
|
||||||
|
if(dist(mx, my, _position.x, _position.y) < _radius) return true;
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
22
day2/sketch_transformable_click_create/Square.pde
Normal file
22
day2/sketch_transformable_click_create/Square.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Square extends Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int _width;
|
||||||
|
int _height;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Square(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
|
||||||
|
super(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_width = w;
|
||||||
|
_height = h;
|
||||||
|
rectMode(CENTER);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){
|
||||||
|
rect(0, 0, _width, _height);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my) {
|
||||||
|
if(dist(mx, my, _position.x, _position.y) < _width /2) return true;
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
86
day2/sketch_transformable_click_create/Transformable.pde
Normal file
86
day2/sketch_transformable_click_create/Transformable.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// attaributes
|
||||||
|
PVector _position;
|
||||||
|
float _rotation;
|
||||||
|
float _scale;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// constructor (without arguments)
|
||||||
|
public Transformable() {
|
||||||
|
_position = new PVector(0, 0);
|
||||||
|
_rotation = 0;
|
||||||
|
_scale = 1.0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// constructor (with arguments)
|
||||||
|
public Transformable(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
_position = new PVector(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_rotation = 0;
|
||||||
|
_scale = 1.0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// (absolute) transforms
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void rotate_to(float r) {
|
||||||
|
_rotation = r;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void translate_to(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
_position.x = x;
|
||||||
|
_position.y = y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void scale_to(float s) {
|
||||||
|
_scale = s;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// (incremental) transforms
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void rotate_increment(float r) {
|
||||||
|
_rotation += r;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void translate_increment(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
_position.x += x;
|
||||||
|
_position.y += y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void scale_increment(float s) {
|
||||||
|
_scale += s;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// display method
|
||||||
|
// + applies transformations
|
||||||
|
// + draws shape of the subclass
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void display() {
|
||||||
|
pushMatrix();
|
||||||
|
translate(_position.x, _position.y);
|
||||||
|
rotate(_rotation);
|
||||||
|
scale(_scale);
|
||||||
|
draw_shape();
|
||||||
|
popMatrix();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// helper method - distance_from
|
||||||
|
// + computes distance from other position
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float distance_from(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
return dist(_position.x, _position.y, x, y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// ** METHODS FOR SUBCLASSES **
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// draws a (subclass) shape (in own coordinates)
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// evaluates if mx and my are inside the (subclass) shape
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my){return false;}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
37
day2/sketch_transformable_click_create/Triangle.pde
Normal file
37
day2/sketch_transformable_click_create/Triangle.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Triangle extends Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int _radius;
|
||||||
|
PVector A, B, C;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Triangle(int x, int y, int r) {
|
||||||
|
super(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_radius = r;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A = new PVector();
|
||||||
|
B = new PVector();
|
||||||
|
C = new PVector();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float theta = TWO_PI/3;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A.x = cos(0 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
A.y = sin(0 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
B.x = cos(1 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
B.y = sin(1 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
C.x = cos(2 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
C.y = sin(2 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){
|
||||||
|
triangle(A.x, A.y, B.x, B.y, C.x, C.y);
|
||||||
|
line(0, 0, A.x, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my) {
|
||||||
|
if(dist(mx, my, _position.x, _position.y) < _radius) return true;
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
2
day2/sketch_transformable_click_create/sketch.properties
Normal file
2
day2/sketch_transformable_click_create/sketch.properties
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||||||
|
mode.id=processing.mode.java.JavaMode
|
||||||
|
mode=Java
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
|||||||
|
final int CANVAS_WIDTH = 500;
|
||||||
|
final int CANVAS_HEIGHT = 500;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ArrayList<Transformable> elements = new ArrayList<Transformable>();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(CANVAS_WIDTH, CANVAS_HEIGHT, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
background(23, 68, 250);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
background(23, 68, 250);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if(frameCount % 2 == 0) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for(int i = 0; i < elements.size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
Transformable t = elements.get(i);
|
||||||
|
t.rotate_increment(0.01);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
stroke(255);
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for(int i = 0; i < elements.size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
Transformable t = elements.get(i);
|
||||||
|
t.display();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void mousePressed() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float r = random(0, 3);
|
||||||
|
Transformable t;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if(r < 1) {
|
||||||
|
t = new Circle(mouseX, mouseY, 25);
|
||||||
|
} else if(r < 2) {
|
||||||
|
t = new Square(mouseX, mouseY, 35, 35);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
t = new Triangle(mouseX, mouseY, 25);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
elements.add(t);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void mouseDragged() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for(int i = 0; i < elements.size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
Transformable t = elements.get(i);
|
||||||
|
if(t.inside(mouseX, mouseY)) {
|
||||||
|
t.translate_to(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
21
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/Circle.pde
Normal file
21
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/Circle.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Circle extends Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Circle(int x, int y, int r) {
|
||||||
|
super(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_radius = r;
|
||||||
|
ellipseMode(RADIUS);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){
|
||||||
|
ellipse(0, 0, _radius, _radius);
|
||||||
|
line(0, 0, _radius, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my) {
|
||||||
|
if(dist(mx, my, _position.x, _position.y) < _radius) return true;
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
20
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/Oscillator.pde
Normal file
20
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/Oscillator.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Oscillator {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float _step, _theta;
|
||||||
|
float _min, _max, _length;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Oscillator(float min, float max, float step) {
|
||||||
|
_min = min;
|
||||||
|
_max = max;
|
||||||
|
_length = max - min;
|
||||||
|
_step = step;
|
||||||
|
_theta = 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float update() {
|
||||||
|
_theta += _step;
|
||||||
|
return (sin(_theta) * (_length / 2)) + (_length / 2) + _min;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
22
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/Square.pde
Normal file
22
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/Square.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Square extends Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int _width;
|
||||||
|
int _height;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Square(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
|
||||||
|
super(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_width = w;
|
||||||
|
_height = h;
|
||||||
|
rectMode(CENTER);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){
|
||||||
|
rect(0, 0, _width, _height);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my) {
|
||||||
|
if(dist(mx, my, _position.x, _position.y) < _width /2) return true;
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
86
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/Transformable.pde
Normal file
86
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/Transformable.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// attaributes
|
||||||
|
PVector _position;
|
||||||
|
float _rotation;
|
||||||
|
float _scale;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// constructor (without arguments)
|
||||||
|
public Transformable() {
|
||||||
|
_position = new PVector(0, 0);
|
||||||
|
_rotation = 0;
|
||||||
|
_scale = 1.0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// constructor (with arguments)
|
||||||
|
public Transformable(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
_position = new PVector(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_rotation = 0;
|
||||||
|
_scale = 1.0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// (absolute) transforms
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void rotate_to(float r) {
|
||||||
|
_rotation = r;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void translate_to(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
_position.x = x;
|
||||||
|
_position.y = y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void scale_to(float s) {
|
||||||
|
_scale = s;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// (incremental) transforms
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void rotate_increment(float r) {
|
||||||
|
_rotation += r;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void translate_increment(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
_position.x += x;
|
||||||
|
_position.y += y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void scale_increment(float s) {
|
||||||
|
_scale += s;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// display method
|
||||||
|
// + applies transformations
|
||||||
|
// + draws shape of the subclass
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void display() {
|
||||||
|
pushMatrix();
|
||||||
|
translate(_position.x, _position.y);
|
||||||
|
rotate(_rotation);
|
||||||
|
scale(_scale);
|
||||||
|
draw_shape();
|
||||||
|
popMatrix();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// helper method - distance_from
|
||||||
|
// + computes distance from other position
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float distance_from(int x, int y) {
|
||||||
|
return dist(_position.x, _position.y, x, y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
///////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// ** METHODS FOR SUBCLASSES **
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// draws a (subclass) shape (in own coordinates)
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// evaluates if mx and my are inside the (subclass) shape
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my){return false;}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
37
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/Triangle.pde
Normal file
37
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/Triangle.pde
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
|||||||
|
class Triangle extends Transformable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int _radius;
|
||||||
|
PVector A, B, C;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Triangle(int x, int y, int r) {
|
||||||
|
super(x, y);
|
||||||
|
_radius = r;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A = new PVector();
|
||||||
|
B = new PVector();
|
||||||
|
C = new PVector();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float theta = TWO_PI/3;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A.x = cos(0 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
A.y = sin(0 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
B.x = cos(1 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
B.y = sin(1 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
C.x = cos(2 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
C.y = sin(2 * theta) * _radius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void draw_shape(){
|
||||||
|
triangle(A.x, A.y, B.x, B.y, C.x, C.y);
|
||||||
|
line(0, 0, A.x, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean inside(int mx, int my) {
|
||||||
|
if(dist(mx, my, _position.x, _position.y) < _radius) return true;
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
2
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/sketch.properties
Normal file
2
day2/sketch_transformable_oscillator/sketch.properties
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||||||
|
mode.id=processing.mode.java.JavaMode
|
||||||
|
mode=Java
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final int CANVAS_WIDTH = 500;
|
||||||
|
final int CANVAS_HEIGHT = 500;
|
||||||
|
final int NBR_ELEMENTS = 16;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Transformable t;
|
||||||
|
Oscillator osc = new Oscillator(0, 5, 0.01);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
size(CANVAS_WIDTH, CANVAS_HEIGHT);
|
||||||
|
background(23, 68, 250);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
t = new Triangle(CANVAS_WIDTH / 2, CANVAS_HEIGHT / 2, 50);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
background(23, 68, 250);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
t.rotate_increment(0.01);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
t.scale_to(osc.update());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
stroke(255);
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
t.display();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
BIN
day3/libs/mathematik/library/mathematik.jar
Executable file
BIN
day3/libs/mathematik/library/mathematik.jar
Executable file
Binary file not shown.
89
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/BSpline.java
Executable file
89
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/BSpline.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Vector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* b-spline source code from: Tim Lambert 'nice page on curves, splines etc.'
|
||||||
|
* http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~lambert/splines/
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public abstract class BSpline {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* the basis function for a cubic B spline */
|
||||||
|
private static float b(int i, float t) {
|
||||||
|
switch (i) {
|
||||||
|
case -2:
|
||||||
|
return (((-t + 3) * t - 3) * t + 1) / 6;
|
||||||
|
case -1:
|
||||||
|
return (((3 * t - 6) * t) * t + 4) / 6;
|
||||||
|
case 0:
|
||||||
|
return (((-3 * t + 3) * t + 3) * t + 1) / 6;
|
||||||
|
case 1:
|
||||||
|
return (t * t * t) / 6;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return 0; //we only get here if an invalid i is specified
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* evaluate a point on the B spline */
|
||||||
|
private static Vector3f p(Vector<Vector3f> thePoints, int i, float t) {
|
||||||
|
Vector3f p = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
for (int j = -2; j <= 1; j++) {
|
||||||
|
p.x += b(j, t) * thePoints.get(i + j).x;
|
||||||
|
p.y += b(j, t) * thePoints.get(i + j).y;
|
||||||
|
p.z += b(j, t) * thePoints.get(i + j).z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return p;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static Vector<Vector3f> curve(Vector<Vector3f> thePoints, int theSteps, Vector<Vector3f> theResult) {
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 2; i < thePoints.size() - 1; i++) {
|
||||||
|
for (int j = 1; j <= theSteps; j++) {
|
||||||
|
theResult.add(p(thePoints, i, j / (float) theSteps));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return theResult;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static Vector<Vector3f> curve(Vector<Vector3f> thePoints, int theSteps) {
|
||||||
|
return curve(thePoints, theSteps, new Vector<Vector3f>());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static Vector<Vector3f> closeCurve(Vector<Vector3f> thePoints) {
|
||||||
|
/* copy points */
|
||||||
|
Vector<Vector3f> myClosedPoints = new Vector<Vector3f>();
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < thePoints.size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
myClosedPoints.add(thePoints.get(i));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* repeat first three points */
|
||||||
|
if (thePoints.size() > 2) {
|
||||||
|
myClosedPoints.add(thePoints.get(0));
|
||||||
|
myClosedPoints.add(thePoints.get(1));
|
||||||
|
myClosedPoints.add(thePoints.get(2));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return myClosedPoints;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
916
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Intersection.java
Executable file
916
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Intersection.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,916 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* beware this is not really in good shape. i ll read my linear algebra book and
|
||||||
|
* fix this class. someday. hopefully.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public final class Intersection
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable,
|
||||||
|
Mathematik {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5392974339890719551L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f h = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f s = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f q = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f _myTempEdge1 = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f _myTempEdge2 = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f _myTempNormal = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f pvec = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f tvec = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f qvec = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static boolean intersectRayPlane(final Ray3f theRay,
|
||||||
|
final Plane3f thePlane,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theResult,
|
||||||
|
final boolean doPlanar,
|
||||||
|
final boolean quad) {
|
||||||
|
Vector3f diff = mathematik.Util.sub(theRay.origin, thePlane.origin); // mathematik.Util.sub(theRay.origin, v0);
|
||||||
|
Vector3f edge1 = thePlane.vectorA; // mathematik.Util.sub(v1, v0);
|
||||||
|
Vector3f edge2 = thePlane.vectorB; // mathematik.Util.sub(v2, v0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector3f norm = thePlane.normal; //new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (thePlane.normal == null) {
|
||||||
|
thePlane.updateNormal();
|
||||||
|
norm = thePlane.normal;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float dirDotNorm = theRay.direction.dot(norm);
|
||||||
|
float sign;
|
||||||
|
if (dirDotNorm > EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
sign = 1;
|
||||||
|
} else if (dirDotNorm < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
sign = -1f;
|
||||||
|
dirDotNorm = -dirDotNorm;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
// ray and triangle are parallel
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myCross;
|
||||||
|
myCross = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
myCross.cross(diff, edge2);
|
||||||
|
float dirDotDiffxEdge2 = sign * theRay.direction.dot(myCross);
|
||||||
|
if (dirDotDiffxEdge2 > 0.0f) {
|
||||||
|
myCross = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
myCross.cross(edge1, diff);
|
||||||
|
float dirDotEdge1xDiff = sign * theRay.direction.dot(myCross);
|
||||||
|
if (dirDotEdge1xDiff >= 0.0f) {
|
||||||
|
if (!quad ? dirDotDiffxEdge2 + dirDotEdge1xDiff <= dirDotNorm : dirDotEdge1xDiff <= dirDotNorm) {
|
||||||
|
float diffDotNorm = -sign * diff.dot(norm);
|
||||||
|
if (diffDotNorm >= 0.0f) {
|
||||||
|
// ray intersects triangle
|
||||||
|
// if storage vector is null, just return true,
|
||||||
|
if (theResult == null) {
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// else fill in.
|
||||||
|
float inv = 1f / dirDotNorm;
|
||||||
|
float t = diffDotNorm * inv;
|
||||||
|
if (!doPlanar) {
|
||||||
|
theResult.set(theRay.origin);
|
||||||
|
theResult.add(theRay.direction.x * t,
|
||||||
|
theRay.direction.y * t,
|
||||||
|
theRay.direction.z * t);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
// these weights can be used to determine
|
||||||
|
// interpolated values, such as texture coord.
|
||||||
|
// eg. texcoord s,t at intersection point:
|
||||||
|
// s = w0*s0 + w1*s1 + w2*s2;
|
||||||
|
// t = w0*t0 + w1*t1 + w2*t2;
|
||||||
|
float w1 = dirDotDiffxEdge2 * inv;
|
||||||
|
float w2 = dirDotEdge1xDiff * inv;
|
||||||
|
//float w0 = 1.0f - w1 - w2;
|
||||||
|
theResult.set(t, w1, w2);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// /**
|
||||||
|
// * @deprecated not in good state.
|
||||||
|
// * @param v0 first point of the triangle.
|
||||||
|
// * @param v1 second point of the triangle.
|
||||||
|
// * @param v2 third point of the triangle.
|
||||||
|
// * @param store storage vector - if null, no intersection is calc'd
|
||||||
|
// * @param doPlanar true if we are calcing planar results.
|
||||||
|
// * @param quad
|
||||||
|
// * @return true if ray intersects triangle
|
||||||
|
// */
|
||||||
|
// public static boolean intersectRayTriangle(final Ray3f theRay,
|
||||||
|
// final Vector3f v0,
|
||||||
|
// final Vector3f v1,
|
||||||
|
// final Vector3f v2,
|
||||||
|
// final Vector3f store,
|
||||||
|
// final boolean doPlanar,
|
||||||
|
// final boolean quad) {
|
||||||
|
// Vector3f diff = mathematik.Util.sub(theRay.origin, v0);
|
||||||
|
// Vector3f edge1 = mathematik.Util.sub(v1, v0);
|
||||||
|
// Vector3f edge2 = mathematik.Util.sub(v2, v0);
|
||||||
|
// Vector3f norm = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
// norm.cross(edge1, edge2);
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// float dirDotNorm = theRay.direction.dot(norm);
|
||||||
|
// float sign;
|
||||||
|
// if (dirDotNorm > EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
// sign = 1;
|
||||||
|
// } else if (dirDotNorm < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
// sign = -1f;
|
||||||
|
// dirDotNorm = -dirDotNorm;
|
||||||
|
// } else {
|
||||||
|
// // ray and triangle are parallel
|
||||||
|
// return false;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// Vector3f myCross;
|
||||||
|
// myCross = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
// myCross.cross(diff, edge2);
|
||||||
|
// float dirDotDiffxEdge2 = sign * theRay.direction.dot(myCross);
|
||||||
|
// if (dirDotDiffxEdge2 > 0.0f) {
|
||||||
|
// myCross = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
// myCross.cross(edge1, diff);
|
||||||
|
// float dirDotEdge1xDiff = sign * theRay.direction.dot(myCross);
|
||||||
|
// if (dirDotEdge1xDiff >= 0.0f) {
|
||||||
|
// if (!quad ? dirDotDiffxEdge2 + dirDotEdge1xDiff <= dirDotNorm : dirDotEdge1xDiff <= dirDotNorm) {
|
||||||
|
// float diffDotNorm = -sign * diff.dot(norm);
|
||||||
|
// if (diffDotNorm >= 0.0f) {
|
||||||
|
// // ray intersects triangle
|
||||||
|
// // if storage vector is null, just return true,
|
||||||
|
// if (store == null) {
|
||||||
|
// return true;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// // else fill in.
|
||||||
|
// float inv = 1f / dirDotNorm;
|
||||||
|
// float t = diffDotNorm * inv;
|
||||||
|
// if (!doPlanar) {
|
||||||
|
// store.set(theRay.origin);
|
||||||
|
// store.add(theRay.direction.x * t,
|
||||||
|
// theRay.direction.y * t,
|
||||||
|
// theRay.direction.z * t);
|
||||||
|
// } else {
|
||||||
|
// // these weights can be used to determine
|
||||||
|
// // interpolated values, such as texture coord.
|
||||||
|
// // eg. texcoord s,t at intersection point:
|
||||||
|
// // s = w0*s0 + w1*s1 + w2*s2;
|
||||||
|
// // t = w0*t0 + w1*t1 + w2*t2;
|
||||||
|
// float w1 = dirDotDiffxEdge2 * inv;
|
||||||
|
// float w2 = dirDotEdge1xDiff * inv;
|
||||||
|
// //float w0 = 1.0f - w1 - w2;
|
||||||
|
// store.set(t, w1, w2);
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// return true;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// return false;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Practical Analysis of Optimized Ray-Triangle Intersection
|
||||||
|
* Tomas Moeller
|
||||||
|
* Department of Computer Engineering, Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* code rewritten to do tests on the sign of the determinant
|
||||||
|
* the division is before the test of the sign of the det
|
||||||
|
* and one CROSS has been moved out from the if-else if-else
|
||||||
|
* from -- http://www.cs.lth.se/home/Tomas_Akenine_Moller/raytri/raytri.c
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static boolean intersectRayTriangle(final Vector3f orig,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f dir,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f vert0,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f vert1,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f vert2,
|
||||||
|
float[] result) {
|
||||||
|
final int T = 0;
|
||||||
|
final int U = 1;
|
||||||
|
final int V = 2;
|
||||||
|
Vector3f edge1;
|
||||||
|
Vector3f edge2;
|
||||||
|
Vector3f tvec;
|
||||||
|
Vector3f pvec;
|
||||||
|
Vector3f qvec;
|
||||||
|
float det;
|
||||||
|
float inv_det;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* find vectors for two edges sharing vert0 */
|
||||||
|
edge1 = mathematik.Util.sub(vert1, vert0);
|
||||||
|
edge2 = mathematik.Util.sub(vert2, vert0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* begin calculating determinant - also used to calculate U parameter */
|
||||||
|
pvec = mathematik.Util.cross(dir, edge2);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* if determinant is near zero, ray lies in plane of triangle */
|
||||||
|
det = edge1.dot(pvec);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* calculate distance from vert0 to ray origin */
|
||||||
|
tvec = mathematik.Util.sub(orig, vert0);
|
||||||
|
inv_det = 1.0f / det;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
qvec = mathematik.Util.cross(tvec, edge1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (det > EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
result[U] = tvec.dot(pvec);
|
||||||
|
if (result[U] < 0.0f || result[U] > det) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* calculate V parameter and test bounds */
|
||||||
|
result[V] = dir.dot(qvec);
|
||||||
|
if (result[V] < 0.0f || result[U] + result[V] > det) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
} else if (det < -EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
/* calculate U parameter and test bounds */
|
||||||
|
result[U] = tvec.dot(pvec);
|
||||||
|
if (result[U] > 0.0f || result[U] < det) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* calculate V parameter and test bounds */
|
||||||
|
result[V] = dir.dot(qvec);
|
||||||
|
if (result[V] > 0.0f || result[U] + result[V] < det) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return false; /* ray is parallell to the plane of the triangle */
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
result[T] = edge2.dot(qvec) * inv_det;
|
||||||
|
result[U] *= inv_det;
|
||||||
|
result[V] *= inv_det;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* grabbed from Xith
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @todo not sure whether this is for ray-plane or line-plane intersection.
|
||||||
|
* but i think it s for latter, hence the method name.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param thePlane Plane3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theRay Ray3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theIntersectionPoint Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return float
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static float intersectLinePlane(final Ray3f theRay,
|
||||||
|
final Plane3f thePlane,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theIntersectionPoint) {
|
||||||
|
double time = 0;
|
||||||
|
_myTempNormal.cross(thePlane.vectorA, thePlane.vectorB);
|
||||||
|
double denom = _myTempNormal.dot(theRay.direction);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (denom == 0) {
|
||||||
|
System.err.println("### ERROR @ Intersection / NEGATIVE_INFINITY");
|
||||||
|
return Float.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
double numer = _myTempNormal.dot(theRay.origin);
|
||||||
|
double D = -(thePlane.origin.dot(_myTempNormal));
|
||||||
|
time = -((numer + D) / denom);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (theIntersectionPoint != null) {
|
||||||
|
theIntersectionPoint.set(theRay.direction);
|
||||||
|
theIntersectionPoint.scale((float) time);
|
||||||
|
theIntersectionPoint.add(theRay.origin);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return (float) time;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// /**
|
||||||
|
// * @deprecated this method might contain errors.
|
||||||
|
// * @param theRay Ray3f
|
||||||
|
// * @param thePlane Plane3f
|
||||||
|
// * @param theResult Vector3f
|
||||||
|
// * @param theCullingFlag boolean
|
||||||
|
// * @return float
|
||||||
|
// */
|
||||||
|
// public static float intersectRayTriangle(final Ray3f theRay,
|
||||||
|
// final Plane3f thePlane,
|
||||||
|
// final Vector3f theResult,
|
||||||
|
// final boolean theCullingFlag) {
|
||||||
|
// float a;
|
||||||
|
// float f;
|
||||||
|
// float u;
|
||||||
|
// float v;
|
||||||
|
// float t;
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// _myTempEdge1.set(thePlane.vectorA);
|
||||||
|
// _myTempEdge2.set(thePlane.vectorB);
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// h.cross(theRay.direction, _myTempEdge2);
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// a = _myTempEdge1.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
// if (a > -EPSILON && a < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
// return Float.NaN;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// if (theCullingFlag) {
|
||||||
|
// // u
|
||||||
|
// s.sub(theRay.origin,
|
||||||
|
// thePlane.origin);
|
||||||
|
// u = s.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
// if (u < 0.0f || u > a) {
|
||||||
|
// return Float.NaN;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// // v
|
||||||
|
// v = theRay.direction.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
// if (v < 0.0f || u + v > a) {
|
||||||
|
// return Float.NaN;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// // t
|
||||||
|
// q.cross(s,
|
||||||
|
// _myTempEdge1);
|
||||||
|
// t = _myTempEdge2.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
// // invert
|
||||||
|
// f = 1.0f / a;
|
||||||
|
// u *= f;
|
||||||
|
// v *= f;
|
||||||
|
// t *= f;
|
||||||
|
// } else {
|
||||||
|
// f = 1f / a;
|
||||||
|
// // u
|
||||||
|
// s.sub(theRay.origin,
|
||||||
|
// thePlane.origin);
|
||||||
|
// u = f * s.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
// if (u < 0.0f || u > 1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
// return Float.NaN;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// // v
|
||||||
|
// q.cross(s,
|
||||||
|
// _myTempEdge1);
|
||||||
|
// v = f * theRay.direction.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
// if (v < 0.0 || u + v > 1.0) {
|
||||||
|
// return Float.NaN;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// // t
|
||||||
|
// t = _myTempEdge2.dot(q) * f;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
// // result
|
||||||
|
// theResult.scale(t,
|
||||||
|
// theRay.direction);
|
||||||
|
// theResult.add(theRay.origin);
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// return t;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @deprecated this method might contain errors.
|
||||||
|
* @param theRayOrigin Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theRayDirection Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param thePlanePointA Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param thePlanePointB Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param thePlanePointC Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theResult Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return boolean
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static boolean intersectRayPlane(final Vector3f theRayOrigin,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theRayDirection,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f thePlanePointA,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f thePlanePointB,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f thePlanePointC,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theResult) {
|
||||||
|
float a;
|
||||||
|
float f;
|
||||||
|
float u;
|
||||||
|
float v;
|
||||||
|
float t;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge1.sub(thePlanePointB,
|
||||||
|
thePlanePointA);
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge2.sub(thePlanePointC,
|
||||||
|
thePlanePointA);
|
||||||
|
h.cross(theRayDirection,
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge2);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
a = _myTempEdge1.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
if (a > -EPSILON && a < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
return false; // parallel
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// u
|
||||||
|
s.sub(theRayOrigin,
|
||||||
|
thePlanePointA);
|
||||||
|
u = s.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
// v
|
||||||
|
v = theRayDirection.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
// t
|
||||||
|
q.cross(s,
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge1);
|
||||||
|
t = _myTempEdge2.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
// invert
|
||||||
|
f = 1.0f / a;
|
||||||
|
u *= f;
|
||||||
|
v *= f;
|
||||||
|
t *= f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// result
|
||||||
|
theResult.scale(t,
|
||||||
|
theRayDirection);
|
||||||
|
theResult.add(theRayOrigin);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @deprecated this method might contain errors.
|
||||||
|
* @param theRay Ray3f
|
||||||
|
* @param thePlane Plane3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theResult Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return boolean
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static boolean intersectRayPlane(final Ray3f theRay,
|
||||||
|
final Plane3f thePlane,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theResult) {
|
||||||
|
float a;
|
||||||
|
float f;
|
||||||
|
float u;
|
||||||
|
float v;
|
||||||
|
float t;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge1.set(thePlane.vectorA);
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge2.set(thePlane.vectorB);
|
||||||
|
h.cross(theRay.direction,
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge2);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
a = _myTempEdge1.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
if (a > -EPSILON && a < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
return false; // parallel
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// u
|
||||||
|
s.sub(theRay.origin,
|
||||||
|
thePlane.origin);
|
||||||
|
u = s.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
// v
|
||||||
|
v = theRay.direction.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
// t
|
||||||
|
q.cross(s,
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge1);
|
||||||
|
t = _myTempEdge2.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
// invert
|
||||||
|
f = 1.0f / a;
|
||||||
|
u *= f;
|
||||||
|
v *= f;
|
||||||
|
t *= f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// result
|
||||||
|
theResult.scale(t,
|
||||||
|
theRay.direction);
|
||||||
|
theResult.add(theRay.origin);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @deprecated this method might contain errors.
|
||||||
|
* @param theRay Ray3f
|
||||||
|
* @param thePlane Plane3f
|
||||||
|
* @return float
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static float intersectRayPlane(final Ray3f theRay,
|
||||||
|
final Plane3f thePlane) {
|
||||||
|
float a;
|
||||||
|
float f;
|
||||||
|
float u;
|
||||||
|
float v;
|
||||||
|
float t;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge1.set(thePlane.vectorA);
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge2.set(thePlane.vectorB);
|
||||||
|
h.cross(theRay.direction, _myTempEdge2);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
a = _myTempEdge1.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
if (a > -EPSILON && a < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
return Float.NaN; // parallel
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// u
|
||||||
|
s.sub(theRay.origin,
|
||||||
|
thePlane.origin);
|
||||||
|
u = s.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
// v
|
||||||
|
v = theRay.direction.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
// t
|
||||||
|
q.cross(s,
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge1);
|
||||||
|
t = _myTempEdge2.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
// invert
|
||||||
|
f = 1.0f / a;
|
||||||
|
u *= f;
|
||||||
|
v *= f;
|
||||||
|
t *= f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return t;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Fast, Minimum Storage Ray-Triangle Intersection by Tomas Moeller & Ben
|
||||||
|
* Trumbore http://jgt.akpeters.com/papers/MollerTrumbore97/code.html
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theRayOrigin Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theRayDirection Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVertex0 Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVertex1 Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVertex2 Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theResult Result
|
||||||
|
* @param theCullingFlag boolean
|
||||||
|
* @return boolean
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static boolean intersectRayTriangle(final Vector3f theRayOrigin,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theRayDirection,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theVertex0,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theVertex1,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theVertex2,
|
||||||
|
final IntersectionResult theResult,
|
||||||
|
final boolean theCullingFlag) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float det;
|
||||||
|
float inv_det;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* find vectors for two edges sharing vert0 */
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge1.sub(theVertex1, theVertex0);
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge2.sub(theVertex2, theVertex0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* begin calculating determinant - also used to calculate U parameter */
|
||||||
|
pvec.cross(theRayDirection, _myTempEdge2);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* if determinant is near zero, ray lies in plane of triangle */
|
||||||
|
det = _myTempEdge1.dot(pvec);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (theCullingFlag) { /* define TEST_CULL if culling is desired */
|
||||||
|
if (det < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
/* calculate distance from vert0 to ray origin */
|
||||||
|
tvec.sub(theRayOrigin, theVertex0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* calculate U parameter and test bounds */
|
||||||
|
theResult.u = tvec.dot(pvec);
|
||||||
|
if (theResult.u < 0.0f || theResult.u > det) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* prepare to test V parameter */
|
||||||
|
qvec.cross(tvec, _myTempEdge1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* calculate V parameter and test bounds */
|
||||||
|
theResult.v = theRayDirection.dot(qvec);
|
||||||
|
if (theResult.v < 0.0f || theResult.u + theResult.v > det) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* calculate t, scale parameters, ray intersects triangle */
|
||||||
|
theResult.t = _myTempEdge2.dot(qvec);
|
||||||
|
inv_det = 1.0f / det;
|
||||||
|
theResult.t *= inv_det;
|
||||||
|
theResult.u *= inv_det;
|
||||||
|
theResult.v *= inv_det;
|
||||||
|
} else { /* the non-culling branch */
|
||||||
|
if (det > -EPSILON && det < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
inv_det = 1.0f / det;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* calculate distance from vert0 to ray origin */
|
||||||
|
tvec.sub(theRayOrigin, theVertex0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* calculate U parameter and test bounds */
|
||||||
|
theResult.u = tvec.dot(pvec) * inv_det;
|
||||||
|
if (theResult.u < 0.0f || theResult.u > 1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* prepare to test V parameter */
|
||||||
|
qvec.cross(tvec, _myTempEdge1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* calculate V parameter and test bounds */
|
||||||
|
theResult.v = theRayDirection.dot(qvec) * inv_det;
|
||||||
|
if (theResult.v < 0.0f || theResult.u + theResult.v > 1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* calculate t, ray intersects triangle */
|
||||||
|
theResult.t = _myTempEdge2.dot(qvec) * inv_det;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static class IntersectionResult {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float t;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float u;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float v;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static float intersectRayTriangle(final Vector3f theRayOrigin,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theRayDirection,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f thePlanePointA,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f thePlanePointB,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f thePlanePointC,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theResult,
|
||||||
|
final boolean theCullingFlag) {
|
||||||
|
float a;
|
||||||
|
float f;
|
||||||
|
float u;
|
||||||
|
float v;
|
||||||
|
float t;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge1.sub(thePlanePointB,
|
||||||
|
thePlanePointA);
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge2.sub(thePlanePointC,
|
||||||
|
thePlanePointA);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
h.cross(theRayDirection,
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge2);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
a = _myTempEdge1.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
if (a > -EPSILON && a < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
return Float.NaN;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (theCullingFlag) {
|
||||||
|
// u
|
||||||
|
s.sub(theRayOrigin,
|
||||||
|
thePlanePointA);
|
||||||
|
u = s.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
if (u < 0.0f || u > a) {
|
||||||
|
return Float.NaN;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// v
|
||||||
|
v = theRayDirection.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
if (v < 0.0f || u + v > a) {
|
||||||
|
return Float.NaN;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// t
|
||||||
|
q.cross(s,
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge1);
|
||||||
|
t = _myTempEdge2.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
// invert
|
||||||
|
f = 1.0f / a;
|
||||||
|
u *= f;
|
||||||
|
v *= f;
|
||||||
|
t *= f;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
f = 1f / a;
|
||||||
|
// u
|
||||||
|
s.sub(theRayOrigin,
|
||||||
|
thePlanePointA);
|
||||||
|
u = f * s.dot(h);
|
||||||
|
if (u < 0.0f || u > 1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
return Float.NaN;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// v
|
||||||
|
q.cross(s,
|
||||||
|
_myTempEdge1);
|
||||||
|
v = f * theRayDirection.dot(q);
|
||||||
|
if (v < 0.0 || u + v > 1.0) {
|
||||||
|
return Float.NaN;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// t
|
||||||
|
t = _myTempEdge2.dot(q) * f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// result
|
||||||
|
theResult.scale(t,
|
||||||
|
theRayDirection);
|
||||||
|
theResult.add(theRayOrigin);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return t;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* http://local.wasp.uwa.edu.au/~pbourke/geometry/sphereline/raysphere.c
|
||||||
|
* Calculate the intersection of a ray and a sphere The line segment is
|
||||||
|
* defined from p1 to p2 The sphere is of radius r and centered at sc There
|
||||||
|
* are potentially two points of intersection given by p = p1 + mu1 (p2 -
|
||||||
|
* p1) p = p1 + mu2 (p2 - p1) Return FALSE if the ray doesn't intersect the
|
||||||
|
* sphere.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static boolean RaySphere(Vector3f p1,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f p2,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f sc,
|
||||||
|
float r) {
|
||||||
|
float a, b, c;
|
||||||
|
float bb4ac;
|
||||||
|
Vector3f dp = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
dp.x = p2.x - p1.x;
|
||||||
|
dp.y = p2.y - p1.y;
|
||||||
|
dp.z = p2.z - p1.z;
|
||||||
|
a = dp.x * dp.x + dp.y * dp.y + dp.z * dp.z;
|
||||||
|
b = 2 * (dp.x * (p1.x - sc.x) + dp.y * (p1.y - sc.y) + dp.z * (p1.z - sc.z));
|
||||||
|
c = sc.x * sc.x + sc.y * sc.y + sc.z * sc.z;
|
||||||
|
c += p1.x * p1.x + p1.y * p1.y + p1.z * p1.z;
|
||||||
|
c -= 2 * (sc.x * p1.x + sc.y * p1.y + sc.z * p1.z);
|
||||||
|
c -= r * r;
|
||||||
|
bb4ac = b * b - 4 * a * c;
|
||||||
|
if (Math.abs(a) < EPSILON || bb4ac < 0) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// float mu1 = ( -b + (float) Math.sqrt(bb4ac)) / (2 * a);
|
||||||
|
// float mu2 = ( -b - (float) Math.sqrt(bb4ac)) / (2 * a);
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// Vector3f myP1 = new Vector3f(dp);
|
||||||
|
// myP1.scale(mu1);
|
||||||
|
// myP1.add(p1);
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// Vector3f myP2 = new Vector3f(dp);
|
||||||
|
// myP2.scale(mu2);
|
||||||
|
// myP2.add(p1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* from paul bourke (
|
||||||
|
* http://local.wasp.uwa.edu.au/~pbourke/geometry/lineline2d/ )
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final int COINCIDENT = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final int PARALLEL = 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final int INTERESECTING = 2;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final int NOT_INTERESECTING = 3;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static int lineLineIntersect(Vector2f aBegin, Vector2f aEnd,
|
||||||
|
Vector2f bBegin, Vector2f bEnd,
|
||||||
|
Vector2f theIntersection) {
|
||||||
|
float denom = ((bEnd.y - bBegin.y) * (aEnd.x - aBegin.x))
|
||||||
|
- ((bEnd.x - bBegin.x) * (aEnd.y - aBegin.y));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float nume_a = ((bEnd.x - bBegin.x) * (aBegin.y - bBegin.y))
|
||||||
|
- ((bEnd.y - bBegin.y) * (aBegin.x - bBegin.x));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float nume_b = ((aEnd.x - aBegin.x) * (aBegin.y - bBegin.y))
|
||||||
|
- ((aEnd.y - aBegin.y) * (aBegin.x - bBegin.x));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (denom == 0.0f) {
|
||||||
|
if (nume_a == 0.0f && nume_b == 0.0f) {
|
||||||
|
return COINCIDENT;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return PARALLEL;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float ua = nume_a / denom;
|
||||||
|
float ub = nume_b / denom;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (ua >= 0.0f && ua <= 1.0f && ub >= 0.0f && ub <= 1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
if (theIntersection != null) {
|
||||||
|
// Get the intersection point.
|
||||||
|
theIntersection.x = aBegin.x + ua * (aEnd.x - aBegin.x);
|
||||||
|
theIntersection.y = aBegin.y + ua * (aEnd.y - aBegin.y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return INTERESECTING;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return NOT_INTERESECTING;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* from paul bourke (
|
||||||
|
* http://local.wasp.uwa.edu.au/~pbourke/geometry/lineline3d/ )
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Calculate the line segment PaPb that is the shortest route between two
|
||||||
|
* lines P1P2 and P3P4. Calculate also the values of mua and mub where Pa =
|
||||||
|
* P1 + mua (P2 - P1) Pb = P3 + mub (P4 - P3) Return FALSE if no solution
|
||||||
|
* exists.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static boolean lineLineIntersect(Vector3f p1, Vector3f p2, Vector3f p3, Vector3f p4,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f pa, Vector3f pb,
|
||||||
|
float[] theResult) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f p13 = mathematik.Util.sub(p1, p3);
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f p43 = mathematik.Util.sub(p4, p3);
|
||||||
|
if (Math.abs(p43.x) < EPSILON && Math.abs(p43.y) < EPSILON && Math.abs(p43.z) < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f p21 = mathematik.Util.sub(p2, p1);
|
||||||
|
if (Math.abs(p21.x) < EPSILON && Math.abs(p21.y) < EPSILON && Math.abs(p21.z) < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final float d1343 = p13.x * p43.x + p13.y * p43.y + p13.z * p43.z;
|
||||||
|
final float d4321 = p43.x * p21.x + p43.y * p21.y + p43.z * p21.z;
|
||||||
|
final float d1321 = p13.x * p21.x + p13.y * p21.y + p13.z * p21.z;
|
||||||
|
final float d4343 = p43.x * p43.x + p43.y * p43.y + p43.z * p43.z;
|
||||||
|
final float d2121 = p21.x * p21.x + p21.y * p21.y + p21.z * p21.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final float denom = d2121 * d4343 - d4321 * d4321;
|
||||||
|
if (Math.abs(denom) < EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
final float numer = d1343 * d4321 - d1321 * d4343;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final float mua = numer / denom;
|
||||||
|
final float mub = (d1343 + d4321 * mua) / d4343;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
pa.x = p1.x + mua * p21.x;
|
||||||
|
pa.y = p1.y + mua * p21.y;
|
||||||
|
pa.z = p1.z + mua * p21.z;
|
||||||
|
pb.x = p3.x + mub * p43.x;
|
||||||
|
pb.y = p3.y + mub * p43.y;
|
||||||
|
pb.z = p3.z + mub * p43.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (theResult != null) {
|
||||||
|
theResult[0] = mua;
|
||||||
|
theResult[1] = mub;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static Vector3f[] intersectRaySpherePoints(Vector3f pSphereCenter,
|
||||||
|
float pSphereRadius,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f pRayDirection,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f pRayOrigin) {
|
||||||
|
// Solve quadratic equation
|
||||||
|
float a = pRayDirection.lengthSquared();
|
||||||
|
if (a == 0.0) {
|
||||||
|
return null;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
float b = 2.0f * (pRayOrigin.dot(pRayDirection) - pRayDirection.dot(pSphereCenter));
|
||||||
|
Vector3f tempDiff = mathematik.Util.sub(pSphereCenter, pRayOrigin);
|
||||||
|
float c = tempDiff.lengthSquared() - (pSphereRadius * pSphereRadius);
|
||||||
|
float disc = b * b - 4 * a * c;
|
||||||
|
if (disc < 0.0f) {
|
||||||
|
return null;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
int numIntersections;
|
||||||
|
if (disc == 0.0f) {
|
||||||
|
numIntersections = 1;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
numIntersections = 2;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Atleast one intersection
|
||||||
|
Vector3f[] points = new Vector3f[numIntersections];
|
||||||
|
float t0;
|
||||||
|
float t1 = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
t0 = ((0.5f * (-1.0f * b + (float) Math.sqrt(disc))) / a);
|
||||||
|
if (numIntersections == 2) {
|
||||||
|
t1 = ((0.5f * (-1.0f * b - (float) Math.sqrt(disc))) / a);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// point 1 of intersection
|
||||||
|
points[0] = new Vector3f(pRayDirection);
|
||||||
|
points[0].scale(t0);
|
||||||
|
points[0].add(pRayOrigin);
|
||||||
|
if (numIntersections == 2) {
|
||||||
|
points[1] = new Vector3f(pRayDirection);
|
||||||
|
points[1].scale(t1);
|
||||||
|
points[1].add(pRayOrigin);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return points;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myP1 = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myP2 = new Vector3f(10, 10, 10);
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myP3 = new Vector3f(10, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myP4 = new Vector3f(0, 10, 10);
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myPA = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myPB = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
lineLineIntersect(myP1, myP2, myP3, myP4, myPA, myPB, null);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myPA);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myPB);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
52
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Linef.java
Executable file
52
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Linef.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Linef<T extends Vectorf>
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1748179277316146123L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public T p1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public T p2;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Linef(Class<T> theClass) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
p1 = theClass.newInstance();
|
||||||
|
p2 = theClass.newInstance();
|
||||||
|
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
|
||||||
|
ex.printStackTrace();
|
||||||
|
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
|
||||||
|
ex.printStackTrace();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Linef<Vector2f> myLine = new Linef<Vector2f> (Vector2f.class);
|
||||||
|
* Linef<Vector3f> myLine3f = new Linef<Vector3f> (Vector3f.class);
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
29
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Mathematik.java
Executable file
29
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Mathematik.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public interface Mathematik {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float EPSILON = 0.00001f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
619
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Matrix3f.java
Executable file
619
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Matrix3f.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,619 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* a 3x3 matrix.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* rotation
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* rxx ryx rzx rxy ryy rzy rxz ryy rzz
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* scale
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* sx 0 0 0 sy 0 0 0 sz
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* also read 'The Matrix and Quaternions FAQ' at
|
||||||
|
* http://www.flipcode.com/documents/matrfaq.html
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Matrix3f
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = 104839874874759581L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final int IDENTITY = 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float xx;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float xy;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float xz;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float yx;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float yy;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float yz;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float zx;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float zy;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float zz;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final float[] _myArrayRepresentation = new float[9];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final float[] _myArray4fRepresentation = new float[16];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Matrix3f() {
|
||||||
|
xx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
xy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
xz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Matrix3f(Matrix3f theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
set(theMatrix);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Matrix3f(int theType) {
|
||||||
|
switch (theType) {
|
||||||
|
case IDENTITY:
|
||||||
|
setIdentity();
|
||||||
|
break;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private void set(float xx,
|
||||||
|
float yx,
|
||||||
|
float zx,
|
||||||
|
float xy,
|
||||||
|
float yy,
|
||||||
|
float zy,
|
||||||
|
float xz,
|
||||||
|
float yz,
|
||||||
|
float zz) {
|
||||||
|
this.xx = xx;
|
||||||
|
this.xy = xy;
|
||||||
|
this.xz = xz;
|
||||||
|
this.yx = yx;
|
||||||
|
this.yy = yy;
|
||||||
|
this.yz = yz;
|
||||||
|
this.zx = zx;
|
||||||
|
this.zy = zy;
|
||||||
|
this.zz = zz;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(float[] _myArrayRepresentation) {
|
||||||
|
xx = _myArrayRepresentation[0];
|
||||||
|
yx = _myArrayRepresentation[1];
|
||||||
|
zx = _myArrayRepresentation[2];
|
||||||
|
xy = _myArrayRepresentation[3];
|
||||||
|
yy = _myArrayRepresentation[4];
|
||||||
|
zy = _myArrayRepresentation[5];
|
||||||
|
xz = _myArrayRepresentation[6];
|
||||||
|
yz = _myArrayRepresentation[7];
|
||||||
|
zz = _myArrayRepresentation[8];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(Matrix3f theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
xx = theMatrix.xx;
|
||||||
|
xy = theMatrix.xy;
|
||||||
|
xz = theMatrix.xz;
|
||||||
|
yx = theMatrix.yx;
|
||||||
|
yy = theMatrix.yy;
|
||||||
|
yz = theMatrix.yz;
|
||||||
|
zx = theMatrix.zx;
|
||||||
|
zy = theMatrix.zy;
|
||||||
|
zz = theMatrix.zz;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setIdentity() {
|
||||||
|
xx = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
xy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
xz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yy = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
yz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zz = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setZero() {
|
||||||
|
xx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
xy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
xz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void add(float theValue) {
|
||||||
|
xx += theValue;
|
||||||
|
xy += theValue;
|
||||||
|
xz += theValue;
|
||||||
|
yx += theValue;
|
||||||
|
yy += theValue;
|
||||||
|
yz += theValue;
|
||||||
|
zx += theValue;
|
||||||
|
zy += theValue;
|
||||||
|
zz += theValue;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void add(Matrix3f theMatrixA,
|
||||||
|
Matrix3f theMatrixB) {
|
||||||
|
xx = theMatrixA.xx + theMatrixB.xx;
|
||||||
|
xy = theMatrixA.xy + theMatrixB.xy;
|
||||||
|
xz = theMatrixA.xz + theMatrixB.xz;
|
||||||
|
yx = theMatrixA.yx + theMatrixB.yx;
|
||||||
|
yy = theMatrixA.yy + theMatrixB.yy;
|
||||||
|
yz = theMatrixA.yz + theMatrixB.yz;
|
||||||
|
zx = theMatrixA.zx + theMatrixB.zx;
|
||||||
|
zy = theMatrixA.zy + theMatrixB.zy;
|
||||||
|
zz = theMatrixA.zz + theMatrixB.zz;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void add(Matrix3f theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
xx += theMatrix.xx;
|
||||||
|
xy += theMatrix.xy;
|
||||||
|
xz += theMatrix.xz;
|
||||||
|
yx += theMatrix.yx;
|
||||||
|
yy += theMatrix.yy;
|
||||||
|
yz += theMatrix.yz;
|
||||||
|
zx += theMatrix.zx;
|
||||||
|
zy += theMatrix.zy;
|
||||||
|
zz += theMatrix.zz;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void sub(Matrix3f theMatrixA,
|
||||||
|
Matrix3f theMatrixB) {
|
||||||
|
xx = theMatrixA.xx - theMatrixB.xx;
|
||||||
|
xy = theMatrixA.xy - theMatrixB.xy;
|
||||||
|
xz = theMatrixA.xz - theMatrixB.xz;
|
||||||
|
yx = theMatrixA.yx - theMatrixB.yx;
|
||||||
|
yy = theMatrixA.yy - theMatrixB.yy;
|
||||||
|
yz = theMatrixA.yz - theMatrixB.yz;
|
||||||
|
zx = theMatrixA.zx - theMatrixB.zx;
|
||||||
|
zy = theMatrixA.zy - theMatrixB.zy;
|
||||||
|
zz = theMatrixA.zz - theMatrixB.zz;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void sub(Matrix3f theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
xx -= theMatrix.xx;
|
||||||
|
xy -= theMatrix.xy;
|
||||||
|
xz -= theMatrix.xz;
|
||||||
|
yx -= theMatrix.yx;
|
||||||
|
yy -= theMatrix.yy;
|
||||||
|
yz -= theMatrix.yz;
|
||||||
|
zx -= theMatrix.zx;
|
||||||
|
zy -= theMatrix.zy;
|
||||||
|
zz -= theMatrix.zz;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void transpose() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* NOTE if the matrix is a rotation matrix ie the determinant is 1, the
|
||||||
|
* transpose is equivalent to the invers of the matrix.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float mySwap = yx;
|
||||||
|
yx = xy;
|
||||||
|
xy = mySwap;
|
||||||
|
mySwap = zx;
|
||||||
|
zx = xz;
|
||||||
|
xz = mySwap;
|
||||||
|
mySwap = zy;
|
||||||
|
zy = yz;
|
||||||
|
yz = mySwap;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void transpose(Matrix3f theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
if (this != theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
xx = theMatrix.xx;
|
||||||
|
xy = theMatrix.yx;
|
||||||
|
xz = theMatrix.zx;
|
||||||
|
yx = theMatrix.xy;
|
||||||
|
yy = theMatrix.yy;
|
||||||
|
yz = theMatrix.zy;
|
||||||
|
zx = theMatrix.xz;
|
||||||
|
zy = theMatrix.yz;
|
||||||
|
zz = theMatrix.zz;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
transpose();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float determinant() {
|
||||||
|
return xx * (yy * zz - yz * zy) + xy * (yz * zx - yx * zz) + xz * (yx * zy - yy * zx);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void invert() {
|
||||||
|
float myDeterminant = determinant();
|
||||||
|
if (myDeterminant == 0.0) {
|
||||||
|
return;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
myDeterminant = 1 / myDeterminant;
|
||||||
|
set(yy * zz - zy * yz,
|
||||||
|
zx * yz - yx * zz,
|
||||||
|
yx * zy - zx * yy,
|
||||||
|
zy * xz - xy * zz,
|
||||||
|
xx * zz - zx * xz,
|
||||||
|
zx * xy - xx * zy,
|
||||||
|
xy * yz - yy * xz,
|
||||||
|
yx * xz - xx * yz,
|
||||||
|
xx * yy - yx * xy);
|
||||||
|
multiply(myDeterminant);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setXAxis(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
xx = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
yx = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
zx = theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setYAxis(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
xy = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
yy = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
zy = theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setZAxis(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
xz = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
yz = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
zz = theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void getXAxis(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
theVector.x = xx;
|
||||||
|
theVector.y = yx;
|
||||||
|
theVector.z = zx;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void getYAxis(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
theVector.x = xy;
|
||||||
|
theVector.y = yy;
|
||||||
|
theVector.z = zy;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void getZAxis(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
theVector.x = xz;
|
||||||
|
theVector.y = yz;
|
||||||
|
theVector.z = zz;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f getXAxis() {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3f(xx, yx, zx);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f getYAxis() {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3f(xy, yy, zy);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f getZAxis() {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3f(xz, yz, zz);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setXRotation(float theRadians) {
|
||||||
|
float sin = (float) Math.sin(theRadians);
|
||||||
|
float cos = (float) Math.cos(theRadians);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xx = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
yx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yy = cos;
|
||||||
|
zy = sin;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yz = -sin;
|
||||||
|
zz = cos;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setYRotation(float theRadians) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo check why these differ from 'the matrix and quaternions faq'
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* cos 0 sin(!) 0 1 0 -sin(!) 0 cos
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
float sin = (float) Math.sin(theRadians);
|
||||||
|
float cos = (float) Math.cos(theRadians);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xx = cos;
|
||||||
|
yx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zx = -sin;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yy = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
zy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xz = sin;
|
||||||
|
yz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zz = cos;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setZRotation(float theRadians) {
|
||||||
|
float sin = (float) Math.sin(theRadians);
|
||||||
|
float cos = (float) Math.cos(theRadians);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xx = cos;
|
||||||
|
yx = sin;
|
||||||
|
zx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xy = -sin;
|
||||||
|
yy = cos;
|
||||||
|
zy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zz = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setXYZRotation(Vector3f theRotation) {
|
||||||
|
setXYZRotation(theRotation.x,
|
||||||
|
theRotation.y,
|
||||||
|
theRotation.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setXYZRotation(float theX,
|
||||||
|
float theY,
|
||||||
|
float theZ) {
|
||||||
|
/* using radiants */
|
||||||
|
final float a = (float) Math.cos(theX);
|
||||||
|
final float b = (float) Math.sin(theX);
|
||||||
|
final float c = (float) Math.cos(theY);
|
||||||
|
final float d = (float) Math.sin(theY);
|
||||||
|
final float e = (float) Math.cos(theZ);
|
||||||
|
final float f = (float) Math.sin(theZ);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final float ad = a * d;
|
||||||
|
final float bd = b * d;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xx = c * e;
|
||||||
|
yx = bd * e + a * f;
|
||||||
|
zx = -ad * e + b * f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xy = -c * f;
|
||||||
|
yy = -bd * f + a * e;
|
||||||
|
zy = ad * f + b * e;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xz = d;
|
||||||
|
yz = -b * c;
|
||||||
|
zz = a * c;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setRotation(final Vector4f theRotation) {
|
||||||
|
final float u = theRotation.x;
|
||||||
|
final float v = theRotation.y;
|
||||||
|
final float w = theRotation.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final float rcos = (float) Math.cos(theRotation.w);
|
||||||
|
final float rsin = (float) Math.sin(theRotation.w);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xx = rcos + u * u * (1 - rcos);
|
||||||
|
yx = w * rsin + v * u * (1 - rcos);
|
||||||
|
zx = -v * rsin + w * u * (1 - rcos);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xy = -w * rsin + u * v * (1 - rcos);
|
||||||
|
yy = rcos + v * v * (1 - rcos);
|
||||||
|
zy = u * rsin + w * v * (1 - rcos);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xz = v * rsin + u * w * (1 - rcos);
|
||||||
|
yz = -u * rsin + v * w * (1 - rcos);
|
||||||
|
zz = rcos + w * w * (1 - rcos);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void multiply(float theValue) {
|
||||||
|
xx *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
xy *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
xz *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
yx *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
yy *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
yz *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
zx *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
zy *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
zz *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void multiply(Matrix3f theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
float tmp1 = xx * theMatrix.xx + xy * theMatrix.yx + xz * theMatrix.zx;
|
||||||
|
float tmp2 = xx * theMatrix.xy + xy * theMatrix.yy + xz * theMatrix.zy;
|
||||||
|
float tmp3 = xx * theMatrix.xz + xy * theMatrix.yz + xz * theMatrix.zz;
|
||||||
|
float tmp4 = yx * theMatrix.xx + yy * theMatrix.yx + yz * theMatrix.zx;
|
||||||
|
float tmp5 = yx * theMatrix.xy + yy * theMatrix.yy + yz * theMatrix.zy;
|
||||||
|
float tmp6 = yx * theMatrix.xz + yy * theMatrix.yz + yz * theMatrix.zz;
|
||||||
|
float tmp7 = zx * theMatrix.xx + zy * theMatrix.yx + zz * theMatrix.zx;
|
||||||
|
float tmp8 = zx * theMatrix.xy + zy * theMatrix.yy + zz * theMatrix.zy;
|
||||||
|
float tmp9 = zx * theMatrix.xz + zy * theMatrix.yz + zz * theMatrix.zz;
|
||||||
|
xx = tmp1;
|
||||||
|
xy = tmp2;
|
||||||
|
xz = tmp3;
|
||||||
|
yx = tmp4;
|
||||||
|
yy = tmp5;
|
||||||
|
yz = tmp6;
|
||||||
|
zx = tmp7;
|
||||||
|
zy = tmp8;
|
||||||
|
zz = tmp9;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void transform(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
theVector.set(xx * theVector.x + yx * theVector.y + zx * theVector.z,
|
||||||
|
xy * theVector.x + yy * theVector.y + zy * theVector.z,
|
||||||
|
theVector.z = xz * theVector.x + yz * theVector.y + zz * theVector.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setScale(Vector3f theScale) {
|
||||||
|
xx = theScale.x;
|
||||||
|
yx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zx = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yy = theScale.y;
|
||||||
|
zy = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
yz = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
zz = theScale.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float[] toArray() {
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[0] = xx;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[1] = yx;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[2] = zx;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[3] = xy;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[4] = yy;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[5] = zy;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[6] = xz;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[7] = yz;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[8] = zz;
|
||||||
|
return _myArrayRepresentation;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float[] toArray4f() {
|
||||||
|
/* so that opengl can understand it */
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[0] = xx;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[1] = yx;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[2] = zx;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[3] = 0;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[4] = xy;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[5] = yy;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[6] = zy;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[7] = 0;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[8] = xz;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[9] = yz;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[10] = zz;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[11] = 0;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[12] = 0;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[13] = 0;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[14] = 0;
|
||||||
|
_myArray4fRepresentation[15] = 1;
|
||||||
|
return _myArray4fRepresentation;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public String toString() {
|
||||||
|
return xx + ", " + yx + ", " + zx + "\n" + xy + ", " + yy + ", " + zy + "\n" + xz + ", " + yz + ", " + zz;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||||
|
Matrix3f myMatrix;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
/* invert and transpose */
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("### invert and transpose\n");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix = new Matrix3f(Matrix3f.IDENTITY);
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.setXYZRotation(new Vector3f(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.transpose();
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.transpose();
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix = new Matrix3f(Matrix3f.IDENTITY);
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.setXYZRotation(new Vector3f(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.invert();
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.invert();
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
/* x */
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix = new Matrix3f(Matrix3f.IDENTITY);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("### rotation x\n");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.setXYZRotation(new Vector3f(0.2f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.setXRotation(0.2f);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.setRotation(new Vector4f(1, 0, 0, 0.2f));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* y */
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("### rotation y\n");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.setXYZRotation(new Vector3f(0.0f, 0.3f, 0.0f));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.setYRotation(0.3f);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.setRotation(new Vector4f(0, 1, 0, 0.3f));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* z */
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("### rotation z\n");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.setXYZRotation(new Vector3f(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.4f));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.setZRotation(0.4f);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.setRotation(new Vector4f(0, 0, 1, 0.4f));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
433
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Matrix4f.java
Executable file
433
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Matrix4f.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,433 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* a more general 4x4 matrix.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* xx yx zx wx xy yy zy wy xz yz zz wz xw yw zw ww
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* also read 'The Matrix and Quaternions FAQ' at
|
||||||
|
* http://www.flipcode.com/documents/matrfaq.html
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Matrix4f
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1088603850006298206L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float xx;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float xy;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float xz;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float xw;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float yx;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float yy;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float yz;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float yw;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float zx;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float zy;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float zz;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float zw;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float wx;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float wy;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float wz;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float ww;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final float[] _myArrayRepresentation = new float[16];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Matrix4f() {
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Matrix4f(TransformMatrix4f theTransformMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
xx = theTransformMatrix.rotation.xx;
|
||||||
|
yx = theTransformMatrix.rotation.yx;
|
||||||
|
zx = theTransformMatrix.rotation.zx;
|
||||||
|
wx = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xy = theTransformMatrix.rotation.xy;
|
||||||
|
yy = theTransformMatrix.rotation.yy;
|
||||||
|
zy = theTransformMatrix.rotation.zy;
|
||||||
|
wy = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xz = theTransformMatrix.rotation.xz;
|
||||||
|
yz = theTransformMatrix.rotation.yz;
|
||||||
|
zz = theTransformMatrix.rotation.zz;
|
||||||
|
wz = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xw = theTransformMatrix.translation.x;
|
||||||
|
yw = theTransformMatrix.translation.y;
|
||||||
|
zw = theTransformMatrix.translation.z;
|
||||||
|
ww = 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Matrix4f(Matrix4f theTransformMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
xx = theTransformMatrix.xx;
|
||||||
|
yx = theTransformMatrix.yx;
|
||||||
|
zx = theTransformMatrix.zx;
|
||||||
|
wx = theTransformMatrix.wx;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xy = theTransformMatrix.xy;
|
||||||
|
yy = theTransformMatrix.yy;
|
||||||
|
zy = theTransformMatrix.zy;
|
||||||
|
wy = theTransformMatrix.wy;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xz = theTransformMatrix.xz;
|
||||||
|
yz = theTransformMatrix.yz;
|
||||||
|
zz = theTransformMatrix.zz;
|
||||||
|
wz = theTransformMatrix.wz;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xw = theTransformMatrix.xw;
|
||||||
|
yw = theTransformMatrix.yw;
|
||||||
|
zw = theTransformMatrix.zw;
|
||||||
|
ww = theTransformMatrix.ww;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Matrix4f(float[] theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
set(theMatrix);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Matrix4f(double[] theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
set(theMatrix);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Matrix4f(float xx,
|
||||||
|
float yx,
|
||||||
|
float zx,
|
||||||
|
float wx,
|
||||||
|
float xy,
|
||||||
|
float yy,
|
||||||
|
float zy,
|
||||||
|
float wy,
|
||||||
|
float xz,
|
||||||
|
float yz,
|
||||||
|
float zz,
|
||||||
|
float wz,
|
||||||
|
float xw,
|
||||||
|
float yw,
|
||||||
|
float zw,
|
||||||
|
float ww) {
|
||||||
|
this.xx = xx;
|
||||||
|
this.xy = xy;
|
||||||
|
this.xz = xz;
|
||||||
|
this.xw = xw;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
this.yx = yx;
|
||||||
|
this.yy = yy;
|
||||||
|
this.yz = yz;
|
||||||
|
this.yw = yw;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
this.zx = zx;
|
||||||
|
this.zy = zy;
|
||||||
|
this.zz = zz;
|
||||||
|
this.zw = zw;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
this.wx = wx;
|
||||||
|
this.wy = wy;
|
||||||
|
this.wz = wz;
|
||||||
|
this.ww = ww;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(float[] theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
xx = theMatrix[0];
|
||||||
|
yx = theMatrix[1];
|
||||||
|
zx = theMatrix[2];
|
||||||
|
wx = theMatrix[3];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xy = theMatrix[4];
|
||||||
|
yy = theMatrix[5];
|
||||||
|
zy = theMatrix[6];
|
||||||
|
wy = theMatrix[7];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xz = theMatrix[8];
|
||||||
|
yz = theMatrix[9];
|
||||||
|
zz = theMatrix[10];
|
||||||
|
wz = theMatrix[11];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xw = theMatrix[12];
|
||||||
|
yw = theMatrix[13];
|
||||||
|
zw = theMatrix[14];
|
||||||
|
ww = theMatrix[15];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(double[] theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
xx = (float) theMatrix[0];
|
||||||
|
yx = (float) theMatrix[1];
|
||||||
|
zx = (float) theMatrix[2];
|
||||||
|
wx = (float) theMatrix[3];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xy = (float) theMatrix[4];
|
||||||
|
yy = (float) theMatrix[5];
|
||||||
|
zy = (float) theMatrix[6];
|
||||||
|
wy = (float) theMatrix[7];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xz = (float) theMatrix[8];
|
||||||
|
yz = (float) theMatrix[9];
|
||||||
|
zz = (float) theMatrix[10];
|
||||||
|
wz = (float) theMatrix[11];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
xw = (float) theMatrix[12];
|
||||||
|
yw = (float) theMatrix[13];
|
||||||
|
zw = (float) theMatrix[14];
|
||||||
|
ww = (float) theMatrix[15];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(float xx,
|
||||||
|
float yx,
|
||||||
|
float zx,
|
||||||
|
float wx,
|
||||||
|
float xy,
|
||||||
|
float yy,
|
||||||
|
float zy,
|
||||||
|
float wy,
|
||||||
|
float xz,
|
||||||
|
float yz,
|
||||||
|
float zz,
|
||||||
|
float wz,
|
||||||
|
float xw,
|
||||||
|
float yw,
|
||||||
|
float zw,
|
||||||
|
float ww) {
|
||||||
|
this.xx = xx;
|
||||||
|
this.xy = xy;
|
||||||
|
this.xz = xz;
|
||||||
|
this.xw = xw;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
this.yx = yx;
|
||||||
|
this.yy = yy;
|
||||||
|
this.yz = yz;
|
||||||
|
this.yw = yw;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
this.zx = zx;
|
||||||
|
this.zy = zy;
|
||||||
|
this.zz = zz;
|
||||||
|
this.zw = zw;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
this.wx = wx;
|
||||||
|
this.wy = wy;
|
||||||
|
this.wz = wz;
|
||||||
|
this.ww = ww;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void invert() {
|
||||||
|
float myDeterminant = determinant();
|
||||||
|
if (myDeterminant == 0.0) {
|
||||||
|
return;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
myDeterminant = 1 / myDeterminant;
|
||||||
|
set(yy * (zz * ww - zw * wz) + yz * (zw * wy - zy * ww) + yw * (zy * wz - zz * wy),
|
||||||
|
zy * (xz * ww - xw * wz) + zz * (xw * wy - xy * ww) + zw * (xy * wz - xz * wy),
|
||||||
|
wy * (xz * yw - xw * yz) + wz * (xw * yy - xy * yw) + ww * (xy * yz - xz * yy),
|
||||||
|
xy * (yw * zz - yz * zw) + xz * (yy * zw - yw * zy) + xw * (yz * zy - yy * zz),
|
||||||
|
yz * (zx * ww - zw * wx) + yw * (zz * wx - zx * wz) + yx * (zw * wz - zz * ww),
|
||||||
|
zz * (xx * ww - xw * wx) + zw * (xz * wx - xx * wz) + zx * (xw * wz - xz * ww),
|
||||||
|
wz * (xx * yw - xw * yx) + ww * (xz * yx - xx * yz) + wx * (xw * yz - xz * yw),
|
||||||
|
xz * (yw * zx - yx * zw) + xw * (yx * zz - yz * zx) + xx * (yz * zw - yw * zz),
|
||||||
|
yw * (zx * wy - zy * wx) + yx * (zy * ww - zw * wy) + yy * (zw * wx - zx * ww),
|
||||||
|
zw * (xx * wy - xy * wx) + zx * (xy * ww - xw * wy) + zy * (xw * wx - xx * ww),
|
||||||
|
ww * (xx * yy - xy * yx) + wx * (xy * yw - xw * yy) + wy * (xw * yx - xx * yw),
|
||||||
|
xw * (yy * zx - yx * zy) + xx * (yw * zy - yy * zw) + xy * (yx * zw - yw * zx),
|
||||||
|
yx * (zz * wy - zy * wz) + yy * (zx * wz - zz * wx) + yz * (zy * wx - zx * wy),
|
||||||
|
zx * (xz * wy - xy * wz) + zy * (xx * wz - xz * wx) + zz * (xy * wx - xx * wy),
|
||||||
|
wx * (xz * yy - xy * yz) + wy * (xx * yz - xz * yx) + wz * (xy * yx - xx * yy),
|
||||||
|
xx * (yy * zz - yz * zy) + xy * (yz * zx - yx * zz) + xz * (yx * zy - yy * zx));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
multiply(myDeterminant);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void multiply(float scalar) {
|
||||||
|
xx *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
xy *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
xz *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
xw *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
yx *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
yy *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
yz *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
yw *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
zx *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
zy *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
zz *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
zw *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
wx *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
wy *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
wz *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
ww *= scalar;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void multiply(Matrix4f theMatrix) {
|
||||||
|
multiply(this,
|
||||||
|
theMatrix);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void multiply(Matrix4f theA,
|
||||||
|
Matrix4f theB) {
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo here we still have an ugly bug :(
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
set(theA.xx * theB.xx + theA.yx * theB.xy + theA.zx * theB.xz + theA.wx * theB.xw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xx * theB.yx + theA.yx * theB.yy + theA.zx * theB.yz + theA.wx * theB.yw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xx * theB.zx + theA.yx * theB.zy + theA.zx * theB.zz + theA.wx * theB.zw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xx * theB.wx + theA.yx * theB.wy + theA.zx * theB.wz + theA.wx * theB.ww,
|
||||||
|
theA.xy * theB.xx + theA.yy * theB.xy + theA.zy * theB.xz + theA.wy * theB.xw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xy * theB.yx + theA.yy * theB.yy + theA.zy * theB.yz + theA.wy * theB.yw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xy * theB.zx + theA.yy * theB.zy + theA.zy * theB.zz + theA.wy * theB.zw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xy * theB.wx + theA.yy * theB.wy + theA.zy * theB.wz + theA.wy * theB.ww,
|
||||||
|
theA.xz * theB.xx + theA.yz * theB.xy + theA.zz * theB.xz + theA.wz * theB.xw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xz * theB.yx + theA.yz * theB.yy + theA.zz * theB.yz + theA.wz * theB.yw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xz * theB.zx + theA.yz * theB.zy + theA.zz * theB.zz + theA.wz * theB.zw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xz * theB.wx + theA.yz * theB.wy + theA.zz * theB.wz + theA.wz * theB.ww,
|
||||||
|
theA.xw * theB.xx + theA.yw * theB.xy + theA.zw * theB.xz + theA.ww * theB.xw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xw * theB.yx + theA.yw * theB.yy + theA.zw * theB.yz + theA.ww * theB.yw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xw * theB.zx + theA.yw * theB.zy + theA.zw * theB.zz + theA.ww * theB.zw,
|
||||||
|
theA.xw * theB.wx + theA.yw * theB.wy + theA.zw * theB.wz + theA.ww * theB.ww);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float determinant() {
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo check if this is correct
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
return (xx * yy - xy * yx) * (zz * ww - zw * wz) - (xx * yz - xz * yx) * (zy * ww - zw * wy)
|
||||||
|
+ (xx * yw - xw * yx) * (zy * wz - zz * wy) + (xy * yz - xz * yy) * (zx * ww - zw * wx)
|
||||||
|
- (xy * yw - xw * yy) * (zx * wz - zz * wx) + (xz * yw - xw * yz) * (zx * wy - zy * wx);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void transform(Vector3f theResult) {
|
||||||
|
theResult.set(xx * theResult.x + xy * theResult.y + xz * theResult.z + xw,
|
||||||
|
yx * theResult.x + yy * theResult.y + yz * theResult.z + yw,
|
||||||
|
zx * theResult.x + zy * theResult.y + zz * theResult.z + zw);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void transform(Vector4f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
theVector.set(xx * theVector.x + xy * theVector.y + xz * theVector.z + xw * theVector.w,
|
||||||
|
yx * theVector.x + yy * theVector.y + yz * theVector.z + yw * theVector.w,
|
||||||
|
zx * theVector.x + zy * theVector.y + zz * theVector.z + zw * theVector.w,
|
||||||
|
wx * theVector.x + wy * theVector.y + wz * theVector.z + ww * theVector.w);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float[] toArray() {
|
||||||
|
/* opengl format */
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[0] = xx;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[1] = yx;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[2] = zx;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[3] = wx;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[4] = xy;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[5] = yy;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[6] = zy;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[7] = wy;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[8] = xz;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[9] = yz;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[10] = zz;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[11] = wz;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[12] = wx;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[13] = wy;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[14] = wz;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[15] = ww;
|
||||||
|
return _myArrayRepresentation;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void transpose() {
|
||||||
|
float swap = yx;
|
||||||
|
yx = xy;
|
||||||
|
xy = swap;
|
||||||
|
swap = zx;
|
||||||
|
zx = xz;
|
||||||
|
xz = swap;
|
||||||
|
swap = wx;
|
||||||
|
wx = xw;
|
||||||
|
xw = swap;
|
||||||
|
swap = zy;
|
||||||
|
zy = yz;
|
||||||
|
yz = swap;
|
||||||
|
swap = wy;
|
||||||
|
wy = yw;
|
||||||
|
yw = swap;
|
||||||
|
swap = wz;
|
||||||
|
wz = zw;
|
||||||
|
zw = swap;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public String toString() {
|
||||||
|
return xx + ", " + yx + ", " + zx + ", " + wx + "\n" + xy + ", " + yy + ", " + zy + ", " + wy + "\n" + xz
|
||||||
|
+ ", " + yz + ", " + zz + ", " + wz + "\n" + xw + ", " + yw + ", " + zw + ", " + ww;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||||
|
TransformMatrix4f myTransMatrix = new TransformMatrix4f(TransformMatrix4f.IDENTITY);
|
||||||
|
myTransMatrix.rotation.setXYZRotation(new Vector3f(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f));
|
||||||
|
myTransMatrix.translation.set(2,
|
||||||
|
3,
|
||||||
|
4);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("### transform matrix\n");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myTransMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Matrix4f myMatrix = new Matrix4f(myTransMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.invert();
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.invert();
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* transform */
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myVector3f = new Vector3f(5, 8, 7);
|
||||||
|
Vector4f myVector4f = new Vector4f(5, 8, 7, 1);
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myVectorOther3f = new Vector3f(5, 8, 7);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.transform(myVector3f);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myVector3f);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myMatrix.transform(myVector4f);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myVector4f);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myTransMatrix.transform(myVectorOther3f);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myVectorOther3f);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
178
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/PerlinNoise.java
Executable file
178
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/PerlinNoise.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,178 @@
|
|||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Random;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public abstract class PerlinNoise {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
|
||||||
|
// PERLIN NOISE
|
||||||
|
// [toxi 040903]
|
||||||
|
// octaves and amplitude amount per octave are now user controlled
|
||||||
|
// via the noiseDetail() function.
|
||||||
|
// [toxi 030902]
|
||||||
|
// cleaned up code and now using bagel's cosine table to speed up
|
||||||
|
// [toxi 030901]
|
||||||
|
// implementation by the german demo group farbrausch
|
||||||
|
// as used in their demo "art": http://www.farb-rausch.de/fr010src.zip
|
||||||
|
static final int PERLIN_YWRAPB = 4;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final int PERLIN_YWRAP = 1 << PERLIN_YWRAPB;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final int PERLIN_ZWRAPB = 8;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final int PERLIN_ZWRAP = 1 << PERLIN_ZWRAPB;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final int PERLIN_SIZE = 4095;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static int perlin_octaves = 4; // default to medium smooth
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static float perlin_amp_falloff = 0.5f; // 50% reduction/octave
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// [toxi 031112]
|
||||||
|
// new vars needed due to recent change of cos table in PGraphics
|
||||||
|
static int perlin_TWOPI, perlin_PI;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static float[] perlin_cosTable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static float[] perlin;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static Random perlinRandom;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static int SEED = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Computes the Perlin noise function value at point x.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static float noise(float x) {
|
||||||
|
// is this legit? it's a dumb way to do it (but repair it later)
|
||||||
|
return noise(x, 0f, 0f);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Computes the Perlin noise function value at the point x, y.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static float noise(float x, float y) {
|
||||||
|
return noise(x, y, 0f);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static float noise(float x, float y, float z) {
|
||||||
|
if (perlin == null) {
|
||||||
|
if (perlinRandom == null) {
|
||||||
|
perlinRandom = new Random(SEED);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
perlin = new float[PERLIN_SIZE + 1];
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < PERLIN_SIZE + 1; i++) {
|
||||||
|
perlin[i] = perlinRandom.nextFloat(); //(float)Math.random();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// [toxi 031112]
|
||||||
|
// noise broke due to recent change of cos table in PGraphics
|
||||||
|
// this will take care of it
|
||||||
|
perlin_cosTable = cosLUT;
|
||||||
|
perlin_TWOPI = perlin_PI = SINCOS_LENGTH;
|
||||||
|
perlin_PI >>= 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (x < 0) {
|
||||||
|
x = -x;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (y < 0) {
|
||||||
|
y = -y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (z < 0) {
|
||||||
|
z = -z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int xi = (int) x, yi = (int) y, zi = (int) z;
|
||||||
|
float xf = (float) (x - xi);
|
||||||
|
float yf = (float) (y - yi);
|
||||||
|
float zf = (float) (z - zi);
|
||||||
|
float rxf, ryf;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float r = 0;
|
||||||
|
float ampl = 0.5f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float n1, n2, n3;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < perlin_octaves; i++) {
|
||||||
|
int of = xi + (yi << PERLIN_YWRAPB) + (zi << PERLIN_ZWRAPB);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
rxf = noise_fsc(xf);
|
||||||
|
ryf = noise_fsc(yf);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
n1 = perlin[of & PERLIN_SIZE];
|
||||||
|
n1 += rxf * (perlin[(of + 1) & PERLIN_SIZE] - n1);
|
||||||
|
n2 = perlin[(of + PERLIN_YWRAP) & PERLIN_SIZE];
|
||||||
|
n2 += rxf * (perlin[(of + PERLIN_YWRAP + 1) & PERLIN_SIZE] - n2);
|
||||||
|
n1 += ryf * (n2 - n1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
of += PERLIN_ZWRAP;
|
||||||
|
n2 = perlin[of & PERLIN_SIZE];
|
||||||
|
n2 += rxf * (perlin[(of + 1) & PERLIN_SIZE] - n2);
|
||||||
|
n3 = perlin[(of + PERLIN_YWRAP) & PERLIN_SIZE];
|
||||||
|
n3 += rxf * (perlin[(of + PERLIN_YWRAP + 1) & PERLIN_SIZE] - n3);
|
||||||
|
n2 += ryf * (n3 - n2);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
n1 += noise_fsc(zf) * (n2 - n1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
r += n1 * ampl;
|
||||||
|
ampl *= perlin_amp_falloff;
|
||||||
|
xi <<= 1;
|
||||||
|
xf *= 2;
|
||||||
|
yi <<= 1;
|
||||||
|
yf *= 2;
|
||||||
|
zi <<= 1;
|
||||||
|
zf *= 2;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (xf >= 1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
xi++;
|
||||||
|
xf--;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (yf >= 1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
yi++;
|
||||||
|
yf--;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (zf >= 1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
zi++;
|
||||||
|
zf--;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return r;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// [toxi 031112]
|
||||||
|
// now adjusts to the size of the cosLUT used via
|
||||||
|
// the new variables, defined above
|
||||||
|
private static float noise_fsc(float i) {
|
||||||
|
// using bagel's cosine table instead
|
||||||
|
return 0.5f * (1.0f - perlin_cosTable[(int) (i * perlin_PI) % perlin_TWOPI]);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// precalculate sin/cos lookup tables [toxi]
|
||||||
|
// circle resolution is determined from the actual used radii
|
||||||
|
// passed to ellipse() method. this will automatically take any
|
||||||
|
// scale transformations into account too
|
||||||
|
// [toxi 031031]
|
||||||
|
// changed table's precision to 0.5 degree steps
|
||||||
|
// introduced new vars for more flexible code
|
||||||
|
static final protected float sinLUT[];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final protected float cosLUT[];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final protected float SINCOS_PRECISION = 0.5f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final protected int SINCOS_LENGTH = (int) (360f / SINCOS_PRECISION);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final float DEG_TO_RAD = (float) Math.PI / 180.0f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final float RAD_TO_DEG = 180.0f / (float) Math.PI;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static {
|
||||||
|
sinLUT = new float[SINCOS_LENGTH];
|
||||||
|
cosLUT = new float[SINCOS_LENGTH];
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < SINCOS_LENGTH; i++) {
|
||||||
|
sinLUT[i] = (float) Math.sin(i * DEG_TO_RAD * SINCOS_PRECISION);
|
||||||
|
cosLUT[i] = (float) Math.cos(i * DEG_TO_RAD * SINCOS_PRECISION);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
87
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Plane3f.java
Executable file
87
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Plane3f.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Plane3f
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2390391570305327484L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f origin;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f vectorA;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f vectorB;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* these fields are not used by default and left uninitialized 'null'
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f normal;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float d = Float.NaN;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Plane3f() {
|
||||||
|
origin = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
vectorA = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
vectorB = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Plane3f(Vector3f theOrigin,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f theVectorA,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
origin = theOrigin;
|
||||||
|
vectorA = theVectorA;
|
||||||
|
vectorB = theVectorB;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void updateNormal() {
|
||||||
|
if (normal == null) {
|
||||||
|
normal = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
Util.calculateNormal(vectorA, vectorB, normal);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void updateD() {
|
||||||
|
if (normal != null) {
|
||||||
|
d = -normal.dot(origin);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// private float intersection(Vector3f a, Vector3f b) {
|
||||||
|
// /*
|
||||||
|
// * updateNormal();
|
||||||
|
// * updateD();
|
||||||
|
// */
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// float u = normal.x * a.x +
|
||||||
|
// normal.y * a.y +
|
||||||
|
// normal.z * a.z +
|
||||||
|
// d;
|
||||||
|
// u /= normal.x * (a.x - b.x) +
|
||||||
|
// normal.y * (a.y - b.y) +
|
||||||
|
// normal.z * (a.z - b.z);
|
||||||
|
// return u;
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
89
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Quaternion.java
Executable file
89
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Quaternion.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Quaternion {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float w;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float x;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float y;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Quaternion() {
|
||||||
|
reset();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Quaternion(float theW, float theX, float theY, float theZ) {
|
||||||
|
w = theW;
|
||||||
|
x = theX;
|
||||||
|
y = theY;
|
||||||
|
z = theZ;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void reset() {
|
||||||
|
w = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
x = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
y = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
z = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(float theW, Vector3f theVector3f) {
|
||||||
|
w = theW;
|
||||||
|
x = theVector3f.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector3f.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theVector3f.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(Quaternion theQuaternion) {
|
||||||
|
w = theQuaternion.w;
|
||||||
|
x = theQuaternion.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theQuaternion.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theQuaternion.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void multiply(Quaternion theA, Quaternion theB) {
|
||||||
|
w = theA.w * theB.w - theA.x * theB.x - theA.y * theB.y - theA.z * theB.z;
|
||||||
|
x = theA.w * theB.x + theA.x * theB.w + theA.y * theB.z - theA.z * theB.y;
|
||||||
|
y = theA.w * theB.y + theA.y * theB.w + theA.z * theB.x - theA.x * theB.z;
|
||||||
|
z = theA.w * theB.z + theA.z * theB.w + theA.x * theB.y - theA.y * theB.x;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f getVectorAndAngle() {
|
||||||
|
final Vector4f theResult = new Vector4f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float s = (float) Math.sqrt(1.0f - w * w);
|
||||||
|
if (s < Mathematik.EPSILON) {
|
||||||
|
s = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
theResult.w = (float) Math.acos(w) * 2.0f;
|
||||||
|
theResult.x = x / s;
|
||||||
|
theResult.y = y / s;
|
||||||
|
theResult.z = z / s;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return theResult;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
154
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Random.java
Executable file
154
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Random.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* generate random numbers.<br/>
|
||||||
|
* note that if different types are requested the random generator moves on
|
||||||
|
* anyway.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public class Random
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5871934750136232555L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final java.util.Random _mySeedGenerator = new java.util.Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final java.util.Random myRandomNumberGenerator;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Random _myInstance;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static {
|
||||||
|
_myInstance = new Random();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static float FLOAT(float theStart, float theEnd) {
|
||||||
|
return _myInstance.getFloat(theStart, theEnd);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static float INT(int theStart, int theEnd) {
|
||||||
|
return _myInstance.getInt(theStart, theEnd);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Random() {
|
||||||
|
this(_mySeedGenerator.nextLong());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Random(long theSeed) {
|
||||||
|
myRandomNumberGenerator = new java.util.Random(theSeed);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setSeed(long theSeed) {
|
||||||
|
myRandomNumberGenerator.setSeed(theSeed);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* return a random int value from theStart to theEnd, including both values.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theStart int
|
||||||
|
* @param theEnd int
|
||||||
|
* @return int
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public int getInt(int theStart,
|
||||||
|
int theEnd) {
|
||||||
|
int myDiff = (theEnd + 1) - theStart;
|
||||||
|
return myRandomNumberGenerator.nextInt(myDiff) + theStart;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public int getInt() {
|
||||||
|
return myRandomNumberGenerator.nextInt();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* return a random float value from theStart to theEnd, excluding both
|
||||||
|
* values.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theStart float
|
||||||
|
* @param theEnd float
|
||||||
|
* @return float
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public float getFloat(float theStart,
|
||||||
|
float theEnd) {
|
||||||
|
final float myDiff = theEnd - theStart;
|
||||||
|
final float myRandomValue = myRandomNumberGenerator.nextFloat() * myDiff;
|
||||||
|
return myRandomValue + theStart;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float getFloat() {
|
||||||
|
return myRandomNumberGenerator.nextFloat();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// public static float getFloat(float theStart,
|
||||||
|
// float theEnd) {
|
||||||
|
// return _mySeedGenerator.getFloat(theStart, theEnd);
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f getVector3f(float theStart, float theEnd) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3f(getFloat(theStart, theEnd),
|
||||||
|
getFloat(theStart, theEnd),
|
||||||
|
getFloat(theStart, theEnd));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||||
|
long myTime;
|
||||||
|
Random myRandom;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myRandom = new Random();
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myRandom.getFloat(20, 100));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myRandom.getFloat(20, 100));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myRandom.getFloat(20, 100));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myRandom.getFloat(20, 100));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("***");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myRandom = new Random();
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myRandom.getFloat(20, 100));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myRandom.getInt(20, 100));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myRandom.getFloat(20, 100));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myRandom.getFloat(20, 100));
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("***");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* use this random generator */
|
||||||
|
myTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
|
||||||
|
myRandom = new Random(0);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < 50000000; i++) {
|
||||||
|
float myValue = myRandom.getFloat(20, 100);
|
||||||
|
if (myValue < 20 || myValue > 100) {
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(i + "ERROR");
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("DONE: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - myTime));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* use maths random generator */
|
||||||
|
myTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < 50000000; i++) {
|
||||||
|
float myValue = (float) Math.random() * (100 - 20) + 20;
|
||||||
|
if (myValue < 20 || myValue > 100) {
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(i + "ERROR");
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("DONE: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - myTime));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
51
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Ray3f.java
Executable file
51
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Ray3f.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Ray3f
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1748179277316146625L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f origin;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f direction;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Ray3f() {
|
||||||
|
origin = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
direction = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Ray3f(Vector3f theOrigin,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f theDirection) {
|
||||||
|
origin = theOrigin;
|
||||||
|
direction = theDirection;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public String toString() {
|
||||||
|
return "origin + " + origin + " / " + " direction " + direction;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
60
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Rayf.java
Executable file
60
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Rayf.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @deprecated
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public class Rayf<T extends Vectorf>
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable, Vectorf {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1748179277316146234L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public T origin;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public T direction;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Rayf(Class<T> theClass) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
origin = theClass.newInstance();
|
||||||
|
direction = theClass.newInstance();
|
||||||
|
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
|
||||||
|
ex.printStackTrace();
|
||||||
|
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
|
||||||
|
ex.printStackTrace();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Rayf(T theOrigin,
|
||||||
|
T theDirection) {
|
||||||
|
origin = theOrigin;
|
||||||
|
direction = theDirection;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public String toString() {
|
||||||
|
return "origin + " + origin + " / " + " direction " + direction;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
47
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Rectangle3f.java
Executable file
47
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Rectangle3f.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Rectangle3f
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -7295490882726338294L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f origin;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f scale;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Rectangle3f() {
|
||||||
|
origin = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
scale = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Rectangle3f(Vector3f theOrigin,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f theScale) {
|
||||||
|
origin = theOrigin;
|
||||||
|
scale = theScale;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
156
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Rotation.java
Executable file
156
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Rotation.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* write the current rotation into the result transformation matrix.
|
||||||
|
* if the velocity sampler is enabled the velocity will averaged
|
||||||
|
* to avoid jerky turning.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo the sampling would be more accurate if the delta time would also be
|
||||||
|
* taken into account when updating the sampler.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Rotation {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector3f[] _myVelocitySampler;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f _myUpVector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f _myCurrentAverageVelocity;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f _myAverageVelocity;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private int _myVelocitySamplerPosition;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f _myTempUpVector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f _myTempSideVector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f _myTempForwardVector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Rotation() {
|
||||||
|
this(1);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Rotation(final int theVelocitySamplerSize) {
|
||||||
|
_myVelocitySamplerPosition = 0;
|
||||||
|
setVelocitySamplerSize(theVelocitySamplerSize);
|
||||||
|
_myUpVector = new Vector3f(0, 0, 1);
|
||||||
|
_myAverageVelocity = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
_myCurrentAverageVelocity = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
_myTempUpVector = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
_myTempSideVector = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
_myTempForwardVector = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setVelocitySamplerSize(final int theVelocitySamplerSize) {
|
||||||
|
_myVelocitySampler = new Vector3f[theVelocitySamplerSize];
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < _myVelocitySampler.length; ++i) {
|
||||||
|
_myVelocitySampler[i] = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void flattenVelocitySampler(final Vector3f theVelocity) {
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < _myVelocitySampler.length; i++) {
|
||||||
|
add(theVelocity);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void add(final Vector3f theVelocity) {
|
||||||
|
_myVelocitySamplerPosition++;
|
||||||
|
_myVelocitySamplerPosition %= _myVelocitySampler.length;
|
||||||
|
_myAverageVelocity.sub(_myVelocitySampler[_myVelocitySamplerPosition]);
|
||||||
|
_myVelocitySampler[_myVelocitySamplerPosition].set(theVelocity);
|
||||||
|
_myAverageVelocity.add(theVelocity);
|
||||||
|
_myCurrentAverageVelocity.set(_myAverageVelocity);
|
||||||
|
_myCurrentAverageVelocity.scale(1.0f / (float) _myVelocitySampler.length);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(final Vector3f theVelocity,
|
||||||
|
final TransformMatrix4f theResult) {
|
||||||
|
if (_myVelocitySampler.length == 1) {
|
||||||
|
pointAt(theVelocity, theResult);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
add(theVelocity);
|
||||||
|
pointAt(_myCurrentAverageVelocity, theResult);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(final TransformMatrix4f theResult) {
|
||||||
|
pointAt(_myCurrentAverageVelocity, theResult);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(final Matrix3f theResult) {
|
||||||
|
pointAt(_myCurrentAverageVelocity, theResult);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @deprecated use 'set' instead.
|
||||||
|
* @param theVelocity Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theResult TransformMatrix4f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public void setRotationMatrix(final Vector3f theVelocity,
|
||||||
|
final TransformMatrix4f theResult) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVelocity, theResult);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f getAverageVelocity() {
|
||||||
|
return _myCurrentAverageVelocity;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setUpVector(final Vector3f theUpVector) {
|
||||||
|
_myUpVector.set(theUpVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setUpVectorByAngle(final float roll) {
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo this is not thought through...
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
_myUpVector.x = (float) Math.sin(roll);
|
||||||
|
_myUpVector.z = -(float) Math.cos(roll);
|
||||||
|
_myUpVector.y = 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private void pointAt(final Vector3f theForwardVector,
|
||||||
|
final Matrix3f theResult) {
|
||||||
|
/* get sideVector */
|
||||||
|
_myTempSideVector.cross(_myUpVector, theForwardVector);
|
||||||
|
_myTempSideVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
/* get 'real' upVector */
|
||||||
|
_myTempUpVector.cross(_myTempSideVector, theForwardVector);
|
||||||
|
_myTempUpVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
/* get forwardVector */
|
||||||
|
_myTempForwardVector.set(theForwardVector);
|
||||||
|
_myTempForwardVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
/* fill transformation matrix */
|
||||||
|
theResult.setXAxis(_myTempForwardVector);
|
||||||
|
theResult.setYAxis(_myTempSideVector);
|
||||||
|
theResult.setZAxis(_myTempUpVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private void pointAt(final Vector3f theForwardVector,
|
||||||
|
final TransformMatrix4f theResult) {
|
||||||
|
pointAt(theForwardVector, theResult.rotation);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
333
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/TransformMatrix4f.java
Executable file
333
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/TransformMatrix4f.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,333 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* special form of a 4x4 matrix. first of all the way we represent the matrix in
|
||||||
|
* this class is similar to the way opengl handles the row column issue.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* transform matrix -- r = rotation, t = translation
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* rxx rxy rxz 0 ryx ryy ryz 0 rzx rzy rzz 0 tx ty tz 1
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* the transform matrix is special in the way that is a 3x3 matrix for rotation
|
||||||
|
* and scale and a translation vector. the remaining four values a constants.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* this is the way opengl specifies a 4x4 matrix and also the way 'toArray'
|
||||||
|
* returns an array.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* m[0] m[4] m[8] m[12]
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* m[1] m[5] m[9] m[13]
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* M=( )
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* m[2] m[6] m[10] m[14]
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* m[3] m[7] m[11] m[15]
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* here is an excerpt from the glMultMatrix man page.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* "In many computer languages 4x4 arrays are represented in row-major order.
|
||||||
|
* The transformations just described represent these matrices in column-major
|
||||||
|
* order. The order of the multiplication is important. For example, if the
|
||||||
|
* current transformation is a rotation, and glMultMatrix is called with a
|
||||||
|
* translation matrix, the translation is done directly on the coordinates to be
|
||||||
|
* transformed, while the rotation is done on the results of that translation."
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* also read 'The Matrix and Quaternions FAQ' at
|
||||||
|
* http://www.flipcode.com/documents/matrfaq.html
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public class TransformMatrix4f
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static int IDENTITY = 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Matrix3f rotation;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f translation;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2946060493174800199L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final float ZERO = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final float ONE = 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final float[] _myArrayRepresentation = new float[16];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public TransformMatrix4f() {
|
||||||
|
translation = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
rotation = new Matrix3f();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public TransformMatrix4f(int theType) {
|
||||||
|
translation = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
rotation = new Matrix3f(theType);
|
||||||
|
toArray();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public TransformMatrix4f(TransformMatrix4f theMatrix4f) {
|
||||||
|
this();
|
||||||
|
set(theMatrix4f);
|
||||||
|
toArray();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public TransformMatrix4f(float[] theMatrixArray) {
|
||||||
|
this();
|
||||||
|
set(theMatrixArray);
|
||||||
|
toArray();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setIdentity() {
|
||||||
|
translation.set(0,
|
||||||
|
0,
|
||||||
|
0);
|
||||||
|
rotation.setIdentity();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setRotationIdentity() {
|
||||||
|
rotation.setIdentity();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void setZero() {
|
||||||
|
translation.set(0,
|
||||||
|
0,
|
||||||
|
0);
|
||||||
|
rotation.setZero();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float determinant() {
|
||||||
|
float d = rotation.xx
|
||||||
|
* ((rotation.yy * rotation.zz * ONE + rotation.yz * translation.z * ZERO
|
||||||
|
+ translation.y * rotation.zy * ZERO)
|
||||||
|
- translation.y * rotation.zz * ZERO - rotation.yy * translation.z * ZERO - rotation.yz
|
||||||
|
* rotation.zy * ONE);
|
||||||
|
d -= rotation.xy
|
||||||
|
* ((rotation.yx * rotation.zz * ONE + rotation.yz * translation.z * ZERO
|
||||||
|
+ translation.y * rotation.zx * ZERO)
|
||||||
|
- translation.y * rotation.zz * ZERO - rotation.yx * translation.z * ZERO - rotation.yz
|
||||||
|
* rotation.zx * ONE);
|
||||||
|
d += rotation.xz
|
||||||
|
* ((rotation.yx * rotation.zy * ONE + rotation.yy * translation.z * ZERO
|
||||||
|
+ translation.y * rotation.zx * ZERO)
|
||||||
|
- translation.y * rotation.zy * ZERO - rotation.yx * translation.z * ZERO - rotation.yy
|
||||||
|
* rotation.zx * ONE);
|
||||||
|
d -= translation.x
|
||||||
|
* ((rotation.yx * rotation.zy * ZERO + rotation.yy * rotation.zz * ZERO + rotation.yz * rotation.zx * ZERO)
|
||||||
|
- rotation.yz * rotation.zy * ZERO - rotation.yx * rotation.zz * ZERO - rotation.yy
|
||||||
|
* rotation.zx * ZERO);
|
||||||
|
return d;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(TransformMatrix4f mat) {
|
||||||
|
rotation.set(mat.rotation);
|
||||||
|
translation.set(mat.translation);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(float[] theArrayRepresentation) {
|
||||||
|
rotation.xx = theArrayRepresentation[0];
|
||||||
|
rotation.yx = theArrayRepresentation[1];
|
||||||
|
rotation.zx = theArrayRepresentation[2];
|
||||||
|
/* 3 */
|
||||||
|
rotation.xy = theArrayRepresentation[4];
|
||||||
|
rotation.yy = theArrayRepresentation[5];
|
||||||
|
rotation.zy = theArrayRepresentation[6];
|
||||||
|
/* 7 */
|
||||||
|
rotation.xz = theArrayRepresentation[8];
|
||||||
|
rotation.yz = theArrayRepresentation[9];
|
||||||
|
rotation.zz = theArrayRepresentation[10];
|
||||||
|
/* 11 */
|
||||||
|
translation.x = theArrayRepresentation[12];
|
||||||
|
translation.y = theArrayRepresentation[13];
|
||||||
|
translation.z = theArrayRepresentation[14];
|
||||||
|
/* 15 */
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void multiply(float theValue) {
|
||||||
|
rotation.xx *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.xy *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.xz *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
translation.x *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.yx *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.yy *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.yz *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
translation.y *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.zx *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.zy *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.zz *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
translation.z *= theValue;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void multiply(float theValue,
|
||||||
|
TransformMatrix4f theMatrix4f) {
|
||||||
|
rotation.xx = theMatrix4f.rotation.xx * theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.xy = theMatrix4f.rotation.xy * theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.xz = theMatrix4f.rotation.xz * theValue;
|
||||||
|
translation.x = theMatrix4f.translation.x * theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.yx = theMatrix4f.rotation.yx * theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.yy = theMatrix4f.rotation.yy * theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.yz = theMatrix4f.rotation.yz * theValue;
|
||||||
|
translation.y = theMatrix4f.translation.y * theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.zx = theMatrix4f.rotation.zx * theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.zy = theMatrix4f.rotation.zy * theValue;
|
||||||
|
rotation.zz = theMatrix4f.rotation.zz * theValue;
|
||||||
|
translation.z = theMatrix4f.translation.z * theValue;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void multiply(TransformMatrix4f theMatrix4f) {
|
||||||
|
float tmp1 = rotation.xx * theMatrix4f.rotation.xx + rotation.xy * theMatrix4f.rotation.yx
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.xz * theMatrix4f.rotation.zx + translation.x * TransformMatrix4f.ZERO;
|
||||||
|
float tmp2 = rotation.xx * theMatrix4f.rotation.xy + rotation.xy * theMatrix4f.rotation.yy
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.xz * theMatrix4f.rotation.zy + translation.x * TransformMatrix4f.ZERO;
|
||||||
|
float tmp3 = rotation.xx * theMatrix4f.rotation.xz + rotation.xy * theMatrix4f.rotation.yz
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.xz * theMatrix4f.rotation.zz + translation.x * TransformMatrix4f.ZERO;
|
||||||
|
float tmp4 = rotation.xx * theMatrix4f.translation.x + rotation.xy * theMatrix4f.translation.y
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.xz * theMatrix4f.translation.z + translation.x * TransformMatrix4f.ONE;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float tmp5 = rotation.yx * theMatrix4f.rotation.xx + rotation.yy * theMatrix4f.rotation.yx
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.yz * theMatrix4f.rotation.zx + translation.y * TransformMatrix4f.ZERO;
|
||||||
|
float tmp6 = rotation.yx * theMatrix4f.rotation.xy + rotation.yy * theMatrix4f.rotation.yy
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.yz * theMatrix4f.rotation.zy + translation.y * TransformMatrix4f.ZERO;
|
||||||
|
float tmp7 = rotation.yx * theMatrix4f.rotation.xz + rotation.yy * theMatrix4f.rotation.yz
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.yz * theMatrix4f.rotation.zz + translation.y * TransformMatrix4f.ZERO;
|
||||||
|
float tmp8 = rotation.yx * theMatrix4f.translation.x + rotation.yy * theMatrix4f.translation.y
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.yz * theMatrix4f.translation.z + translation.y * TransformMatrix4f.ONE;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float tmp9 = rotation.zx * theMatrix4f.rotation.xx + rotation.zy * theMatrix4f.rotation.yx
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.zz * theMatrix4f.rotation.zx + translation.z * TransformMatrix4f.ZERO;
|
||||||
|
float tmp10 = rotation.zx * theMatrix4f.rotation.xy + rotation.zy * theMatrix4f.rotation.yy
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.zz * theMatrix4f.rotation.zy + translation.z * TransformMatrix4f.ZERO;
|
||||||
|
float tmp11 = rotation.zx * theMatrix4f.rotation.xz + rotation.zy * theMatrix4f.rotation.yz
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.zz * theMatrix4f.rotation.zz + translation.z * TransformMatrix4f.ZERO;
|
||||||
|
float tmp12 = rotation.zx * theMatrix4f.translation.x + rotation.zy * theMatrix4f.translation.y
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.zz * theMatrix4f.translation.z + translation.z * TransformMatrix4f.ONE;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
float temp13 = m30 * in2.m00 +
|
||||||
|
m31 * in2.m10 +
|
||||||
|
m32 * in2.m20 +
|
||||||
|
m33 * in2.m30;
|
||||||
|
float temp14 = m30 * in2.m01 +
|
||||||
|
m31 * in2.m11 +
|
||||||
|
m32 * in2.m21 +
|
||||||
|
m33 * in2.m31;
|
||||||
|
float temp15 = m30 * in2.m02 +
|
||||||
|
m31 * in2.m12 +
|
||||||
|
m32 * in2.m22 +
|
||||||
|
m33 * in2.m32;
|
||||||
|
float temp16 = m30 * in2.m03 +
|
||||||
|
m31 * in2.m13 +
|
||||||
|
m32 * in2.m23 +
|
||||||
|
m33 * in2.m33;
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
rotation.xx = tmp1;
|
||||||
|
rotation.xy = tmp2;
|
||||||
|
rotation.xz = tmp3;
|
||||||
|
translation.x = tmp4;
|
||||||
|
rotation.yx = tmp5;
|
||||||
|
rotation.yy = tmp6;
|
||||||
|
rotation.yz = tmp7;
|
||||||
|
translation.y = tmp8;
|
||||||
|
rotation.zx = tmp9;
|
||||||
|
rotation.zy = tmp10;
|
||||||
|
rotation.zz = tmp11;
|
||||||
|
translation.z = tmp12;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void transform(Vector3f theResult) {
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo check if this is right...
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
theResult.set(rotation.xx * theResult.x
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.xy * theResult.y
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.xz * theResult.z
|
||||||
|
+ translation.x,
|
||||||
|
rotation.yx * theResult.x
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.yy * theResult.y
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.yz * theResult.z
|
||||||
|
+ translation.y,
|
||||||
|
rotation.zx * theResult.x
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.zy * theResult.y
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.zz * theResult.z
|
||||||
|
+ translation.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float[] toArray() {
|
||||||
|
/* so that opengl can understand it */
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[0] = rotation.xx;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[1] = rotation.yx;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[2] = rotation.zx;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[3] = ZERO;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[4] = rotation.xy;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[5] = rotation.yy;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[6] = rotation.zy;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[7] = ZERO;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[8] = rotation.xz;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[9] = rotation.yz;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[10] = rotation.zz;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[11] = ZERO;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[12] = translation.x;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[13] = translation.y;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[14] = translation.z;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[15] = ONE;
|
||||||
|
return _myArrayRepresentation;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public String toString() {
|
||||||
|
return rotation.xx + ", " + rotation.yx + ", " + rotation.zx + ", " + "0.0" + "\n" + rotation.xy + ", "
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.yy + ", " + rotation.zy + ", " + "0.0" + "\n" + rotation.xz + ", " + rotation.yz + ", "
|
||||||
|
+ rotation.zz + ", " + "0.0" + "\n" + translation.x + ", " + translation.y + ", " + translation.z
|
||||||
|
+ ", " + "1.0";
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||||
|
/* multiplying matrices */
|
||||||
|
TransformMatrix4f myScaleMatrix = new TransformMatrix4f(TransformMatrix4f.IDENTITY);
|
||||||
|
myScaleMatrix.rotation.setXAxis(new Vector3f(2, 0, 0));
|
||||||
|
myScaleMatrix.rotation.setYAxis(new Vector3f(0, 2, 0));
|
||||||
|
myScaleMatrix.rotation.setZAxis(new Vector3f(0, 0, 2));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
TransformMatrix4f myTranslateMatrix = new TransformMatrix4f(TransformMatrix4f.IDENTITY);
|
||||||
|
myTranslateMatrix.translation.set(2,
|
||||||
|
3,
|
||||||
|
4);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myScaleMatrix.multiply(myScaleMatrix);
|
||||||
|
myScaleMatrix.multiply(myTranslateMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myScaleMatrix);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* transform position */
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("\n### translate");
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myTranslateMatrix);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println();
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myVector = new Vector3f(10, 5, 7);
|
||||||
|
myTranslateMatrix.transform(myVector);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println(myVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
931
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Util.java
Executable file
931
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Util.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,931 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Vector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* a loose collection of linear algebra methods that are not connected to a
|
||||||
|
* specific class.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public class Util {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector3f AXIS_X = new Vector3f(1, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector3f AXIS_Y = new Vector3f(0, 1, 0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector3f AXIS_Z = new Vector3f(0, 0, 1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final float areaTriangle(final Vector3f v0,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f v1,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f v2) {
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f myAB = sub(v1, v0);
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f myAC = sub(v2, v0);
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f myCross = cross(myAB, myAC);
|
||||||
|
return 0.5f * myCross.magnitude();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float length(Vector3f theVector3f) {
|
||||||
|
return theVector3f.length();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final boolean isPointInTriangle(final Vector3f v0,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f v1,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f v2,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f thePoint) {
|
||||||
|
// // Compute vectors
|
||||||
|
// v0 = C - A
|
||||||
|
// v1 = B - A
|
||||||
|
// v2 = P - A
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector3f v00 = new Vector3f(v2);
|
||||||
|
v00.sub(v0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector3f v01 = new Vector3f(v1);
|
||||||
|
v01.sub(v0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector3f v02 = new Vector3f(thePoint);
|
||||||
|
v02.sub(v0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Compute dot products
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float dot00 = v00.dot(v00);
|
||||||
|
float dot01 = v00.dot(v01);
|
||||||
|
float dot02 = v00.dot(v02);
|
||||||
|
float dot11 = v01.dot(v01);
|
||||||
|
float dot12 = v01.dot(v02);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Compute barycentric coordinates
|
||||||
|
float invDenom = 1 / (dot00 * dot11 - dot01 * dot01);
|
||||||
|
float u = (dot11 * dot02 - dot01 * dot12) * invDenom;
|
||||||
|
float v = (dot00 * dot12 - dot01 * dot02) * invDenom;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Check if point is in triangle
|
||||||
|
return (u > 0) && (v > 0) && (u + v < 1);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* contain */
|
||||||
|
public static final boolean contains(final Vector3f thePosition,
|
||||||
|
final WorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox theWorldAlignedBox) {
|
||||||
|
return (contains(thePosition.x, theWorldAlignedBox.position.x, theWorldAlignedBox.scale.x)
|
||||||
|
&& contains(thePosition.y, theWorldAlignedBox.position.y, theWorldAlignedBox.scale.y)
|
||||||
|
&& contains(thePosition.z, theWorldAlignedBox.position.z, theWorldAlignedBox.scale.z));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final boolean contains(final float theTestValue,
|
||||||
|
final float theContainerValue,
|
||||||
|
final float theRange) {
|
||||||
|
return (theTestValue > theContainerValue - theRange * 0.5f
|
||||||
|
&& theTestValue < theContainerValue + theRange * 0.5f);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static boolean insidePolygon(Vector2f thePoint, Vector2f[] thePolygon) {
|
||||||
|
float x = thePoint.x;
|
||||||
|
float y = thePoint.y;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int c = 0;
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0, j = thePolygon.length - 1; i < thePolygon.length; j = i++) {
|
||||||
|
if ((((thePolygon[i].y <= y) && (y < thePolygon[j].y))
|
||||||
|
|| ((thePolygon[j].y <= y) && (y < thePolygon[i].y)))
|
||||||
|
&& (x < (thePolygon[j].x - thePolygon[i].x) * (y - thePolygon[i].y)
|
||||||
|
/ (thePolygon[j].y - thePolygon[i].y) + thePolygon[i].x)) {
|
||||||
|
c = (c + 1) % 2;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return c == 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final boolean insidePolygon(final Vector2f thePoint, final Vector<Vector2f> thePolygon) {
|
||||||
|
float x = thePoint.x;
|
||||||
|
float y = thePoint.y;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int c = 0;
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0, j = thePolygon.size() - 1; i < thePolygon.size(); j = i++) {
|
||||||
|
if ((((thePolygon.get(i).y <= y) && (y < thePolygon.get(j).y))
|
||||||
|
|| ((thePolygon.get(j).y <= y) && (y < thePolygon.get(i).y)))
|
||||||
|
&& (x < (thePolygon.get(j).x - thePolygon.get(i).x) * (y - thePolygon.get(i).y)
|
||||||
|
/ (thePolygon.get(j).y - thePolygon.get(i).y) + thePolygon.get(i).x)) {
|
||||||
|
c = (c + 1) % 2;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return c == 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final boolean inside2DPolygon(final Vector3f thePoint, final Vector<Vector3f> thePolygon) {
|
||||||
|
float x = thePoint.x;
|
||||||
|
float y = thePoint.y;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int c = 0;
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0, j = thePolygon.size() - 1; i < thePolygon.size(); j = i++) {
|
||||||
|
if ((((thePolygon.get(i).y <= y) && (y < thePolygon.get(j).y))
|
||||||
|
|| ((thePolygon.get(j).y <= y) && (y < thePolygon.get(i).y)))
|
||||||
|
&& (x < (thePolygon.get(j).x - thePolygon.get(i).x) * (y - thePolygon.get(i).y)
|
||||||
|
/ (thePolygon.get(j).y - thePolygon.get(i).y) + thePolygon.get(i).x)) {
|
||||||
|
c = (c + 1) % 2;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return c == 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f _myTempMin = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f _myTempMax = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static void updateBoundingBox(final WorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox theWorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f[] myVectors) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (myVectors == null || myVectors.length == 0) {
|
||||||
|
return;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* get minimum and maximum */
|
||||||
|
_myTempMin.set(myVectors[0]);
|
||||||
|
_myTempMax.set(myVectors[0]);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 1; i < myVectors.length; i++) {
|
||||||
|
/* minimum */
|
||||||
|
if (_myTempMin.x > myVectors[i].x) {
|
||||||
|
_myTempMin.x = myVectors[i].x;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (_myTempMin.y > myVectors[i].y) {
|
||||||
|
_myTempMin.y = myVectors[i].y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (_myTempMin.z > myVectors[i].z) {
|
||||||
|
_myTempMin.z = myVectors[i].z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
/* maximum */
|
||||||
|
if (_myTempMax.x < myVectors[i].x) {
|
||||||
|
_myTempMax.x = myVectors[i].x;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (_myTempMax.y < myVectors[i].y) {
|
||||||
|
_myTempMax.y = myVectors[i].y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (_myTempMax.z < myVectors[i].z) {
|
||||||
|
_myTempMax.z = myVectors[i].z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create world aligned boundingbox */
|
||||||
|
/* bb position */
|
||||||
|
theWorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.position.sub(_myTempMax, _myTempMin);
|
||||||
|
theWorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.position.scale(0.5f);
|
||||||
|
theWorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.position.add(_myTempMin);
|
||||||
|
/* bb scale */
|
||||||
|
theWorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.scale.sub(_myTempMax, _myTempMin);
|
||||||
|
theWorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.scale.x = Math.abs(theWorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.scale.x);
|
||||||
|
theWorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.scale.y = Math.abs(theWorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.scale.y);
|
||||||
|
theWorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.scale.z = Math.abs(theWorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.scale.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
/* transforms */
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f _myTempForwardVector = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f _myTempSideVector = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f _myTempUpVector = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static void pointAt(final TransformMatrix4f theResult,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theUpVector,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f thePointAtPosition) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
pointAt(theResult,
|
||||||
|
theResult.translation,
|
||||||
|
theUpVector,
|
||||||
|
thePointAtPosition);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// /* forward */
|
||||||
|
// _myTempForwardVector.sub(theResult.translation, thePointAtPosition);
|
||||||
|
// _myTempForwardVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// /* side */
|
||||||
|
// _myTempSideVector.cross(theUpVector, _myTempForwardVector);
|
||||||
|
// _myTempSideVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// /* up */
|
||||||
|
// _myTempUpVector.cross(_myTempForwardVector, _myTempSideVector);
|
||||||
|
// _myTempUpVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// if (!_myTempSideVector.isNaN() &&
|
||||||
|
// !_myTempUpVector.isNaN() &&
|
||||||
|
// !_myTempForwardVector.isNaN()) {
|
||||||
|
// theResult.rotation.setXAxis(_myTempSideVector);
|
||||||
|
// theResult.rotation.setYAxis(_myTempUpVector);
|
||||||
|
// theResult.rotation.setZAxis(_myTempForwardVector);
|
||||||
|
// }
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static void pointAt(final TransformMatrix4f theResult,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f thePosition,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theUpVector,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f thePointAtPosition) {
|
||||||
|
/* forward */
|
||||||
|
_myTempForwardVector.sub(thePosition, thePointAtPosition);
|
||||||
|
_myTempForwardVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* side */
|
||||||
|
_myTempSideVector.cross(theUpVector, _myTempForwardVector);
|
||||||
|
_myTempSideVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* up */
|
||||||
|
_myTempUpVector.cross(_myTempForwardVector, _myTempSideVector);
|
||||||
|
_myTempUpVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (!_myTempSideVector.isNaN()
|
||||||
|
&& !_myTempUpVector.isNaN()
|
||||||
|
&& !_myTempForwardVector.isNaN()) {
|
||||||
|
theResult.rotation.setXAxis(_myTempSideVector);
|
||||||
|
theResult.rotation.setYAxis(_myTempUpVector);
|
||||||
|
theResult.rotation.setZAxis(_myTempForwardVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static void pointAlong(final TransformMatrix4f theResult,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theForwardVector,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theUpVector) {
|
||||||
|
/* forward */
|
||||||
|
_myTempForwardVector.set(theForwardVector);
|
||||||
|
_myTempForwardVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* side */
|
||||||
|
_myTempSideVector.cross(theUpVector, _myTempForwardVector);
|
||||||
|
_myTempSideVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* up */
|
||||||
|
_myTempUpVector.cross(_myTempForwardVector, _myTempSideVector);
|
||||||
|
_myTempUpVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (!_myTempSideVector.isNaN()
|
||||||
|
&& !_myTempUpVector.isNaN()
|
||||||
|
&& !_myTempForwardVector.isNaN()) {
|
||||||
|
theResult.rotation.setXAxis(_myTempSideVector);
|
||||||
|
theResult.rotation.setYAxis(_myTempUpVector);
|
||||||
|
theResult.rotation.setZAxis(_myTempForwardVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final void toLocalSpace(TransformMatrix4f theLocalSpace, Vector3f theLocalResult) {
|
||||||
|
theLocalResult.sub(theLocalSpace.translation);
|
||||||
|
theLocalSpace.rotation.transform(theLocalResult);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final float bilinearInterp(final float x, final float y,
|
||||||
|
final float q00,
|
||||||
|
final float q10,
|
||||||
|
final float q01,
|
||||||
|
final float q11) {
|
||||||
|
return q00 * (1 - x) * (1 - y)
|
||||||
|
+ q10 * x * (1 - y)
|
||||||
|
+ q01 * (1 - x) * y
|
||||||
|
+ q11 * x * y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
/* normal */
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f TMP_BA = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f TMP_BC = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* calculate a normal from a set of three vectors.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param pointA
|
||||||
|
* @param pointB
|
||||||
|
* @param pointC
|
||||||
|
* @param theResultNormal
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final void calculateNormal(final Vector3f pointA,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f pointB,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f pointC,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theResultNormal) {
|
||||||
|
TMP_BA.sub(pointB, pointA);
|
||||||
|
TMP_BC.sub(pointC, pointB);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
theResultNormal.cross(TMP_BA, TMP_BC);
|
||||||
|
theResultNormal.normalize();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorAB Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorBC Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theResultNormal Vector3f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static void calculateNormal(final Vector3f theVectorAB,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theVectorBC,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theResultNormal) {
|
||||||
|
theResultNormal.cross(theVectorAB, theVectorBC);
|
||||||
|
theResultNormal.normalize();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param pointA Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param pointB Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param pointC Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector3f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static Vector3f createNormal(final Vector3f pointA,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f pointB,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f pointC) {
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f myResultNormal = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
calculateNormal(pointA,
|
||||||
|
pointB,
|
||||||
|
pointC,
|
||||||
|
myResultNormal);
|
||||||
|
return myResultNormal;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorAB Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorBC Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector3f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static Vector3f createNormal(final Vector3f theVectorAB,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theVectorBC) {
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f myResultNormal = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
calculateNormal(theVectorAB,
|
||||||
|
theVectorBC,
|
||||||
|
myResultNormal);
|
||||||
|
return myResultNormal;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static void createNormals(float[] theVertices, float[] theNormals) {
|
||||||
|
final int NUMBER_OF_VERTEX_COMPONENTS = 3;
|
||||||
|
final int myNumberOfPoints = 3;
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < theVertices.length;
|
||||||
|
i += (myNumberOfPoints * NUMBER_OF_VERTEX_COMPONENTS)) {
|
||||||
|
Vector3f a = new Vector3f(theVertices[i + 0], theVertices[i + 1], theVertices[i + 2]);
|
||||||
|
Vector3f b = new Vector3f(theVertices[i + 3], theVertices[i + 4], theVertices[i + 5]);
|
||||||
|
Vector3f c = new Vector3f(theVertices[i + 6], theVertices[i + 7], theVertices[i + 8]);
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myNormal = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mathematik.Util.calculateNormal(a, b, c, myNormal);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
theNormals[i + 0] = myNormal.x;
|
||||||
|
theNormals[i + 1] = myNormal.y;
|
||||||
|
theNormals[i + 2] = myNormal.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
theNormals[i + 3] = myNormal.x;
|
||||||
|
theNormals[i + 4] = myNormal.y;
|
||||||
|
theNormals[i + 5] = myNormal.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
theNormals[i + 6] = myNormal.x;
|
||||||
|
theNormals[i + 7] = myNormal.y;
|
||||||
|
theNormals[i + 8] = myNormal.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
/* distance */
|
||||||
|
private static final Vector3f _myTempVector = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* return the distance between to points defined by two vectors.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return float
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final float distance(Vector3f theVectorA, Vector3f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
_myTempVector.set(theVectorA);
|
||||||
|
return _myTempVector.distance(theVectorB);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* add */
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* add two vectors and return the result in a new instance.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector4f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector4f
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector4f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector4f add(Vector4f theVectorA, Vector4f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector4f(theVectorA.w + theVectorB.w,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.x + theVectorB.x,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.y + theVectorB.y,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.z + theVectorB.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* add two vectors and return the result in a new instance.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector3f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector3f add(Vector3f theVectorA, Vector3f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3f(theVectorA.x + theVectorB.x, theVectorA.y + theVectorB.y, theVectorA.z + theVectorB.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* add two vectors and return the result in a new instance.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector2f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector2f
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector2f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector2f add(Vector2f theVectorA, Vector2f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector2f(theVectorA.x + theVectorB.x,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.y + theVectorB.y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* add two vectors and return the result in a new instance.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector3i
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector3i
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector3i
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector3i add(Vector3i theVectorA, Vector3i theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3i(theVectorA.x + theVectorB.x, theVectorA.y + theVectorB.y, theVectorA.z + theVectorB.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* add two vectors and return the result in a new instance.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector2i
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector2i
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector2i
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector2i add(Vector2i theVectorA, Vector2i theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector2i(theVectorA.x + theVectorB.x, theVectorA.y + theVectorB.y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* sub */
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* subtract two vectors and return the result in a new instance.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector4f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector4f
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector4f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector4f sub(Vector4f theVectorA, Vector4f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector4f(theVectorA.w - theVectorB.w, theVectorA.x - theVectorB.x, theVectorA.y - theVectorB.y,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.z - theVectorB.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* subtract two vectors and return the result in a new instance.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector3f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector3f sub(Vector3f theVectorA, Vector3f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3f(theVectorA.x - theVectorB.x, theVectorA.y - theVectorB.y, theVectorA.z - theVectorB.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* subtract two vectors and return the result in a new instance.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector2f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector2f
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector2f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector2f sub(Vector2f theVectorA, Vector2f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector2f(theVectorA.x - theVectorB.x, theVectorA.y - theVectorB.y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* subtract two vectors and return the result in a new instance.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector3i
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector3i
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector3i
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector3i sub(Vector3i theVectorA, Vector3i theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3i(theVectorA.x - theVectorB.x,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.y - theVectorB.y,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.z - theVectorB.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* subtract two vectors and return the result in a new instance.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector2i
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector2i
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector2i
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector2i sub(Vector2i theVectorA, Vector2i theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector2i(theVectorA.x - theVectorB.x,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.y - theVectorB.y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* return the cross between two vectors in a new vector.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector3f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector3f cross(Vector3f theVectorA, Vector3f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f myVector = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
myVector.cross(theVectorA, theVectorB);
|
||||||
|
return myVector;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* return a normalized vector in a new vector.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVector Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector3f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector3f normalized(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f myVector = new Vector3f(theVector);
|
||||||
|
myVector.normalize();
|
||||||
|
return myVector;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA Vector2f
|
||||||
|
* @param theValue float
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector2f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector2f scale(Vector2f theVectorA, float theValue) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector2f(theVectorA.x * theValue,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.y * theValue);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector3f scale(Vector3f theVectorA, float theValue) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3f(theVectorA.x * theValue,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.y * theValue,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.z * theValue);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector3f scale(Vector3f theVectorA, Vector3f theValue) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3f(theVectorA.x * theValue.x,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.y * theValue.y,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.z * theValue.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final Vector4f scale(Vector4f theVectorA, float theValue) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector4f(theVectorA.x * theValue,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.y * theValue,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.z * theValue,
|
||||||
|
theVectorA.w * theValue);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final float clamp(float theValue, float theMin, float theMax) {
|
||||||
|
if (theValue > theMax) {
|
||||||
|
theValue = theMax;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (theValue < theMin) {
|
||||||
|
theValue = theMin;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return theValue;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final float normalize(float theValue, float theStart, float theEnd) {
|
||||||
|
return (theValue - theStart) / (theEnd - theStart);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final float map(float theValue, float theInStart, float theInEnd, float theOutStart, float theOutEnd) {
|
||||||
|
return theOutStart + (theOutEnd - theOutStart) * ((theValue - theInStart) / (theInEnd - theInStart));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static Vector2f parseVector2f(String theString) {
|
||||||
|
String splitter;
|
||||||
|
if (contains(theString, ",")) {
|
||||||
|
splitter = ",";
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
String[] coords = theString.split(splitter);
|
||||||
|
return new Vector2f(Float.parseFloat(coords[0]),
|
||||||
|
Float.parseFloat(coords[1]));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static Vector3f parseVector3f(String theString) {
|
||||||
|
String splitter;
|
||||||
|
if (contains(theString, ",")) {
|
||||||
|
splitter = ",";
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
String[] coords = theString.split(splitter);
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3f(Float.parseFloat(coords[0]),
|
||||||
|
Float.parseFloat(coords[1]),
|
||||||
|
Float.parseFloat(coords[2]));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static boolean contains(String theString, CharSequence theContainedString) {
|
||||||
|
return theString.indexOf(theContainedString.toString()) > -1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* the following point rotation methods are from the famous paul bourke.
|
||||||
|
* read more on his website at
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* http://local.wasp.uwa.edu.au/~pbourke/geometry/rotate/
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Rotate a point p by angle theta around an arbitrary axis r Return the
|
||||||
|
* rotated point. Positive angles are anticlockwise looking down the axis
|
||||||
|
* towards the origin. Assume right hand coordinate system.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param p Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theta double
|
||||||
|
* @param theAxis Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return Vector3f
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static Vector3f rotatePoint(Vector3f p,
|
||||||
|
double theta,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f theAxis) {
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myR = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
Vector3f q = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
double costheta, sintheta;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myR.normalize(theAxis);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
costheta = Math.cos(theta);
|
||||||
|
sintheta = Math.sin(theta);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
q.x += (costheta + (1 - costheta) * myR.x * myR.x) * p.x;
|
||||||
|
q.x += ((1 - costheta) * myR.x * myR.y - myR.z * sintheta) * p.y;
|
||||||
|
q.x += ((1 - costheta) * myR.x * myR.z + myR.y * sintheta) * p.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
q.y += ((1 - costheta) * myR.x * myR.y + myR.z * sintheta) * p.x;
|
||||||
|
q.y += (costheta + (1 - costheta) * myR.y * myR.y) * p.y;
|
||||||
|
q.y += ((1 - costheta) * myR.y * myR.z - myR.x * sintheta) * p.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
q.z += ((1 - costheta) * myR.x * myR.z - myR.y * sintheta) * p.x;
|
||||||
|
q.z += ((1 - costheta) * myR.y * myR.z + myR.x * sintheta) * p.y;
|
||||||
|
q.z += (costheta + (1 - costheta) * myR.z * myR.z) * p.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return q;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Rotate a point p by angle theta around an arbitrary line segment p1-p2
|
||||||
|
* Return the rotated point.
|
||||||
|
* Positive angles are anticlockwise looking down the axis towards the origin.
|
||||||
|
* Assume right hand coordinate system.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static Vector3f rotatePoint(Vector3f p,
|
||||||
|
double theta,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f p1,
|
||||||
|
Vector3f p2) {
|
||||||
|
Vector3f r = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
Vector3f q = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
Vector3f myP = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
double costheta, sintheta;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
myP.set(p);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
r.x = p2.x - p1.x;
|
||||||
|
r.y = p2.y - p1.y;
|
||||||
|
r.z = p2.z - p1.z;
|
||||||
|
myP.x -= p1.x;
|
||||||
|
myP.y -= p1.y;
|
||||||
|
myP.z -= p1.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
r.normalize();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
costheta = Math.cos(theta);
|
||||||
|
sintheta = Math.sin(theta);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
q.x += (costheta + (1 - costheta) * r.x * r.x) * myP.x;
|
||||||
|
q.x += ((1 - costheta) * r.x * r.y - r.z * sintheta) * myP.y;
|
||||||
|
q.x += ((1 - costheta) * r.x * r.z + r.y * sintheta) * myP.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
q.y += ((1 - costheta) * r.x * r.y + r.z * sintheta) * myP.x;
|
||||||
|
q.y += (costheta + (1 - costheta) * r.y * r.y) * myP.y;
|
||||||
|
q.y += ((1 - costheta) * r.y * r.z - r.x * sintheta) * myP.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
q.z += ((1 - costheta) * r.x * r.z - r.y * sintheta) * myP.x;
|
||||||
|
q.z += ((1 - costheta) * r.y * r.z + r.x * sintheta) * myP.y;
|
||||||
|
q.z += (costheta + (1 - costheta) * r.z * r.z) * myP.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
q.x += p1.x;
|
||||||
|
q.y += p1.y;
|
||||||
|
q.z += p1.z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return q;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* DistancePointLine Unit Test Copyright (c) 2002, All rights reserved
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Damian Coventry Tuesday, 16 July 2002
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Implementation of theory by Paul Bourke
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param thePoint Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theLineStart Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @param theLineEnd Vector3f
|
||||||
|
* @return float
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static float distancePointLineSegment(final Vector3f thePoint,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theLineStart,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theLineEnd) {
|
||||||
|
final float u = distancePointLineU(thePoint, theLineStart, theLineEnd);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (u < 0.0f || u > 1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
return -1; // closest point does not fall within the line segment
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f myIntersection = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
myIntersection.x = theLineStart.x + u * (theLineEnd.x - theLineStart.x);
|
||||||
|
myIntersection.y = theLineStart.y + u * (theLineEnd.y - theLineStart.y);
|
||||||
|
myIntersection.z = theLineStart.z + u * (theLineEnd.z - theLineStart.z);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return thePoint.distance(myIntersection);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static float distancePointLine(final Vector3f thePoint,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theLineStart,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theLineEnd) {
|
||||||
|
final float u = distancePointLineU(thePoint, theLineStart, theLineEnd);
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f myIntersection = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
myIntersection.x = theLineStart.x + u * (theLineEnd.x - theLineStart.x);
|
||||||
|
myIntersection.y = theLineStart.y + u * (theLineEnd.y - theLineStart.y);
|
||||||
|
myIntersection.z = theLineStart.z + u * (theLineEnd.z - theLineStart.z);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return thePoint.distance(myIntersection);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static float distancePointLineU(final Vector3f thePoint,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theLineStart,
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f theLineEnd) {
|
||||||
|
final float myLineMagnitude = theLineStart.distance(theLineEnd);
|
||||||
|
final float u = (((thePoint.x - theLineStart.x) * (theLineEnd.x - theLineStart.x))
|
||||||
|
+ ((thePoint.y - theLineStart.y) * (theLineEnd.y - theLineStart.y))
|
||||||
|
+ ((thePoint.z - theLineStart.z) * (theLineEnd.z - theLineStart.z)))
|
||||||
|
/ (myLineMagnitude * myLineMagnitude);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return u;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static float random(float theStart,
|
||||||
|
float theEnd) {
|
||||||
|
final float myDiff = theEnd - theStart;
|
||||||
|
final float myRandomValue = (float) Math.random() * myDiff;
|
||||||
|
return myRandomValue + theStart;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
public static final int CLOCKWISE = 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final int COUNTERCLOCKWISE = -1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* adapted from genius paul bourke
|
||||||
|
* http://debian.fmi.uni-sofia.bg/~sergei/cgsr/docs/clockwise.htm
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Return the clockwise status of a curve, clockwise or counterclockwise n
|
||||||
|
* vertices making up curve p return 0 for incomputables eg: colinear points
|
||||||
|
* CLOCKWISE == 1 COUNTERCLOCKWISE == -1 It is assumed that - the polygon is
|
||||||
|
* closed - the last point is not repeated. - the polygon is simple (does
|
||||||
|
* not intersect itself or have holes)
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static int isClockWise(final Vector<Vector2f> mPoints) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (mPoints.size() < 3) {
|
||||||
|
return (0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int mCount = 0;
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPoints.size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
final Vector2f p1 = mPoints.get(i);
|
||||||
|
final Vector2f p2 = mPoints.get((i + 1) % mPoints.size());
|
||||||
|
final Vector2f p3 = mPoints.get((i + 2) % mPoints.size());
|
||||||
|
float z;
|
||||||
|
z = (p2.x - p1.x) * (p3.y - p2.y);
|
||||||
|
z -= (p2.y - p1.y) * (p3.x - p2.x);
|
||||||
|
if (z < 0) {
|
||||||
|
mCount--;
|
||||||
|
} else if (z > 0) {
|
||||||
|
mCount++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (mCount > 0) {
|
||||||
|
return (COUNTERCLOCKWISE);
|
||||||
|
} else if (mCount < 0) {
|
||||||
|
return (CLOCKWISE);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return (0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static int isClockWise2D(final Vector<Vector3f> mPoints) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (mPoints.size() < 3) {
|
||||||
|
return (0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int mCount = 0;
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPoints.size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f p1 = mPoints.get(i);
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f p2 = mPoints.get((i + 1) % mPoints.size());
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f p3 = mPoints.get((i + 2) % mPoints.size());
|
||||||
|
float z;
|
||||||
|
z = (p2.x - p1.x) * (p3.y - p2.y);
|
||||||
|
z -= (p2.y - p1.y) * (p3.x - p2.x);
|
||||||
|
if (z < 0) {
|
||||||
|
mCount--;
|
||||||
|
} else if (z > 0) {
|
||||||
|
mCount++;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (mCount > 0) {
|
||||||
|
return (COUNTERCLOCKWISE);
|
||||||
|
} else if (mCount < 0) {
|
||||||
|
return (CLOCKWISE);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return (0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
public static final int CONVEX = 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final int CONCAVE = -1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* adapted from genius paul bourke
|
||||||
|
* http://debian.fmi.uni-sofia.bg/~sergei/cgsr/docs/clockwise.htm
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Return whether a polygon in 2D is concave or convex return 0 for
|
||||||
|
* incomputables eg: colinear points CONVEX == 1 CONCAVE == -1 It is assumed
|
||||||
|
* that the polygon is simple (does not intersect itself or have holes)
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public static int isConvex(final Vector<Vector2f> mPoints) {
|
||||||
|
int flag = 0;
|
||||||
|
double z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (mPoints.size() < 3) {
|
||||||
|
return (0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPoints.size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
final Vector2f p1 = mPoints.get(i);
|
||||||
|
final Vector2f p2 = mPoints.get((i + 1) % mPoints.size());
|
||||||
|
final Vector2f p3 = mPoints.get((i + 2) % mPoints.size());
|
||||||
|
z = (p2.x - p1.x) * (p3.y - p2.y);
|
||||||
|
z -= (p2.y - p1.y) * (p3.x - p2.x);
|
||||||
|
if (z < 0) {
|
||||||
|
flag |= 1;
|
||||||
|
} else if (z > 0) {
|
||||||
|
flag |= 2;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (flag == 3) {
|
||||||
|
return (CONCAVE);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (flag != 0) {
|
||||||
|
return (CONVEX);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return (0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static int isConvex2D(final Vector<Vector3f> mPoints) {
|
||||||
|
int flag = 0;
|
||||||
|
double z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (mPoints.size() < 3) {
|
||||||
|
return (0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPoints.size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f p1 = mPoints.get(i);
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f p2 = mPoints.get((i + 1) % mPoints.size());
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f p3 = mPoints.get((i + 2) % mPoints.size());
|
||||||
|
z = (p2.x - p1.x) * (p3.y - p2.y);
|
||||||
|
z -= (p2.y - p1.y) * (p3.x - p2.x);
|
||||||
|
if (z < 0) {
|
||||||
|
flag |= 1;
|
||||||
|
} else if (z > 0) {
|
||||||
|
flag |= 2;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (flag == 3) {
|
||||||
|
return (CONCAVE);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (flag != 0) {
|
||||||
|
return (CONVEX);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return (0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
330
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vector2f.java
Executable file
330
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vector2f.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,330 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Vector2f
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable, Vectorf {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4652533170291767614L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float x;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float y;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// private float[] _myArrayRepresentation = new float[2];
|
||||||
|
private static final float ALMOST_THRESHOLD = 0.001f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f() {
|
||||||
|
x = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
y = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f(float theX,
|
||||||
|
float theY) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX,
|
||||||
|
theY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f(double theX,
|
||||||
|
double theY) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX,
|
||||||
|
theY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f(float[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f(double[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f(int[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector.x, theVector.y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Object clone() {
|
||||||
|
return cloneVector();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f cloneVector() {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector2f(x, y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector2f set(float theX,
|
||||||
|
float theY) {
|
||||||
|
x = theX;
|
||||||
|
y = theY;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector2f set(double theX,
|
||||||
|
double theY) {
|
||||||
|
x = (float) theX;
|
||||||
|
y = (float) theY;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector2f set(float[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector[0];
|
||||||
|
y = theVector[1];
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector2f set(double[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = (float) theVector[0];
|
||||||
|
y = (float) theVector[1];
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector2f set(int[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector[0];
|
||||||
|
y = theVector[1];
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector2f set(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f add(Vector2f theVectorA,
|
||||||
|
Vector2f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVectorA.x + theVectorB.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVectorA.y + theVectorB.y;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f add(final int theX, final int theY) {
|
||||||
|
x += theX;
|
||||||
|
y += theY;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f add(final float theX, final float theY) {
|
||||||
|
x += theX;
|
||||||
|
y += theY;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f add(final double theX, final double theY) {
|
||||||
|
x += theX;
|
||||||
|
y += theY;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f add(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x += theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y += theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f sub(Vector2f theVectorA,
|
||||||
|
Vector2f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVectorA.x - theVectorB.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVectorA.y - theVectorB.y;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f sub(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x -= theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y -= theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f sub(float theX, float theY) {
|
||||||
|
x -= theX;
|
||||||
|
y -= theY;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f scale(float theScalar,
|
||||||
|
Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theScalar * theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theScalar * theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f scale(float theScalar) {
|
||||||
|
x *= theScalar;
|
||||||
|
y *= theScalar;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f scale(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x *= theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y *= theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f scale(float theXScalar, float theYScalar) {
|
||||||
|
x *= theXScalar;
|
||||||
|
y *= theYScalar;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float direction() {
|
||||||
|
return (float) Math.atan2(y, x);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float dot(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
return x * theVector.x + y * theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f cross(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
y = -theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f cross() {
|
||||||
|
final float myX = y;
|
||||||
|
y = -x;
|
||||||
|
x = myX;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float length() {
|
||||||
|
return (float) Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float lengthSquared() {
|
||||||
|
return x * x + y * y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f normalize(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
float inverseMag = 1.0f / (float) Math.sqrt(theVector.x * theVector.x + theVector.y * theVector.y);
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.x * inverseMag;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector.y * inverseMag;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f normalize() {
|
||||||
|
float inverseMag = 1.0f / (float) Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y);
|
||||||
|
x *= inverseMag;
|
||||||
|
y *= inverseMag;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float angle(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
float d = dot(theVector) / (length() * theVector.length());
|
||||||
|
if (d < -1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
d = -1.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (d > 1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
d = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return (float) Math.acos(d);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2f rotate(float theRadians) {
|
||||||
|
final float myX = (float) (x * Math.cos(theRadians) - y * Math.sin(theRadians));
|
||||||
|
final float myY = (float) (y * Math.cos(theRadians) + x * Math.sin(theRadians));
|
||||||
|
x = myX;
|
||||||
|
y = myY;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float distanceSquared(Vector2f thePoint) {
|
||||||
|
float dx = x - thePoint.x;
|
||||||
|
float dy = y - thePoint.y;
|
||||||
|
return dx * dx + dy * dy;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float distance(Vector2f thePoint) {
|
||||||
|
float dx = x - thePoint.x;
|
||||||
|
float dy = y - thePoint.y;
|
||||||
|
return (float) Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float[] toArray() {
|
||||||
|
final float[] _myArrayRepresentation = new float[2];
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[0] = x;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[1] = y;
|
||||||
|
return _myArrayRepresentation;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean isNaN() {
|
||||||
|
if (Float.isNaN(x) || Float.isNaN(y)) {
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean equals(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
if (x == theVector.x && y == theVector.y) {
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public int hashCode() {
|
||||||
|
int hash = 5;
|
||||||
|
hash = 73 * hash + Float.floatToIntBits(this.x);
|
||||||
|
hash = 73 * hash + Float.floatToIntBits(this.y);
|
||||||
|
return hash;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean equals(final Object theVector) {
|
||||||
|
if (!(theVector instanceof Vector2f)) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return equals((Vector2f) theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Returns true if both x and y are zero
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @return boolean, true if the vector is zero
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public boolean equalsZero() {
|
||||||
|
return x == 0 && y == 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean almost(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
if (Math.abs(x - theVector.x) < ALMOST_THRESHOLD
|
||||||
|
&& Math.abs(y - theVector.y) < ALMOST_THRESHOLD) {
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public String toString() {
|
||||||
|
return "(" + x + ", " + y + ")";
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
123
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vector2i.java
Executable file
123
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vector2i.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Vector2i
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1578087698419866994L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public int x;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public int y;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2i() {
|
||||||
|
x = 0;
|
||||||
|
y = 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2i(int theX,
|
||||||
|
int theY) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX,
|
||||||
|
theY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2i(Vector2i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector2i(int[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(int theX,
|
||||||
|
int theY) {
|
||||||
|
x = theX;
|
||||||
|
y = theY;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(Vector2i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(int[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector[0];
|
||||||
|
y = theVector[1];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void sub(final Vector2i theVectorA,
|
||||||
|
final Vector2i theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVectorA.x - theVectorB.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVectorA.y - theVectorB.y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void sub(final Vector2i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x -= theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y -= theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void sub(final int theX, final int theY) {
|
||||||
|
x -= theX;
|
||||||
|
y -= theY;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void add(final Vector2i theVectorA,
|
||||||
|
final Vector2i theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVectorA.x + theVectorB.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVectorA.y + theVectorB.y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void add(final Vector2i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x += theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y += theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void add(final int theX, final int theY) {
|
||||||
|
x += theX;
|
||||||
|
y += theY;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void scale(float theScalar,
|
||||||
|
Vector2i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = (int) (theScalar * theVector.x);
|
||||||
|
y = (int) (theScalar * theVector.y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void scale(float theScalar) {
|
||||||
|
x *= theScalar;
|
||||||
|
y *= theScalar;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void scale(Vector2i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x *= theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y *= theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final String toString() {
|
||||||
|
return "(" + x + ", " + y + ")";
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
629
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vector3f.java
Executable file
629
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vector3f.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,629 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Random;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Vector3f
|
||||||
|
implements Cloneable, Serializable, Comparable<Vector3f>, Vectorf {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1021495605082676516L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Utility for random
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
static final Random generator = new Random();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* The x coordinate of the vector
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public float x;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* The y coordinate of the vector
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public float y;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* The z coordinate of the vector
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public float z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// /**
|
||||||
|
// * float array for returning an array representation of the vector
|
||||||
|
// */
|
||||||
|
// private float[] _myArrayRepresentation = new float[3];
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* threshold to maintain the minimal difference between two vectors before
|
||||||
|
* they are almost the same
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
private static final float ALMOST_THRESHOLD = 0.001f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Initializes a new vector. x, y, and z are set to zero.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f() {
|
||||||
|
x = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
y = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
z = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Creates a new vector with the given coordinates. Inserted double values
|
||||||
|
* are casted to floats
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theX int, float or double: x coord of the new vector
|
||||||
|
* @param theY int, float or double: y coord of the new vector
|
||||||
|
* @param theZ int, float or double: z coord of the new vector
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(float theX, float theY, float theZ) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX, theY, theZ);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(double theX, double theY, double theZ) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX, theY, theZ);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(float theX, float theY) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX, theY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(double theX, double theY) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX, theY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(float[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(double[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(int[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(Vector3i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(Vector2i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f(String theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(float theX, float theY, float theZ) {
|
||||||
|
x = theX;
|
||||||
|
y = theY;
|
||||||
|
z = theZ;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(double theX, double theY, double theZ) {
|
||||||
|
x = (float) theX;
|
||||||
|
y = (float) theY;
|
||||||
|
z = (float) theZ;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(float theX, float theY) {
|
||||||
|
x = theX;
|
||||||
|
y = theY;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(double theX, double theY) {
|
||||||
|
x = (float) theX;
|
||||||
|
y = (float) theY;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(float[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector[0];
|
||||||
|
y = theVector[1];
|
||||||
|
z = theVector[2];
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(double[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = (float) theVector[0];
|
||||||
|
y = (float) theVector[1];
|
||||||
|
z = (float) theVector[2];
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(int[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector[0];
|
||||||
|
y = theVector[1];
|
||||||
|
z = theVector[2];
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(Vector3i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(Vector2i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f set(String theVectorString) {
|
||||||
|
theVectorString = theVectorString.replace("(", "");
|
||||||
|
theVectorString = theVectorString.replace(")", "");
|
||||||
|
theVectorString = theVectorString.replaceAll(" ", "");
|
||||||
|
String[] myComponents = theVectorString.split(",");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
x = Float.parseFloat(myComponents[0]);
|
||||||
|
} catch (Exception ex) {
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
y = Float.parseFloat(myComponents[1]);
|
||||||
|
} catch (Exception ex1) {
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
z = Float.parseFloat(myComponents[2]);
|
||||||
|
} catch (Exception ex2) {
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f add(Vector3f theVectorA, Vector3f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVectorA.x + theVectorB.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVectorA.y + theVectorB.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theVectorA.z + theVectorB.z;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f add(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x += theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y += theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z += theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f add(float theX, float theY) {
|
||||||
|
x += theX;
|
||||||
|
y += theY;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f add(float theX, float theY, float theZ) {
|
||||||
|
x += theX;
|
||||||
|
y += theY;
|
||||||
|
z += theZ;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f sub(Vector3f theVectorA, Vector3f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVectorA.x - theVectorB.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVectorA.y - theVectorB.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theVectorA.z - theVectorB.z;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f sub(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x -= theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y -= theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z -= theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Use this method to negate a vector. The result of the negation is vector
|
||||||
|
* with the same magnitude but opposite direction. Mathematically the
|
||||||
|
* negation is the additive inverse of the vector. The sum of a value and
|
||||||
|
* its additive inerse is always zero.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @shortdesc Use this method to negate a vector.
|
||||||
|
* @related scale ( )
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f negate() {
|
||||||
|
scale(-1);
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Use this method to scale a vector. To scale a vector each of its
|
||||||
|
* coordinates is multiplied with the given scalar. The result is a vector
|
||||||
|
* that is parallel with its origin, with a different length and possibly
|
||||||
|
* opposite direction.<br>
|
||||||
|
* You can also scale a vector with another vector, in this case each coord
|
||||||
|
* of the vector is multiplied with related coord of the given vector.<br>
|
||||||
|
* Another possibillity is to set and scale the vector, this means the
|
||||||
|
* vector is set to the given vector multiplied with the given scalar.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theScalar float or int: the value the vector is scaled with
|
||||||
|
* @related divide ( )
|
||||||
|
* @related negate ( )
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f scale(final float theScalar) {
|
||||||
|
x *= theScalar;
|
||||||
|
y *= theScalar;
|
||||||
|
z *= theScalar;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVector Vector3f: vector with the value each coord is scaled
|
||||||
|
* with
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f scale(final Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x *= theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y *= theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z *= theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theX float
|
||||||
|
* @param theY float
|
||||||
|
* @param theZ float
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f scale(float theX, float theY, float theZ) {
|
||||||
|
x *= theX;
|
||||||
|
y *= theY;
|
||||||
|
z *= theZ;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @param theScalar float or int: value the given vector is scaled with
|
||||||
|
* @param theVector Vector3f: vector the vector is set to
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f scale(final float theScalar, final Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theScalar * theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theScalar * theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theScalar * theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Dividing is nearly the the same as scaling, except
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theDivisor
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f divide(final float theDivisor) {
|
||||||
|
x /= theDivisor;
|
||||||
|
y /= theDivisor;
|
||||||
|
z /= theDivisor;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f divide(final Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x /= theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y /= theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z /= theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float lengthSquared() {
|
||||||
|
return x * x + y * y + z * z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Use this method to calculate the length of a vector, the length of a
|
||||||
|
* vector is also known as its magnitude. Vectors have a magnitude and a
|
||||||
|
* direction. These values are not explicitly expressed in the vector so
|
||||||
|
* they have to be computed.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @return float: the length of the vector
|
||||||
|
* @shortdesc Calculates the length of the vector.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public float length() {
|
||||||
|
return (float) Math.sqrt(lengthSquared());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float magnitude() {
|
||||||
|
return length();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Sets this vector to the cross product of two given vectors. The cross
|
||||||
|
* product returns a vector standing vertical on the two vectors.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorA
|
||||||
|
* @param theVectorB
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f cross(final Vector3f theVectorA, final Vector3f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
return set(theVectorA.cross(theVectorB));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Returns the cross product of two vectors. The cross product returns a
|
||||||
|
* vector standing vertical on the two vectors.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param i_vector the other vector
|
||||||
|
* @return the cross product
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f cross(final Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
return new Vector3f(y * theVector.z - z * theVector.y,
|
||||||
|
z * theVector.x - x * theVector.z,
|
||||||
|
x * theVector.y - y * theVector.x);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Returns the dot product of two vectors. The dot product is the cosinus of
|
||||||
|
* the angle between two vectors
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param theVector, the other vector
|
||||||
|
* @return float, dot product of two vectors
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public float dot(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
return x * theVector.x + y * theVector.y + z * theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Sets the vector to the given one and norms it to the length of 1
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f normalize(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
normalize();
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Norms the vector to the length of 1
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f normalize() {
|
||||||
|
float inverseMag = 1.0f / (float) Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z);
|
||||||
|
x *= inverseMag;
|
||||||
|
y *= inverseMag;
|
||||||
|
z *= inverseMag;
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Interpolates between this vector and the given vector by a given blend
|
||||||
|
* value. The blend value has to be between 0 and 1. A blend value 0 would
|
||||||
|
* change nothing, a blend value 1 would set this vector to the given one.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param blend float, blend value for interpolation
|
||||||
|
* @param i_vector Vector3f, other vector for interpolation
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public void interpolate(final float blend, final Vector3f i_vector) {
|
||||||
|
x = x + blend * (i_vector.x - x);
|
||||||
|
y = y + blend * (i_vector.y - y);
|
||||||
|
z = z + blend * (i_vector.z - z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Sets a position randomly distributed inside a sphere of unit radius
|
||||||
|
* centered at the origin. Orientation will be random and length will range
|
||||||
|
* between 0 and 1
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public void randomize() {
|
||||||
|
x = generator.nextFloat() * 2.0F - 1.0F;
|
||||||
|
y = generator.nextFloat() * 2.0F - 1.0F;
|
||||||
|
z = generator.nextFloat() * 2.0F - 1.0F;
|
||||||
|
normalize();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float angle(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
float d = dot(theVector) / (length() * theVector.length());
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo check these lines.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
if (d < -1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
d = -1.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (d > 1.0f) {
|
||||||
|
d = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return (float) Math.acos(d);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float distanceSquared(Vector3f thePoint) {
|
||||||
|
float dx = x - thePoint.x;
|
||||||
|
float dy = y - thePoint.y;
|
||||||
|
float dz = z - thePoint.z;
|
||||||
|
return dx * dx + dy * dy + dz * dz;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float distance(Vector3f thePoint) {
|
||||||
|
float dx = x - thePoint.x;
|
||||||
|
float dy = y - thePoint.y;
|
||||||
|
float dz = z - thePoint.z;
|
||||||
|
return (float) Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy + dz * dz);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float distanceL1(Vector3f thePoint) {
|
||||||
|
return Math.abs(x - thePoint.x) + Math.abs(y - thePoint.y)
|
||||||
|
+ Math.abs(z - thePoint.z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f min(Vector3f theMin) {
|
||||||
|
if (x < theMin.x) {
|
||||||
|
x = theMin.x;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (y < theMin.y) {
|
||||||
|
y = theMin.y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (z < theMin.z) {
|
||||||
|
z = theMin.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f min(float theX, float theY, float theZ) {
|
||||||
|
if (x < theX) {
|
||||||
|
x = theX;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (y < theY) {
|
||||||
|
y = theY;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (z < theZ) {
|
||||||
|
z = theZ;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f max(Vector3f theMax) {
|
||||||
|
if (x > theMax.x) {
|
||||||
|
x = theMax.x;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (y > theMax.y) {
|
||||||
|
y = theMax.y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (z > theMax.z) {
|
||||||
|
z = theMax.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f max(float theX, float theY, float theZ) {
|
||||||
|
if (x > theX) {
|
||||||
|
x = theX;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (y > theY) {
|
||||||
|
y = theY;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (z > theZ) {
|
||||||
|
z = theZ;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return this;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float[] toArray() {
|
||||||
|
final float[] _myArrayRepresentation = new float[3];
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[0] = x;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[1] = y;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[2] = z;
|
||||||
|
return _myArrayRepresentation;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean isNaN() {
|
||||||
|
if (Float.isNaN(x) || Float.isNaN(y) || Float.isNaN(z)) {
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean equals(final Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
if (x == theVector.x && y == theVector.y && z == theVector.z) {
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public int hashCode() {
|
||||||
|
int hash = 7;
|
||||||
|
hash = 17 * hash + Float.floatToIntBits(this.x);
|
||||||
|
hash = 17 * hash + Float.floatToIntBits(this.y);
|
||||||
|
hash = 17 * hash + Float.floatToIntBits(this.z);
|
||||||
|
return hash;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean equals(final Object theVector) {
|
||||||
|
if (!(theVector instanceof Vector3f)) {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return equals((Vector3f) theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean almost(final Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
if (Math.abs(x - theVector.x) < ALMOST_THRESHOLD
|
||||||
|
&& Math.abs(y - theVector.y) < ALMOST_THRESHOLD
|
||||||
|
&& Math.abs(z - theVector.z) < ALMOST_THRESHOLD) {
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Object clone() {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
return super.clone();
|
||||||
|
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
|
||||||
|
// this shouldn t happen, since we are Cloneable
|
||||||
|
throw new InternalError();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public String toString() {
|
||||||
|
return "(" + x + ", " + y + ", " + z + ")";
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
public static final int X = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final int Y = 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final int Z = 2;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static final int LENGTH = 3;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static int COMPARE_TYPE = LENGTH;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public int compareTo(Vector3f theVector3f) {
|
||||||
|
if (COMPARE_TYPE == LENGTH) {
|
||||||
|
final float myLengthSquared = lengthSquared();
|
||||||
|
final float myOtherLengthSquared = theVector3f.lengthSquared();
|
||||||
|
return myLengthSquared > myOtherLengthSquared ? 1 : (myLengthSquared < myOtherLengthSquared ? -1 : 0);
|
||||||
|
} else if (COMPARE_TYPE == X) {
|
||||||
|
return x > theVector3f.x ? 1 : (x < theVector3f.x ? -1 : 0);
|
||||||
|
} else if (COMPARE_TYPE == Y) {
|
||||||
|
return y > theVector3f.y ? 1 : (y < theVector3f.y ? -1 : 0);
|
||||||
|
} else if (COMPARE_TYPE == Z) {
|
||||||
|
return z > theVector3f.z ? 1 : (z < theVector3f.z ? -1 : 0);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
86
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vector3i.java
Executable file
86
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vector3i.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Vector3i
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable, Comparable<Vector3i> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1207335169644019377L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public int x;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public int y;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public int z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3i() {
|
||||||
|
x = 0;
|
||||||
|
y = 0;
|
||||||
|
z = 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3i(int theX, int theY, int theZ) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX, theY, theZ);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3i(Vector3i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3i(int[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(int theX, int theY, int theZ) {
|
||||||
|
x = theX;
|
||||||
|
y = theY;
|
||||||
|
z = theZ;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(Vector3i theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void set(int[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector[0];
|
||||||
|
y = theVector[1];
|
||||||
|
z = theVector[2];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final String toString() {
|
||||||
|
return "(" + x + ", " + y + ", " + z + ")";
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float lengthSquared() {
|
||||||
|
return x * x + y * y + z * z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public int compareTo(Vector3i theVector3i) {
|
||||||
|
return (int) (lengthSquared() - theVector3i.lengthSquared());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
307
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vector4f.java
Executable file
307
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vector4f.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,307 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Vector4f
|
||||||
|
implements Serializable, Vectorf {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5083919691492230155L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float w;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float x;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float y;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float z;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final float ALMOST_THRESHOLD = 0.001f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f() {
|
||||||
|
x = 0;
|
||||||
|
y = 0;
|
||||||
|
z = 0;
|
||||||
|
w = 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f(float theX,
|
||||||
|
float theY,
|
||||||
|
float theZ,
|
||||||
|
float theW) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX,
|
||||||
|
theY,
|
||||||
|
theZ,
|
||||||
|
theW);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f(double theX,
|
||||||
|
double theY,
|
||||||
|
double theZ,
|
||||||
|
double theW) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX,
|
||||||
|
theY,
|
||||||
|
theZ,
|
||||||
|
theW);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f(float theX,
|
||||||
|
float theY,
|
||||||
|
float theZ) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX,
|
||||||
|
theY,
|
||||||
|
theZ);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f(double theX,
|
||||||
|
double theY,
|
||||||
|
double theZ) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX,
|
||||||
|
theY,
|
||||||
|
theZ);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f(float theX,
|
||||||
|
float theY) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX,
|
||||||
|
theY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f(double theX,
|
||||||
|
double theY) {
|
||||||
|
set(theX,
|
||||||
|
theY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f(float[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f(double[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f(Vector4f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector4f(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(float theX,
|
||||||
|
float theY,
|
||||||
|
float theZ,
|
||||||
|
float theW) {
|
||||||
|
x = theX;
|
||||||
|
y = theY;
|
||||||
|
z = theZ;
|
||||||
|
w = theW;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(double theX,
|
||||||
|
double theY,
|
||||||
|
double theZ,
|
||||||
|
double theW) {
|
||||||
|
x = (float) theX;
|
||||||
|
y = (float) theY;
|
||||||
|
z = (float) theZ;
|
||||||
|
w = (float) theW;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(float theX,
|
||||||
|
float theY,
|
||||||
|
float theZ) {
|
||||||
|
x = theX;
|
||||||
|
y = theY;
|
||||||
|
z = theZ;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(double theX,
|
||||||
|
double theY,
|
||||||
|
double theZ) {
|
||||||
|
x = (float) theX;
|
||||||
|
y = (float) theY;
|
||||||
|
z = (float) theZ;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(float theX,
|
||||||
|
float theY) {
|
||||||
|
x = theX;
|
||||||
|
y = theY;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(double theX,
|
||||||
|
double theY) {
|
||||||
|
x = (float) theX;
|
||||||
|
y = (float) theY;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(float[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
w = theVector[0];
|
||||||
|
x = theVector[1];
|
||||||
|
y = theVector[2];
|
||||||
|
z = theVector[3];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(double[] theVector) {
|
||||||
|
w = (float) theVector[0];
|
||||||
|
x = (float) theVector[1];
|
||||||
|
y = (float) theVector[2];
|
||||||
|
z = (float) theVector[3];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(Vector4f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
w = theVector.w;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(Vector3f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void set(Vector2f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
x = theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void add(Vector4f theVectorA,
|
||||||
|
Vector4f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
w = theVectorA.w + theVectorB.w;
|
||||||
|
x = theVectorA.x + theVectorB.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVectorA.y + theVectorB.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theVectorA.z + theVectorB.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void add(Vector4f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
w += theVector.w;
|
||||||
|
x += theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y += theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z += theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void sub(Vector4f theVectorA,
|
||||||
|
Vector4f theVectorB) {
|
||||||
|
w = theVectorA.w - theVectorB.w;
|
||||||
|
x = theVectorA.x - theVectorB.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theVectorA.y - theVectorB.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theVectorA.z - theVectorB.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void sub(Vector4f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
w -= theVector.w;
|
||||||
|
x -= theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y -= theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z -= theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void scale(float theScalar,
|
||||||
|
Vector4f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
w = theScalar * theVector.w;
|
||||||
|
x = theScalar * theVector.x;
|
||||||
|
y = theScalar * theVector.y;
|
||||||
|
z = theScalar * theVector.z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void scale(float theScalar) {
|
||||||
|
w *= theScalar;
|
||||||
|
x *= theScalar;
|
||||||
|
y *= theScalar;
|
||||||
|
z *= theScalar;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float lengthSquared() {
|
||||||
|
return w * w + x * x + y * y + z * z;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float length() {
|
||||||
|
return (float) Math.sqrt(w * w + x * x + y * y + z * z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float dot(Vector4f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
return x * theVector.x + y * theVector.y + z * theVector.z + w * theVector.w;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void normalize(Vector4f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
set(theVector);
|
||||||
|
normalize();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final void normalize() {
|
||||||
|
final float d = 1 / length();
|
||||||
|
x *= d;
|
||||||
|
y *= d;
|
||||||
|
z *= d;
|
||||||
|
w *= d;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float[] toArray() {
|
||||||
|
final float[] _myArrayRepresentation = new float[4];
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[0] = x;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[1] = y;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[2] = z;
|
||||||
|
_myArrayRepresentation[3] = w;
|
||||||
|
return _myArrayRepresentation;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final boolean isNaN() {
|
||||||
|
if (Float.isNaN(x) || Float.isNaN(y) || Float.isNaN(z) || Float.isNaN(w)) {
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final boolean equals(Vector4f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
if (w == theVector.w && x == theVector.x && y == theVector.y && z == theVector.z) {
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final boolean almost(Vector4f theVector) {
|
||||||
|
if (Math.abs(w) - Math.abs(theVector.w) < ALMOST_THRESHOLD
|
||||||
|
&& Math.abs(x) - Math.abs(theVector.x) < ALMOST_THRESHOLD
|
||||||
|
&& Math.abs(y) - Math.abs(theVector.y) < ALMOST_THRESHOLD
|
||||||
|
&& Math.abs(z) - Math.abs(theVector.z) < ALMOST_THRESHOLD) {
|
||||||
|
return true;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final String toString() {
|
||||||
|
return "(" + x + ", " + y + ", " + z + ", " + w + ")";
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
26
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vectorf.java
Executable file
26
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/Vectorf.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public interface Vectorf {
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
37
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/WorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.java
Executable file
37
day3/libs/mathematik/src/mathematik/WorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Mathematik
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2012 Patrick Kochlik + Dennis Paul
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package mathematik;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class WorldAxisAlignedBoundingBox {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* center of bounding box
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f position = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* scale around the center
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f scale = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
71
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson00_Particle/Lesson00_Particle.pde
Executable file
71
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson00_Particle/Lesson00_Particle.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
|||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* this sketch show how to create a particle system with a single particle in it.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(30);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle system. */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* a physic-based particle system consists of a few components.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* 1 particles.
|
||||||
|
* there are different kinds of particles. for now we use a simple particle.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* 2 forces.
|
||||||
|
* there are all kinds of forces. one of the most obvious force is the gravitational force,
|
||||||
|
* but there all kinds of different forces like attractors and springs. forces usually
|
||||||
|
* affect all particles in the system.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* 3 behaviors
|
||||||
|
* a behavior is special kind of force. it is something like an internal force or a motor
|
||||||
|
* that only affects a single particle. a typical force is for example the 'seek force'
|
||||||
|
* which constantly pulls a particle into a certain direction.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* 4 integrators.
|
||||||
|
* integrators are used to integrate acceleration and velocity to calculate the new position.
|
||||||
|
* the most well-known is the 'euler' integrator, but there are also optimized versions like 'runge-kutta'
|
||||||
|
* or 'Midpoint' or even slightly different concepts like 'verlet'.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle. note that the particle is automatically added to particle system */
|
||||||
|
mParticle = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
/* update the particle system to the next step. usually the time step is the duration of the las frame */
|
||||||
|
final float mDeltaTime = 1.0 / frameRate;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw particle */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 127);
|
||||||
|
fill(0, 32);
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mParticle.position().x, mParticle.position().y, 12, 12);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* reset particle s position and velocity */
|
||||||
|
if (mousePressed) {
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
mParticle.velocity().set(mouseX - pmouseX, mouseY - pmouseY);
|
||||||
|
mParticle.velocity().scale(10);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
54
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson01_Gravity/Lesson01_Gravity.pde
Executable file
54
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson01_Gravity/Lesson01_Gravity.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
|||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Gravity;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* this sketch show how to create a particle system with a single particle in it.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(30);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle system */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a gravitational force */
|
||||||
|
Gravity mGravity = new Gravity();
|
||||||
|
/* the direction of the gravity is defined by the 'force' vector */
|
||||||
|
mGravity.force().set(0, 30, 0);
|
||||||
|
/* forces, like gravity or any other force, can be added to the system. they will be automatically applied to all particles */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mGravity);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle and add it to the system */
|
||||||
|
mParticle = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
/* update the particle system. this applies the gravity to the particle */
|
||||||
|
final float mDeltaTime = 1.0 / frameRate;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw particle */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 127);
|
||||||
|
fill(0, 32);
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mParticle.position().x, mParticle.position().y, 12, 12);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* reset particle s position and velocity */
|
||||||
|
if (mousePressed) {
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
mParticle.velocity().set(mouseX - pmouseX, mouseY - pmouseY);
|
||||||
|
mParticle.velocity().scale(10);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
58
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson02_Particles/Lesson02_Particles.pde
Executable file
58
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson02_Particles/Lesson02_Particles.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
|||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Gravity;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* this sketch shows how to create and handle multiple particles and remove individual particles.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(30);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle system */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a gravitational force and add it to the particle system */
|
||||||
|
Gravity myGravity = new Gravity(0, 30, 0);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myGravity);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
if (mousePressed) {
|
||||||
|
/* create and add a particle to the system */
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticle = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
/* set particle to mouse position with random velocity */
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
mParticle.velocity().set(random(-20, 20), random(-50));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* update the particle system */
|
||||||
|
final float mDeltaTime = 1.0 / frameRate;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* remove particles right before they hit the edge of the screen */
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.particles().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticle = mPhysics.particles(i);
|
||||||
|
if (mParticle.position().y > height * 0.9f) {
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.particles().remove(i);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw all the particles in the system */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 127);
|
||||||
|
fill(0, 32);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.particles().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticle = mPhysics.particles(i);
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mParticle.position().x, mParticle.position().y, 10, 10);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
88
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson03_Attractors/Lesson03_Attractors.pde
Executable file
88
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson03_Attractors/Lesson03_Attractors.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
|
|||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.constraint.Teleporter;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Attractor;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.ViscousDrag;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* this sketch shows how to create and use attractors.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Attractor mAttractor;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(30);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle system */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a viscous force that slows down all motion */
|
||||||
|
ViscousDrag myDrag = new ViscousDrag();
|
||||||
|
myDrag.coefficient = 0.75f;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myDrag);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* teleport particles from one edge of the screen to the other */
|
||||||
|
Teleporter mTeleporter = new Teleporter();
|
||||||
|
mTeleporter.min().set(0, 0);
|
||||||
|
mTeleporter.max().set(width, height);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mTeleporter);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create some particles */
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
|
||||||
|
Particle myParticle = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
myParticle.position().set(random(width), random(height));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create an attractor */
|
||||||
|
mAttractor = new Attractor();
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.radius(100);
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.strength(150);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mAttractor);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void mousePressed() {
|
||||||
|
/* flip the direction of the attractors strength. */
|
||||||
|
float myInvertedStrength = -1 * mAttractor.strength();
|
||||||
|
/* a negative strength turns the attractor into a repulsor */
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.strength(myInvertedStrength);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
/* set attractor to mouse position */
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* update the particle system */
|
||||||
|
final float mDeltaTime = 1.0 / frameRate;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw all the particles in particle system */
|
||||||
|
fill(245);
|
||||||
|
stroke(164);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.particles().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
Particle myParticle = mPhysics.particles(i);
|
||||||
|
ellipse(myParticle.position().x, myParticle.position().y, 12, 12);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw attractor. green if it is attracting and red if it is repelling */
|
||||||
|
noStroke();
|
||||||
|
if (mAttractor.strength() < 0) {
|
||||||
|
fill(255, 0, 0, 50);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
else {
|
||||||
|
fill(0, 255, 0, 50);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mAttractor.position().x, mAttractor.position().y,
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.radius(), mAttractor.radius());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
102
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson04_Deflectors/Lesson04_Deflectors.pde
Executable file
102
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson04_Deflectors/Lesson04_Deflectors.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
|||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.ShortLivedParticle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Gravity;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.PlaneDeflector;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.ViscousDrag;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* this sketch shows
|
||||||
|
* 1 how to create and use plane deflectors
|
||||||
|
* 2 how to use 'ShortLivedParticle'
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
PlaneDeflector mDeflector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(30);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle system */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a deflector and add it to the particle system.
|
||||||
|
* the that defines the deflection area is defined by an
|
||||||
|
* origin and a normal. this also means that the plane s size
|
||||||
|
* is infinite.
|
||||||
|
* note that there is also a triangle delfector that is constraint
|
||||||
|
* by three points.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
mDeflector = new PlaneDeflector();
|
||||||
|
/* set plane origin into the center of the screen */
|
||||||
|
mDeflector.plane().origin.set(width / 2, height / 2, 0);
|
||||||
|
mDeflector.plane().normal.set(0, -1, 0);
|
||||||
|
/* the coefficient of restitution defines how hard particles bounce of the deflector */
|
||||||
|
mDeflector.coefficientofrestitution(0.7f);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mDeflector);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create gravitiy */
|
||||||
|
Gravity myGravity = new Gravity();
|
||||||
|
myGravity.force().y = 50;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myGravity);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create drag */
|
||||||
|
ViscousDrag myViscousDrag = new ViscousDrag();
|
||||||
|
myViscousDrag.coefficient = 0.1f;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myViscousDrag);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
/* rotate deflector plane */
|
||||||
|
if (mousePressed) {
|
||||||
|
final float myAngle = 2 * PI * (float)mouseX / width - PI;
|
||||||
|
mDeflector.plane().normal.set(sin(myAngle), -cos(myAngle), 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a special particle */
|
||||||
|
ShortLivedParticle myNewParticle = new ShortLivedParticle();
|
||||||
|
myNewParticle.position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
myNewParticle.velocity().set(0, random(100) + 50);
|
||||||
|
/* this particle is removed after a specific interval */
|
||||||
|
myNewParticle.setMaxAge(4);
|
||||||
|
/* add particle manually to the particle system */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myNewParticle);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* update physics */
|
||||||
|
final float mDeltaTime = 1.0 / frameRate;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw all the particles in the particle system */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.particles().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
Particle myParticle = mPhysics.particles(i);
|
||||||
|
/* this special particle can tell you how much time it has to live.
|
||||||
|
* we map this information to its transparency.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
float myRatio = 1 - ((ShortLivedParticle)myParticle).ageRatio();
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 64 * myRatio);
|
||||||
|
fill(0, 32 * myRatio);
|
||||||
|
ellipse(myParticle.position().x, myParticle.position().y, 12, 12);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw deflector */
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 127);
|
||||||
|
line(mDeflector.plane().origin.x - mDeflector.plane().normal.y * -width,
|
||||||
|
mDeflector.plane().origin.y + mDeflector.plane().normal.x * -width,
|
||||||
|
mDeflector.plane().origin.x - mDeflector.plane().normal.y * width,
|
||||||
|
mDeflector.plane().origin.y + mDeflector.plane().normal.x * width);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
stroke(255, 0, 0, 127);
|
||||||
|
line(mDeflector.plane().origin.x,
|
||||||
|
mDeflector.plane().origin.y,
|
||||||
|
mDeflector.plane().origin.x + mDeflector.plane().normal.x * 20,
|
||||||
|
mDeflector.plane().origin.y + mDeflector.plane().normal.y * 20);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
68
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson05_Spring/Lesson05_Spring.pde
Executable file
68
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson05_Spring/Lesson05_Spring.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
|||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Spring;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.ViscousDrag;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* this sketch shows
|
||||||
|
* 1 how to create a viscous drag to slow motion eventually down.
|
||||||
|
* 2 how to create a spring that connects two particles.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Spring mSpring;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(30);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle system */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a viscous force that slows down all motion; 0 means no slowing down. */
|
||||||
|
ViscousDrag myDrag = new ViscousDrag(0.25f);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myDrag);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create two particles that we can connect with a spring */
|
||||||
|
Particle myA = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
myA.position().set(width / 2 - 50, height / 2);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle myB = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
myB.position().set(width / 2 + 50, height / 2);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a spring force that connects two particles.
|
||||||
|
* note that there is more than one way to create a spring.
|
||||||
|
* in our case the restlength of the spring is defined by the
|
||||||
|
* particles current position.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
mSpring = mPhysics.makeSpring(myA, myB);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
/* set first particle to mouse position */
|
||||||
|
if (mousePressed) {
|
||||||
|
mSpring.a().position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* update the particle system */
|
||||||
|
final float mDeltaTime = 1.0 / frameRate;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw particles and connecting line */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
stroke(255, 0, 127, 64);
|
||||||
|
line(mSpring.a().position().x, mSpring.a().position().y,
|
||||||
|
mSpring.b().position().x, mSpring.b().position().y);
|
||||||
|
fill(245);
|
||||||
|
stroke(164);
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mSpring.a().position().x, mSpring.a().position().y, 12, 12);
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mSpring.b().position().x, mSpring.b().position().y, 12, 12);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
70
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson06_Springs/Lesson06_Springs.pde
Executable file
70
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson06_Springs/Lesson06_Springs.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
|||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Spring;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* this sketch shows
|
||||||
|
* 1 how to create a viscous drag to slow motion eventually down.
|
||||||
|
* 2 how to create a spring that connects two particles.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle mRoot;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(30);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle system */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle to which we will connect springs */
|
||||||
|
mRoot = mPhysics.makeParticle(width / 2, height / 2, 0.0);
|
||||||
|
/* we give the root particle a higher mass so it doesn t move as easily */
|
||||||
|
mRoot.mass(30);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle at mouse position and connect it to the root particle through a spring */
|
||||||
|
if (mousePressed) {
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticle = mPhysics.makeParticle(mouseX, mouseY, 0);
|
||||||
|
Spring mSpring = mPhysics.makeSpring(mRoot, mParticle);
|
||||||
|
/* restlength defines the desired length of the spring. in this case it is the distance between the two particles. */
|
||||||
|
float mRestlength = mSpring.restlength();
|
||||||
|
/* we modify the restlength to add a bit of energy into the system */
|
||||||
|
mSpring.restlength(mRestlength * 1.5f);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* update the particle system */
|
||||||
|
final float mDeltaTime = 1.0 / frameRate;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw particles and connecting line */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw springs */
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
stroke(255, 0, 127, 64);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.forces().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
if (mPhysics.forces().get(i) instanceof Spring) {
|
||||||
|
Spring mSSpring = (Spring)mPhysics.forces().get(i);
|
||||||
|
line(mSSpring.a().position().x, mSSpring.a().position().y,
|
||||||
|
mSSpring.b().position().x, mSSpring.b().position().y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
/* draw particles */
|
||||||
|
fill(245);
|
||||||
|
stroke(164);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.particles().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mPhysics.particles().get(i).position().x,
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.particles().get(i).position().y,
|
||||||
|
12, 12);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
83
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson07_StableQuads/Lesson07_StableQuads.pde
Executable file
83
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson07_StableQuads/Lesson07_StableQuads.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
|||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Gravity;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.ViscousDrag;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.util.DrawLib;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.constraint.Box;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.integration.RungeKutta;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.util.StableSpringQuad;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle mRoot;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(60);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
/* we use 'runge kutta' as it is more stable for this application */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.setInegratorRef(new RungeKutta());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Gravity myGravity = new Gravity();
|
||||||
|
myGravity.force().y = 98.1f;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myGravity);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* add drag to smooth the spring interaction */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(new ViscousDrag(0.2f));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* add a container */
|
||||||
|
Box myBox = new Box();
|
||||||
|
myBox.min().set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
myBox.max().set(width, height, 0);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myBox);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create root */
|
||||||
|
Particle a = mPhysics.makeParticle(0, 0);
|
||||||
|
Particle b = mPhysics.makeParticle(100, 0);
|
||||||
|
Particle c = mPhysics.makeParticle(100, 100);
|
||||||
|
Particle d = mPhysics.makeParticle(0, 100);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
new StableSpringQuad(mPhysics, d, c, mPhysics.makeParticle(100, 200), mPhysics.makeParticle(0, 200));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create stable quad from springs */
|
||||||
|
/* first the edge-springs ... */
|
||||||
|
final float mySpringConstant = 100;
|
||||||
|
final float mySpringDamping = 5;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.makeSpring(a, b, mySpringConstant, mySpringDamping);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.makeSpring(b, c, mySpringConstant, mySpringDamping);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.makeSpring(c, d, mySpringConstant, mySpringDamping);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.makeSpring(d, a, mySpringConstant, mySpringDamping).restlength();
|
||||||
|
/* ... then the diagonal-springs */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.makeSpring(a, c, mySpringConstant, mySpringDamping);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.makeSpring(b, d, mySpringConstant, mySpringDamping).restlength();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* define 'a' as root particle for mouse interaction */
|
||||||
|
mRoot = a;
|
||||||
|
mRoot.fixed(true);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* handle particles */
|
||||||
|
if (mousePressed) {
|
||||||
|
mRoot.fixed(true);
|
||||||
|
mRoot.position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
else {
|
||||||
|
mRoot.fixed(false);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(1f / frameRate);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
DrawLib.drawSprings(g, mPhysics, color(255, 0, 127, 64));
|
||||||
|
DrawLib.drawParticles(g, mPhysics, 12, color(164), color(245));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
71
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson08_Sticks/Lesson08_Sticks.pde
Executable file
71
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson08_Sticks/Lesson08_Sticks.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
|||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.constraint.Stick;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Gravity;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.integration.Verlet;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle[] mParticles;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
frameRate(60);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
/* increase the number of iterations for contraints in each step. this can greatly relaxes tensions in the system. */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.contraint_iterations_per_steps = 5;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* add gravity for extra fun */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(new Gravity());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* we chose verlet integration as it integrates much more nicely with sticks ( and constraints in general ) */
|
||||||
|
Verlet myVerlet = new Verlet();
|
||||||
|
myVerlet.damping(0.99f);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.setInegratorRef(myVerlet);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* setup sticks to form a whip */
|
||||||
|
mParticles = new Particle[16];
|
||||||
|
float mSegmentLength = 20.0;
|
||||||
|
/* create root */
|
||||||
|
for (int x = 0; x < mParticles.length; x++) {
|
||||||
|
mParticles[x] = mPhysics.makeParticle(x * mSegmentLength, 0, 0, 0.1f);
|
||||||
|
if (x > 0) {
|
||||||
|
Stick myStick = new Stick(mParticles[x - 1],
|
||||||
|
mParticles[x],
|
||||||
|
mSegmentLength);
|
||||||
|
/* damp the stick to release tensions from the system */
|
||||||
|
myStick.damping(0.99f);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myStick);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* fix root particle so it can stick to the mouse later */
|
||||||
|
mParticles[0].fixed(true);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
/* stick root particle to mouse */
|
||||||
|
mParticles[0].position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* update */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(1.0 / frameRate);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw sticks with descending stroke weight */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 192);
|
||||||
|
for (int x = 1; x < mParticles.length; x++) {
|
||||||
|
Particle p1 = mParticles[x - 1];
|
||||||
|
Particle p2 = mParticles[x];
|
||||||
|
final float mStrokeWeight = 4.0 * (1.0 - (float)x / mParticles.length);
|
||||||
|
strokeWeight(mStrokeWeight);
|
||||||
|
line(p1.position().x, p1.position().y, p1.position().z,
|
||||||
|
p2.position().x, p2.position().y, p2.position().z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
113
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson09_Cloth/Lesson09_Cloth.pde
Executable file
113
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson09_Cloth/Lesson09_Cloth.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
|||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.constraint.IConstraint;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.constraint.Stick;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Attractor;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Gravity;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.integration.Verlet;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle[][] mParticles;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final int GRID_WIDTH = 32;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final int GRID_HEIGHT = 16;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Attractor mAttractor;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
frameRate(60);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.contraint_iterations_per_steps = 5;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Verlet myVerlet = new Verlet();
|
||||||
|
myVerlet.damping(0.9f);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.setInegratorRef(myVerlet);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(new Gravity(new Vector3f(0, 1000f, 0)));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mAttractor = new Attractor();
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.strength(-15000);
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.radius(300);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mAttractor);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mParticles = new Particle[GRID_WIDTH][GRID_HEIGHT];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* setup cloth */
|
||||||
|
float mGridStepX = ((float)width / GRID_WIDTH);
|
||||||
|
float mGridStepY = (((float)height * 0.5f) / GRID_HEIGHT);
|
||||||
|
for (int y = 0; y < GRID_HEIGHT; y++) {
|
||||||
|
for (int x = 0; x < GRID_WIDTH; x++) {
|
||||||
|
mParticles[x][y] = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
mParticles[x][y].position().set((x + 0.5f) * mGridStepX,
|
||||||
|
y * mGridStepY,
|
||||||
|
random(0, 1));
|
||||||
|
mParticles[x][y].old_position().set(mParticles[x][y].position());
|
||||||
|
mParticles[x][y].mass(0.1f);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final float DAMPING = 0.9f;
|
||||||
|
if (y > 0) {
|
||||||
|
Stick myStick = new Stick(mParticles[x][y - 1],
|
||||||
|
mParticles[x][y],
|
||||||
|
mGridStepY);
|
||||||
|
myStick.damping(DAMPING);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myStick);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (x > 0) {
|
||||||
|
Stick myStick = new Stick(mParticles[x - 1][y],
|
||||||
|
mParticles[x][y],
|
||||||
|
mGridStepX);
|
||||||
|
myStick.damping(DAMPING);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myStick);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (x > 0 && y > 0) {
|
||||||
|
Stick myStick1 = new Stick(mParticles[x - 1][y - 1],
|
||||||
|
mParticles[x][y],
|
||||||
|
new Vector3f(mGridStepX, mGridStepY).length());
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myStick1);
|
||||||
|
Stick myStick2 = new Stick(mParticles[x][y - 1],
|
||||||
|
mParticles[x - 1][y],
|
||||||
|
new Vector3f(mGridStepX, mGridStepY).length());
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myStick2);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* fix first row */
|
||||||
|
for (int x = 0; x < mParticles.length; x++) {
|
||||||
|
mParticles[x][0].fixed(true);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* update */
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.position().set(mouseX, mouseY, 50);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(1.0 / frameRate);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw sticks */
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 127);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.constraints().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
IConstraint mConstraint = mPhysics.constraints().get(i);
|
||||||
|
if (mConstraint instanceof Stick) {
|
||||||
|
final Stick myStick = (Stick)mConstraint;
|
||||||
|
line(myStick.a().position().x,
|
||||||
|
myStick.a().position().y,
|
||||||
|
myStick.a().position().z,
|
||||||
|
myStick.b().position().x,
|
||||||
|
myStick.b().position().y,
|
||||||
|
myStick.b().position().z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
73
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson10_Behaviors/Lesson10_Behaviors.pde
Executable file
73
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/Lesson10_Behaviors/Lesson10_Behaviors.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
|||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.BehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.behavior.Arrival;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* this sketch shows how to assign an 'arrival' behavior to a particle.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
BehaviorParticle mParticle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Arrival mArrival;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(120);
|
||||||
|
colorMode(RGB, 1.0f);
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* physics */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create particles */
|
||||||
|
mParticle = mPhysics.makeParticle(BehaviorParticle.class);
|
||||||
|
mParticle.maximumInnerForce(100);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create arrival behavior */
|
||||||
|
mArrival = new Arrival();
|
||||||
|
mArrival.breakforce(mParticle.maximumInnerForce() * 0.25f);
|
||||||
|
mArrival.breakradius(mParticle.maximumInnerForce() * 0.25f);
|
||||||
|
mParticle.behaviors().add(mArrival);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* set the arrival position to the mouse position */
|
||||||
|
mArrival.position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* update particle system */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(1.0f / frameRate);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw behavior particle */
|
||||||
|
background(1);
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 0.5f);
|
||||||
|
if (mArrival.arriving()) {
|
||||||
|
/* color particle red while it is arriving */
|
||||||
|
stroke(1, 0, 0, 0.5f);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (mArrival.arrived()) {
|
||||||
|
/* color particle green when it has arrived */
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 1, 0, 0.5f);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
line(mParticle.position().x,
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().y,
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().x + mParticle.velocity().x,
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().y + mParticle.velocity().y);
|
||||||
|
fill(1);
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mParticle.position().x, mParticle.position().y, 12, 12);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw arrival */
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 0.25f);
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mArrival.position().x,
|
||||||
|
mArrival.position().y,
|
||||||
|
mArrival.breakradius() * 2,
|
||||||
|
mArrival.breakradius() * 2);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
69
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/LessonX01_Overlap/LessonX01_Overlap.pde
Executable file
69
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/LessonX01_Overlap/LessonX01_Overlap.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
|||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Spring;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.util.Overlap;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* this sketch is exactly like Lesson06_Springs, except that it also shows how to remove overlaps.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle mRoot;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final float PARTICLE_RADIUS = 6;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(30);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
mRoot = mPhysics.makeParticle(width / 2, height / 2, 0.0);
|
||||||
|
mRoot.mass(30);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
if (mousePressed) {
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticle = mPhysics.makeParticle(mouseX, mouseY, 0);
|
||||||
|
Spring mSpring = mPhysics.makeSpring(mRoot, mParticle);
|
||||||
|
float mRestlength = mSpring.restlength();
|
||||||
|
mSpring.restlength(mRestlength * 1.5f);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* we define a radius for the particle so the particle has dimensions */
|
||||||
|
mParticle.radius(PARTICLE_RADIUS);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* move overlapping particles away from each other */
|
||||||
|
Overlap.resolveOverlap(mPhysics.particles());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* update the particle system */
|
||||||
|
final float mDeltaTime = 1.0 / frameRate;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw particles and connecting line */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw springs */
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
stroke(255, 0, 127, 64);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.forces().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
if (mPhysics.forces().get(i) instanceof Spring) {
|
||||||
|
Spring mSSpring = (Spring)mPhysics.forces().get(i);
|
||||||
|
line(mSSpring.a().position().x, mSSpring.a().position().y,
|
||||||
|
mSSpring.b().position().x, mSSpring.b().position().y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
/* draw particles */
|
||||||
|
fill(245);
|
||||||
|
stroke(164);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.particles().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mPhysics.particles().get(i).position().x,
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.particles().get(i).position().y,
|
||||||
|
PARTICLE_RADIUS * 2, PARTICLE_RADIUS * 2);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
91
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/LessonX02_Collisions/LessonX02_Collisions.pde
Executable file
91
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/LessonX02_Collisions/LessonX02_Collisions.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
|
|||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.constraint.Box;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Gravity;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Spring;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.ViscousDrag;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.util.CollisionManager;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final float PARTICLE_SIZE = 12;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
CollisionManager mCollision;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(30);
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
ellipseMode(CENTER);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mCollision = new CollisionManager();
|
||||||
|
mCollision.distancemode(CollisionManager.DISTANCE_MODE_FIXED);
|
||||||
|
mCollision.minimumDistance(50);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(new ViscousDrag(0.85f));
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(new Gravity());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Box myBox = new Box();
|
||||||
|
myBox.min().set(50, 50, 0);
|
||||||
|
myBox.max().set(width - 50, height - 50, 0);
|
||||||
|
myBox.coefficientofrestitution(0.7f);
|
||||||
|
myBox.reflect(true);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myBox);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a first particle */
|
||||||
|
final Particle myParticle = mPhysics.makeParticle(new Vector3f(mouseX, mouseY, 0), 10);
|
||||||
|
mCollision.collision().add(myParticle);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
/* create particles */
|
||||||
|
if (mousePressed) {
|
||||||
|
final Particle myParticle = mPhysics.makeParticle(new Vector3f(mouseX, mouseY, 0), 10);
|
||||||
|
mCollision.collision().add(myParticle);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* collision handler */
|
||||||
|
final float mDeltaTime = 1.0 / frameRate;
|
||||||
|
mCollision.createCollisionResolvers();
|
||||||
|
mCollision.loop(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
drawThings();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mCollision.removeCollisionResolver();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void drawThings() {
|
||||||
|
/* collision springs */
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
stroke(255, 0, 127, 64);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mCollision.collision().forces().size(); ++i) {
|
||||||
|
if (mCollision.collision().forces().get(i) instanceof Spring) {
|
||||||
|
Spring mySpring = (Spring)mCollision.collision_forces().get(i);
|
||||||
|
line(mySpring.a().position().x, mySpring.a().position().y, mySpring.a().position().z,
|
||||||
|
mySpring.b().position().x, mySpring.b().position().y, mySpring.b().position().z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* particles */
|
||||||
|
fill(245);
|
||||||
|
stroke(164);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.particles().size(); ++i) {
|
||||||
|
Particle myParticle = mPhysics.particles().get(i);
|
||||||
|
pushMatrix();
|
||||||
|
translate(myParticle.position().x, myParticle.position().y, myParticle.position().z);
|
||||||
|
ellipse(0, 0,
|
||||||
|
PARTICLE_SIZE,
|
||||||
|
PARTICLE_SIZE);
|
||||||
|
popMatrix();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
|
|||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.ShortLivedParticle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.constraint.Box;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Attractor;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Gravity;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.ViscousDrag;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.util.ParticleTrail;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Vector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector<ParticleTrail> mTrails;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Attractor mAttractor;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(60);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a particle system */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create a gravitational force */
|
||||||
|
Gravity myGravity = new Gravity();
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myGravity);
|
||||||
|
myGravity.force().y = 20;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create drag */
|
||||||
|
ViscousDrag myViscousDrag = new ViscousDrag();
|
||||||
|
myViscousDrag.coefficient = 0.1f;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myViscousDrag);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final float mBorder = 40;
|
||||||
|
Box mBox = new Box(new Vector3f(mBorder, mBorder, mBorder), new Vector3f(width - mBorder, height - mBorder, 100 - mBorder));
|
||||||
|
mBox.reflect(true);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mBox);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create an attractor */
|
||||||
|
mAttractor = new Attractor();
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.radius(200);
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.strength(-300);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mAttractor);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* create trails and particles */
|
||||||
|
mTrails = new Vector<ParticleTrail>();
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticle = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
mParticle.mass(2.0f);
|
||||||
|
ParticleTrail myParticleTrail = new ParticleTrail(mPhysics, mParticle, 0.2f, random(0.5f, 1));
|
||||||
|
myParticleTrail.mass(0.5f);
|
||||||
|
mTrails.add(myParticleTrail);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
resetParticles(width / 2, height / 2);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void resetParticles(float x, float y) {
|
||||||
|
for (ParticleTrail myTrails : mTrails) {
|
||||||
|
myTrails.particle().position().set(x + random(-10, 10), y + random(-10, 10), 0);
|
||||||
|
myTrails.particle().velocity().set(random(-10, 10), random(-10, 10), random(-10, 10));
|
||||||
|
myTrails.fragments().clear();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
/* set attractor to mouse position */
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (ParticleTrail myTrails : mTrails) {
|
||||||
|
myTrails.loop(1f / frameRate);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(1f / frameRate);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
for (ParticleTrail myTrail : mTrails) {
|
||||||
|
drawTrail(myTrail);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void drawTrail(ParticleTrail theTrail) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final Vector<Particle> mFragments = theTrail.fragments();
|
||||||
|
final Particle mParticle = theTrail.particle();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw head */
|
||||||
|
if (mFragments.size() > 1) {
|
||||||
|
fill(255, 0, 127);
|
||||||
|
noStroke();
|
||||||
|
pushMatrix();
|
||||||
|
translate(mParticle.position().x,
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().y,
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().z);
|
||||||
|
sphereDetail(4);
|
||||||
|
sphere(3);
|
||||||
|
popMatrix();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw trail */
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mFragments.size() - 1; i++) {
|
||||||
|
if (mFragments.get(i) instanceof ShortLivedParticle) {
|
||||||
|
final float mRatio = 1.0f - ((ShortLivedParticle)mFragments.get(i)).ageRatio();
|
||||||
|
stroke(127, mRatio * 255);
|
||||||
|
strokeWeight(mRatio * 3);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
int j = (i + 1) % mFragments.size();
|
||||||
|
line(mFragments.get(i).position().x,
|
||||||
|
mFragments.get(i).position().y,
|
||||||
|
mFragments.get(i).position().z,
|
||||||
|
mFragments.get(j).position().x,
|
||||||
|
mFragments.get(j).position().y,
|
||||||
|
mFragments.get(j).position().z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (!mFragments.isEmpty()) {
|
||||||
|
line(mFragments.lastElement().position().x,
|
||||||
|
mFragments.lastElement().position().y,
|
||||||
|
mFragments.lastElement().position().z,
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().x,
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().y,
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void mousePressed() {
|
||||||
|
resetParticles(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
146
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/LessonX04_StickMan/LessonX04_StickMan.pde
Executable file
146
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/LessonX04_StickMan/LessonX04_StickMan.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,146 @@
|
|||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.test.cubicle.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.integration.*;
|
||||||
|
import verhalten.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.*;
|
||||||
|
import verhalten.view.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.test.particle.behavior.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.behavior.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.demo.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.test.particle.springs.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.gestalt.test.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.cubicle.*;
|
||||||
|
import verhalten.test.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.flowfield.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.test.particle.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.gestalt.util.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.constraint.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.vectorfield.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.*;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.util.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Attractor;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Gravity;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Spring;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.ViscousDrag;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.integration.RungeKutta;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.util.Overlap;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.util.StickMan;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* this demo shows some advanced use of particles, springs and attractors to create stickmen.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Attractor mAttractor;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Gravity mGravity;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ViscousDrag mViscousDrag;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
StickMan[] mMyStickMan;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
frameRate(60);
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.setInegratorRef(new RungeKutta());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mGravity = new Gravity();
|
||||||
|
mGravity.force().y = 20;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mGravity);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mViscousDrag = new ViscousDrag();
|
||||||
|
mViscousDrag.coefficient = 0.85f;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mViscousDrag);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mAttractor = new Attractor();
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.radius(500);
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.strength(0);
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.position().set(width / 2, height / 2);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mAttractor);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mMyStickMan = new StickMan[20];
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mMyStickMan.length; i++) {
|
||||||
|
mMyStickMan[i] = new StickMan(mPhysics, random(0, width), random(0.3f, 0.6f));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(1f / 60f);
|
||||||
|
Overlap.resolveOverlap(mPhysics.particles());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* constraint particles */
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.particles().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
if (mPhysics.particles(i).position().y > height - 10) {
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.particles(i).position().y = height - 10;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (mPhysics.particles(i).position().x > width) {
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.particles(i).position().x = width;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (mPhysics.particles(i).position().x < 0) {
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.particles(i).position().x = 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* handle particles */
|
||||||
|
if (mousePressed) {
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
if (mouseButton == RIGHT) {
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.strength(-500);
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.radius(500);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
else {
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.strength(500);
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.radius(100);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
else {
|
||||||
|
mAttractor.strength(0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (keyPressed) {
|
||||||
|
mGravity.force().y = -10;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
else {
|
||||||
|
mGravity.force().y = 20;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw */
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw springs */
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 20);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.forces().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
if (mPhysics.forces(i) instanceof Spring) {
|
||||||
|
Spring mySpring = (Spring)mPhysics.forces(i);
|
||||||
|
line(mySpring.a().position().x,
|
||||||
|
mySpring.a().position().y,
|
||||||
|
mySpring.b().position().x,
|
||||||
|
mySpring.b().position().y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw particles */
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.particles().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mPhysics.particles(i).position().x,
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.particles(i).position().y, 5, 5);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw man */
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mMyStickMan.length; i++) {
|
||||||
|
mMyStickMan[i].draw(g);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
|
|||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.constraint.AngleConstraintStick;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.constraint.Stick;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.AngleConstraintSpring;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Gravity;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Spring;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.ViscousDrag;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.integration.RungeKutta;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticleA;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticleB;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticleC;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle mParticleD;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
AngleConstraintSpring mAngleConstraintABC;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
AngleConstraintStick mAngleConstraintBCD;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480);
|
||||||
|
frameRate(30);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.setInegratorRef(new RungeKutta());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ViscousDrag myViscousDrag = new ViscousDrag();
|
||||||
|
myViscousDrag.coefficient = 1f;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myViscousDrag);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Gravity myGravity = new Gravity();
|
||||||
|
myGravity.force().y = 50;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myGravity);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* particles */
|
||||||
|
mParticleA = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
mParticleB = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
mParticleC = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
mParticleD = mPhysics.makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mParticleA.position().set(width / 2 + 50, height / 3);
|
||||||
|
mParticleB.position().set(width / 2, height - height / 1.75f);
|
||||||
|
mParticleC.position().set(width / 2, height - height / 4);
|
||||||
|
mParticleD.position().set(width / 2, height - height / 8);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mParticleA.radius(7);
|
||||||
|
mParticleB.radius(3);
|
||||||
|
mParticleC.radius(10);
|
||||||
|
mParticleD.radius(2);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mParticleB.fixed(true);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* springs */
|
||||||
|
Spring mSpringAB = new Spring(mParticleA, mParticleB);
|
||||||
|
mSpringAB.strength(250);
|
||||||
|
mSpringAB.damping(10);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mSpringAB);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Spring mSpringBC = new Spring(mParticleB, mParticleC);
|
||||||
|
mSpringBC.strength(250);
|
||||||
|
mSpringBC.damping(10);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mSpringBC);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Stick mSpringCD = new Stick(mParticleC, mParticleD);
|
||||||
|
mSpringCD.damping(1);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mSpringCD);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* angle constraint */
|
||||||
|
mAngleConstraintABC = new AngleConstraintSpring(mParticleA, mParticleB, mParticleC);
|
||||||
|
mAngleConstraintABC.min_angle(PI * 0.5f);
|
||||||
|
mAngleConstraintABC.damping(1);
|
||||||
|
mAngleConstraintABC.strength(200);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mAngleConstraintABC);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mAngleConstraintBCD = new AngleConstraintStick(mParticleB, mParticleC, mParticleD);
|
||||||
|
mAngleConstraintBCD.min_angle(PI * 0.8f);
|
||||||
|
mAngleConstraintBCD.damping(0.5f);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(mAngleConstraintBCD);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
/* attach particle to mouse */
|
||||||
|
if (mousePressed) {
|
||||||
|
mParticleA.position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* apply constraints */
|
||||||
|
mAngleConstraintABC.pre_step();
|
||||||
|
mAngleConstraintBCD.pre_step();
|
||||||
|
draw_physics();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(1f / frameRate);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* remove contraints */
|
||||||
|
mAngleConstraintABC.post_step();
|
||||||
|
mAngleConstraintBCD.post_step();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw_physics() {
|
||||||
|
background(255);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
drawSprings();
|
||||||
|
drawSticks();
|
||||||
|
drawParticles();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void drawSprings() {
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.forces().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
if (mPhysics.forces(i) instanceof Spring) {
|
||||||
|
final Spring mSpring = (Spring)mPhysics.forces(i);
|
||||||
|
if (mSpring instanceof AngleConstraintSpring) {
|
||||||
|
strokeWeight(1);
|
||||||
|
if (mSpring.active()) {
|
||||||
|
stroke(255, 0, 0, 64);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
else {
|
||||||
|
stroke(255, 0, 0, 16);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
else {
|
||||||
|
strokeWeight(3);
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 128);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
line(mSpring.a(), mSpring.b());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
strokeWeight(1);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void drawSticks() {
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mPhysics.constraints().size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
if (mPhysics.constraints(i) instanceof Stick) {
|
||||||
|
final Stick mStick = (Stick)mPhysics.constraints(i);
|
||||||
|
if (mStick instanceof AngleConstraintStick) {
|
||||||
|
strokeWeight(1);
|
||||||
|
if (mStick.active()) {
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 127, 255, 64);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
else {
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 127, 255, 16);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
else {
|
||||||
|
strokeWeight(3);
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 128);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
line(mStick.a(), mStick.b());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
strokeWeight(1);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void drawParticles() {
|
||||||
|
stroke(0);
|
||||||
|
fill(92);
|
||||||
|
drawParticle(mParticleA);
|
||||||
|
fill(127);
|
||||||
|
drawParticle(mParticleB);
|
||||||
|
fill(192);
|
||||||
|
drawParticle(mParticleC);
|
||||||
|
fill(64);
|
||||||
|
drawParticle(mParticleD);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void drawParticle(Particle p) {
|
||||||
|
ellipse(p.position().x,
|
||||||
|
p.position().y,
|
||||||
|
p.radius() * 2, p.radius() * 2);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void line(Particle p1, Particle p2) {
|
||||||
|
line(p1.position().x, p1.position().y,
|
||||||
|
p2.position().x, p2.position().y);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
145
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/LessonX06_Ducklings/LessonX06_Ducklings.pde
Executable file
145
day3/libs/teilchen/examples/LessonX06_Ducklings/LessonX06_Ducklings.pde
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
|
|||||||
|
import mathematik.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import processing.opengl.*;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.BehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Physics;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.behavior.Arrival;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Spring;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.ViscousDrag;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.util.CollisionManager;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* this demo shows how to add behaviors to particles. in this example the
|
||||||
|
* arrival behavior.
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Physics mPhysics;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ArrayList<Duckling> mDucklings;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
CollisionManager mCollision;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setup() {
|
||||||
|
size(640, 480, OPENGL);
|
||||||
|
frameRate(60);
|
||||||
|
smooth();
|
||||||
|
colorMode(RGB, 1.0f);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* physics */
|
||||||
|
mPhysics = new Physics();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ViscousDrag myViscousDrag = new ViscousDrag();
|
||||||
|
myViscousDrag.coefficient = 0.25f;
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.add(myViscousDrag);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mCollision = new CollisionManager();
|
||||||
|
mCollision.minimumDistance(25);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* ducklings */
|
||||||
|
mDucklings = new ArrayList<Duckling>();
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++) {
|
||||||
|
final Duckling mDuckling = new Duckling();
|
||||||
|
if (!mDucklings.isEmpty()) {
|
||||||
|
mDuckling.arrival.setPositionRef(mDucklings.get(mDucklings.size()-1).particle.position());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
mCollision.collision().add(mDuckling.particle);
|
||||||
|
mDucklings.add(mDuckling);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void draw() {
|
||||||
|
final float mDeltaTime = 1.0f / frameRate;
|
||||||
|
background(1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* update particles */
|
||||||
|
mCollision.createCollisionResolvers();
|
||||||
|
mCollision.loop(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
mPhysics.step(mDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
drawCollisionSprings();
|
||||||
|
mCollision.removeCollisionResolver();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mDucklings.get(0).arrival.oversteer(!mousePressed);
|
||||||
|
mDucklings.get(0).arrival.position().set(mouseX, mouseY);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw */
|
||||||
|
for (int i=0; i < mDucklings.size(); i++) {
|
||||||
|
Duckling mDuckling = mDucklings.get(i);
|
||||||
|
drawParticle(mDuckling);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw arrival */
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 0.25f);
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mDucklings.get(0).arrival.position().x,
|
||||||
|
mDucklings.get(0).arrival.position().y,
|
||||||
|
20, 20);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void drawParticle(Duckling pDuckling) {
|
||||||
|
final BehaviorParticle mParticle = pDuckling.particle;
|
||||||
|
final Arrival mArrival = pDuckling.arrival;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw particle */
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 0.5f);
|
||||||
|
noFill();
|
||||||
|
if (mArrival.arriving()) {
|
||||||
|
stroke(1, 0, 0, 0.5f);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (mArrival.arrived()) {
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 1, 0, 0.5f);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
ellipse(mParticle.position().x, mParticle.position().y,
|
||||||
|
mParticle.radius() * 2, mParticle.radius() * 2);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* - */
|
||||||
|
pushMatrix();
|
||||||
|
translate(mParticle.position().x,
|
||||||
|
mParticle.position().y);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw velocity */
|
||||||
|
stroke(1, 0, 0, 0.5f);
|
||||||
|
line(0, 0, mParticle.velocity().x, mParticle.velocity().y);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* draw break force */
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 0.5f, 1, 0.5f);
|
||||||
|
line(0, 0, mArrival.force().x, mArrival.force().y);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* - */
|
||||||
|
popMatrix();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void drawCollisionSprings() {
|
||||||
|
stroke(0, 1, 0, 0.25f);
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < mCollision.collision().forces().size(); ++i) {
|
||||||
|
if (mCollision.collision().forces().get(i) instanceof Spring) {
|
||||||
|
Spring mySpring = (Spring) mCollision.collision_forces().get(i);
|
||||||
|
line(mySpring.a().position().x, mySpring.a().position().y, mySpring.a().position().z,
|
||||||
|
mySpring.b().position().x, mySpring.b().position().y, mySpring.b().position().z);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class Duckling {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
BehaviorParticle particle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Arrival arrival;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Duckling() {
|
||||||
|
/* create particles */
|
||||||
|
particle = mPhysics.makeParticle(BehaviorParticle.class);
|
||||||
|
particle.position().set(random(width), random(height));
|
||||||
|
particle.maximumInnerForce(random(50, 150));
|
||||||
|
particle.radius(random(6, 10));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
arrival = new Arrival();
|
||||||
|
arrival.breakforce(random(12, 28));
|
||||||
|
arrival.breakradius(random(45, 55));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
particle.behaviors().add(arrival);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
BIN
day3/libs/teilchen/library/teilchen.jar
Executable file
BIN
day3/libs/teilchen/library/teilchen.jar
Executable file
Binary file not shown.
142
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/BasicParticle.java
Executable file
142
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/BasicParticle.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class BasicParticle
|
||||||
|
implements Particle, Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mFixed;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mAge;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mMass;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector3f mPosition;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f mOldPosition;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f mVelocity;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f mForce;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mTagged;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mStill;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mRadius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3737917975116369338L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public BasicParticle() {
|
||||||
|
mPosition = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mOldPosition = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mVelocity = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mForce = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mMass = 1;
|
||||||
|
mFixed = false;
|
||||||
|
mAge = 0;
|
||||||
|
mTagged = false;
|
||||||
|
mStill = false;
|
||||||
|
mRadius = 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean fixed() {
|
||||||
|
return mFixed;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void fixed(boolean theFixed) {
|
||||||
|
mFixed = theFixed;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float age() {
|
||||||
|
return mAge;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void age(float theAge) {
|
||||||
|
mAge = theAge;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float mass() {
|
||||||
|
return mMass;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void mass(float theMass) {
|
||||||
|
mMass = theMass;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f position() {
|
||||||
|
return mPosition;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f old_position() {
|
||||||
|
return mOldPosition;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setPositionRef(Vector3f thePosition) {
|
||||||
|
mPosition = thePosition;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f velocity() {
|
||||||
|
return mVelocity;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f force() {
|
||||||
|
return mForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean dead() {
|
||||||
|
return false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void accumulateInnerForce(final float theDeltaTime) {
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean tagged() {
|
||||||
|
return mTagged;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void tag(boolean theTag) {
|
||||||
|
mTagged = theTag;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean still() {
|
||||||
|
return mStill;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void still(boolean theStill) {
|
||||||
|
mStill = theStill;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float radius() {
|
||||||
|
return mRadius;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void radius(float theRadius) {
|
||||||
|
mRadius = theRadius;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
72
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/BehaviorParticle.java
Executable file
72
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/BehaviorParticle.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Vector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.behavior.IBehavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class BehaviorParticle
|
||||||
|
extends BasicParticle
|
||||||
|
implements IBehaviorParticle {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector<IBehavior> mBehaviors;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mMaximumInnerForce;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2735849326244271321L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public BehaviorParticle() {
|
||||||
|
mBehaviors = new Vector<IBehavior>();
|
||||||
|
mMaximumInnerForce = 50;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void accumulateInnerForce(final float theDeltaTime) {
|
||||||
|
for (final IBehavior mBehavior : mBehaviors) {
|
||||||
|
if (mBehavior != null) {
|
||||||
|
mBehavior.update(theDeltaTime, this);
|
||||||
|
force().add(mBehavior.force());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
/* clamp to maximum force */
|
||||||
|
if (maximumInnerForce() > 0) {
|
||||||
|
final float mForceLength = force().length();
|
||||||
|
if (mForceLength > maximumInnerForce()) {
|
||||||
|
force().scale(maximumInnerForce() / mForceLength);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float maximumInnerForce() {
|
||||||
|
return mMaximumInnerForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void maximumInnerForce(float theForce) {
|
||||||
|
mMaximumInnerForce = theForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector<IBehavior> behaviors() {
|
||||||
|
return mBehaviors;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
33
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/ConditionalParticle.java
Executable file
33
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/ConditionalParticle.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public abstract class ConditionalParticle
|
||||||
|
extends BasicParticle {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean dead() {
|
||||||
|
return !condition();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public abstract boolean condition();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
36
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/IBehaviorParticle.java
Executable file
36
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/IBehaviorParticle.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Vector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public interface IBehaviorParticle
|
||||||
|
extends Particle {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float maximumInnerForce();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void maximumInnerForce(float theForce);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector<teilchen.behavior.IBehavior> behaviors();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
30
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/IConnection.java
Executable file
30
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/IConnection.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public interface IConnection {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle a();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Particle b();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
70
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/Particle.java
Executable file
70
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/Particle.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.util.SpatialEntity;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public interface Particle
|
||||||
|
extends SpatialEntity {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
boolean fixed();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void fixed(boolean theFixed);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float age();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void age(float theAge);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float mass();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void mass(float theMass);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector3f position();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector3f old_position();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void setPositionRef(Vector3f thePosition);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector3f velocity();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector3f force();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
boolean dead();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
boolean tagged();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void tag(boolean theTag);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void accumulateInnerForce(final float theDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float radius();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void radius(float theRadius);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
boolean still();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void still(boolean theStill);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
374
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/Physics.java
Executable file
374
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/Physics.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,374 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.constraint.IConstraint;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.IForce;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.Spring;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.force.ViscousDrag;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.integration.IIntegrator;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.integration.Midpoint;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.integration.Verlet;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Collection;
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Iterator;
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Vector;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.integration.RungeKutta;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Physics {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector<Particle> mParticles;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector<IForce> mForces;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector<IConstraint> mConstraints;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private IIntegrator mIntegrator;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final float EPSILON = 0.001f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean HINT_OPTIMIZE_STILL = true;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean HINT_REMOVE_DEAD = true;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean HINT_RECOVER_NAN = true;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public int contraint_iterations_per_steps = 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static boolean HINT_UPDATE_OLD_POSITION = true;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Physics() {
|
||||||
|
mParticles = new Vector<Particle>();
|
||||||
|
mForces = new Vector<IForce>();
|
||||||
|
mConstraints = new Vector<IConstraint>();
|
||||||
|
mIntegrator = new Midpoint();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* particles */
|
||||||
|
public void add(Particle theParticle) {
|
||||||
|
mParticles.add(theParticle);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void add(Collection<? extends Particle> theParticles) {
|
||||||
|
mParticles.addAll(theParticles);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void remove(Particle theParticle) {
|
||||||
|
mParticles.remove(theParticle);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void remove(Collection<? extends Particle> theParticles) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mParticles.removeAll(theParticles);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector<Particle> particles() {
|
||||||
|
return mParticles;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Particle particles(final int theIndex) {
|
||||||
|
return mParticles.get(theIndex);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public BasicParticle makeParticle() {
|
||||||
|
BasicParticle myParticle = new BasicParticle();
|
||||||
|
mParticles.add(myParticle);
|
||||||
|
return myParticle;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public BasicParticle makeParticle(final Vector3f thePosition) {
|
||||||
|
BasicParticle myParticle = makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
myParticle.setPositionRef(thePosition);
|
||||||
|
myParticle.old_position().set(myParticle.position());
|
||||||
|
return myParticle;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public BasicParticle makeParticle(final float x, final float y) {
|
||||||
|
BasicParticle myParticle = makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
myParticle.position().set(x, y);
|
||||||
|
myParticle.old_position().set(myParticle.position());
|
||||||
|
return myParticle;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public BasicParticle makeParticle(final float x, final float y, final float z) {
|
||||||
|
BasicParticle myParticle = makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
myParticle.position().set(x, y, z);
|
||||||
|
myParticle.old_position().set(myParticle.position());
|
||||||
|
return myParticle;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public BasicParticle makeParticle(final float x, final float y, final float z, final float pMass) {
|
||||||
|
BasicParticle myParticle = makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
myParticle.position().set(x, y, z);
|
||||||
|
myParticle.mass(pMass);
|
||||||
|
myParticle.old_position().set(myParticle.position());
|
||||||
|
return myParticle;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public BasicParticle makeParticle(final Vector3f thePosition, final float pMass) {
|
||||||
|
BasicParticle myParticle = makeParticle();
|
||||||
|
myParticle.setPositionRef(thePosition);
|
||||||
|
myParticle.old_position().set(myParticle.position());
|
||||||
|
myParticle.mass(pMass);
|
||||||
|
return myParticle;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public <T extends Particle> T makeParticle(Class<T> theParticleClass) {
|
||||||
|
T myParticle;
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
myParticle = theParticleClass.newInstance();
|
||||||
|
mParticles.add(myParticle);
|
||||||
|
} catch (Exception ex) {
|
||||||
|
System.err.println(ex);
|
||||||
|
myParticle = null;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return myParticle;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void removeTags() {
|
||||||
|
for (final Particle myParticle : mParticles) {
|
||||||
|
myParticle.tag(false);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* forces */
|
||||||
|
public void add(IForce theForce) {
|
||||||
|
if (theForce instanceof ViscousDrag && mIntegrator instanceof Verlet) {
|
||||||
|
System.err.println(
|
||||||
|
"### WARNING / 'viscous drag' might have no effect with 'verlet' integration. use 'Verlet.damping(float theDamping)' instead.");
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
mForces.add(theForce);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void addForces(final Vector<? extends IForce> theForces) {
|
||||||
|
mForces.addAll(theForces);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void remove(IForce theForce) {
|
||||||
|
mForces.remove(theForce);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector<IForce> forces() {
|
||||||
|
return mForces;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public IForce forces(final int theIndex) {
|
||||||
|
return mForces.get(theIndex);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void applyForces(final float theDeltaTime) {
|
||||||
|
/* accumulate inner forces */
|
||||||
|
synchronized (mParticles) {
|
||||||
|
final Iterator<Particle> iter = mParticles.iterator();
|
||||||
|
while (iter.hasNext()) {
|
||||||
|
final Particle myParticle = iter.next();
|
||||||
|
if (!myParticle.fixed()) {
|
||||||
|
/* accumulate inner forces */
|
||||||
|
myParticle.accumulateInnerForce(theDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* add new forces to each particle */
|
||||||
|
synchronized (mForces) {
|
||||||
|
Iterator<IForce> iter = mForces.iterator();
|
||||||
|
while (iter.hasNext()) {
|
||||||
|
final IForce mForce = iter.next();
|
||||||
|
if (mForce.active()) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.apply(theDeltaTime, this);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public <T extends IForce> T makeForce(Class<T> theForceClass) {
|
||||||
|
T myForce;
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
myForce = theForceClass.newInstance();
|
||||||
|
mForces.add(myForce);
|
||||||
|
} catch (Exception ex) {
|
||||||
|
System.err.println(ex);
|
||||||
|
myForce = null;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return myForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Spring makeSpring(final Particle theA, final Particle theB) {
|
||||||
|
Spring mySpring = new Spring(theA, theB);
|
||||||
|
mForces.add(mySpring);
|
||||||
|
return mySpring;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Spring makeSpring(final Particle theA,
|
||||||
|
final Particle theB,
|
||||||
|
final float theRestLength) {
|
||||||
|
Spring mySpring = new Spring(theA, theB, theRestLength);
|
||||||
|
mForces.add(mySpring);
|
||||||
|
return mySpring;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Spring makeSpring(final Particle theA,
|
||||||
|
final Particle theB,
|
||||||
|
final float theSpringConstant,
|
||||||
|
final float theSpringDamping) {
|
||||||
|
Spring mySpring = new Spring(theA, theB, theSpringConstant, theSpringDamping);
|
||||||
|
mForces.add(mySpring);
|
||||||
|
return mySpring;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Spring makeSpring(final Particle theA,
|
||||||
|
final Particle theB,
|
||||||
|
final float theSpringConstant,
|
||||||
|
final float theSpringDamping,
|
||||||
|
final float theRestLength) {
|
||||||
|
Spring mySpring = new Spring(theA, theB, theSpringConstant, theSpringDamping, theRestLength);
|
||||||
|
mForces.add(mySpring);
|
||||||
|
return mySpring;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* constraints */
|
||||||
|
public void add(final IConstraint theConstraint) {
|
||||||
|
mConstraints.add(theConstraint);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void addConstraints(final Vector<? extends IConstraint> theConstraints) {
|
||||||
|
mConstraints.addAll(theConstraints);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void remove(final IConstraint theConstraint) {
|
||||||
|
mConstraints.remove(theConstraint);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector<IConstraint> constraints() {
|
||||||
|
return mConstraints;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public IConstraint constraints(final int theIndex) {
|
||||||
|
return mConstraints.get(theIndex);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* integration */
|
||||||
|
public void setInegratorRef(IIntegrator theIntegrator) {
|
||||||
|
mIntegrator = theIntegrator;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public IIntegrator getIntegrator() {
|
||||||
|
return mIntegrator;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void loop(final float theDeltaTime, final int theIterations) {
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < theIterations; i++) {
|
||||||
|
step(theDeltaTime / (float) theIterations);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void step(final float theDeltaTime) {
|
||||||
|
prepareParticles(theDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
handleForces();
|
||||||
|
integrate(theDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
handleParticles(theDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
handleContraints();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
protected synchronized void integrate(float theDeltaTime) {
|
||||||
|
mIntegrator.step(theDeltaTime, this);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
protected synchronized void handleForces() {
|
||||||
|
synchronized (mForces) {
|
||||||
|
final Iterator<IForce> iter = mForces.iterator();
|
||||||
|
while (iter.hasNext()) {
|
||||||
|
final IForce myForce = iter.next();
|
||||||
|
if (myForce.dead()) {
|
||||||
|
iter.remove();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
protected synchronized void handleContraints() {
|
||||||
|
synchronized (mConstraints) {
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < contraint_iterations_per_steps; i++) {
|
||||||
|
final Iterator<IConstraint> iter = mConstraints.iterator();
|
||||||
|
while (iter.hasNext()) {
|
||||||
|
final IConstraint myContraint = iter.next();
|
||||||
|
myContraint.apply(this);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
protected synchronized void handleParticles(float theDeltaTime) {
|
||||||
|
synchronized (mParticles) {
|
||||||
|
final Iterator<Particle> iter = mParticles.iterator();
|
||||||
|
while (iter.hasNext()) {
|
||||||
|
final Particle myParticle = iter.next();
|
||||||
|
/* clear force */
|
||||||
|
myParticle.force().set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
/* age particle */
|
||||||
|
myParticle.age(myParticle.age() + theDeltaTime);
|
||||||
|
/* remove dead */
|
||||||
|
if (HINT_REMOVE_DEAD) {
|
||||||
|
if (myParticle.dead()) {
|
||||||
|
iter.remove();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
/* recover NAN */
|
||||||
|
if (HINT_RECOVER_NAN) {
|
||||||
|
if (myParticle.position().isNaN()) {
|
||||||
|
if (myParticle.old_position().isNaN()) {
|
||||||
|
myParticle.position().set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
myParticle.position().set(myParticle.old_position());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (myParticle.velocity().isNaN()) {
|
||||||
|
myParticle.velocity().set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
/* still */
|
||||||
|
if (HINT_OPTIMIZE_STILL) {
|
||||||
|
final float mySpeed = myParticle.velocity().lengthSquared();
|
||||||
|
myParticle.still(mySpeed > -EPSILON && mySpeed < EPSILON);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
protected synchronized void prepareParticles(float theDeltaTime) {
|
||||||
|
synchronized (mParticles) {
|
||||||
|
final Iterator<Particle> iter = mParticles.iterator();
|
||||||
|
while (iter.hasNext()) {
|
||||||
|
final Particle myParticle = iter.next();
|
||||||
|
if (HINT_UPDATE_OLD_POSITION) {
|
||||||
|
myParticle.old_position().set(myParticle.position());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
49
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/ShortLivedParticle.java
Executable file
49
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/ShortLivedParticle.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class ShortLivedParticle
|
||||||
|
extends BasicParticle {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float _myMaxAge;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public ShortLivedParticle(float theMaxAge) {
|
||||||
|
_myMaxAge = theMaxAge;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public ShortLivedParticle() {
|
||||||
|
this(1);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setMaxAge(float theMaxAge) {
|
||||||
|
_myMaxAge = theMaxAge;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float ageRatio() {
|
||||||
|
return Math.min(age() / _myMaxAge, 1);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean dead() {
|
||||||
|
return age() >= _myMaxAge;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
48
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/VectorfieldParticle.java
Executable file
48
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/VectorfieldParticle.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3i;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class VectorfieldParticle
|
||||||
|
extends BasicParticle {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector3i _myLastUnit;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public VectorfieldParticle() {
|
||||||
|
super();
|
||||||
|
_myLastUnit = new Vector3i();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setLastUnit(Vector3i theUnit) {
|
||||||
|
_myLastUnit = theUnit;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3i getLastUnit() {
|
||||||
|
return _myLastUnit;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void accumulateInnerForce(final float theDeltaTime) {
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
107
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Alignment.java
Executable file
107
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Alignment.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.IBehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.behavior.Util.ProximityStructure;
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Vector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Alignment
|
||||||
|
implements IBehavior,
|
||||||
|
Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4953599448151741585L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mProximity;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mWeight;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f mForce;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector<IBehaviorParticle> mNeighbors;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Alignment() {
|
||||||
|
mProximity = 100.0f;
|
||||||
|
mWeight = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
mForce = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void update(float theDeltaTime, IBehaviorParticle pParent) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
if (mNeighbors != null) {
|
||||||
|
Vector<ProximityStructure> mCloseNeighbors = ProximityStructure.findProximityEntities(pParent, mNeighbors, mProximity);
|
||||||
|
findCommonVelocity(mCloseNeighbors, mForce);
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(weight());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static void findCommonVelocity(Vector<ProximityStructure> mCloseNeighbors, final Vector3f pForce) {
|
||||||
|
/* find away vector */
|
||||||
|
pForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
if (!mCloseNeighbors.isEmpty()) {
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo the vectors could be weighted according to distance: 1.0 -
|
||||||
|
* distance ( for example )
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
for (ProximityStructure p : mCloseNeighbors) {
|
||||||
|
pForce.add(p.particle.velocity());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
pForce.scale(1.0f / mCloseNeighbors.size());
|
||||||
|
pForce.normalize();
|
||||||
|
if (pForce.isNaN()) {
|
||||||
|
pForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public <E extends IBehaviorParticle> void neighbors(final Vector<E> pNeighbors) {
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo well is this OK?
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
mNeighbors = (Vector<IBehaviorParticle>) pNeighbors;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f force() {
|
||||||
|
return mForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float weight() {
|
||||||
|
return mWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void weight(float pWeight) {
|
||||||
|
mWeight = pWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float proximity() {
|
||||||
|
return mProximity;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void proximity(float thePrivacyRadius) {
|
||||||
|
mProximity = thePrivacyRadius;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
159
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Arrival.java
Executable file
159
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Arrival.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.IBehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Arrival
|
||||||
|
implements IBehavior, Verhalten {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final long serialVersionUID = 6897889750581191781L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector3f mSeekPosition;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f mForce;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mWeight;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mBreakRadius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mBreakForce;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mIsArriving;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mHasArrived;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mOverSteer;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Arrival() {
|
||||||
|
mBreakRadius = 50.0f;
|
||||||
|
mBreakForce = 50.0f;
|
||||||
|
mForce = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mSeekPosition = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mWeight = 1;
|
||||||
|
mIsArriving = false;
|
||||||
|
mHasArrived = false;
|
||||||
|
mOverSteer = true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean arriving() {
|
||||||
|
return mIsArriving;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean arrived() {
|
||||||
|
return mHasArrived;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean oversteer() {
|
||||||
|
return mOverSteer;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void oversteer(boolean pOverSteer) {
|
||||||
|
mOverSteer = pOverSteer;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f position() {
|
||||||
|
return mSeekPosition;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setPositionRef(final Vector3f pPoint) {
|
||||||
|
mSeekPosition = pPoint;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void breakforce(float pBreakForce) {
|
||||||
|
mBreakForce = pBreakForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float breakforce() {
|
||||||
|
return mBreakForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void breakradius(float pOutterRadius) {
|
||||||
|
mBreakRadius = pOutterRadius;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float breakradius() {
|
||||||
|
return mBreakRadius;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void update(float theDeltaTime, IBehaviorParticle pParent) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.sub(mSeekPosition, pParent.position());
|
||||||
|
final float myDistanceToArrivalPoint = mForce.length();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/* get direction */
|
||||||
|
if (myDistanceToArrivalPoint < mBreakRadius) {
|
||||||
|
mIsArriving = true;
|
||||||
|
final float mSpeed = pParent.velocity().length();
|
||||||
|
final float MIN_ACCEPTABLE_SPEED = 10.0f;
|
||||||
|
if (mSpeed < MIN_ACCEPTABLE_SPEED) {
|
||||||
|
/* sleep */
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
mHasArrived = true;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
/* break */
|
||||||
|
final boolean USE_WEIGHTED_BREAK_FORCE = true;
|
||||||
|
if (USE_WEIGHTED_BREAK_FORCE) {
|
||||||
|
final float mRatio = myDistanceToArrivalPoint / mBreakRadius;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f mBreakForceVector = new Vector3f(pParent.velocity());
|
||||||
|
mBreakForceVector.scale(-mBreakForce);
|
||||||
|
mBreakForceVector.scale(1.0f - mRatio);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f mSteerForce = new Vector3f(mForce);
|
||||||
|
mSteerForce.scale(pParent.maximumInnerForce() / myDistanceToArrivalPoint);
|
||||||
|
mSteerForce.scale(mRatio);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mForce.add(mBreakForceVector, mSteerForce);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(pParent.velocity().x * -mBreakForce,
|
||||||
|
pParent.velocity().y * -mBreakForce,
|
||||||
|
pParent.velocity().z * -mBreakForce);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
mHasArrived = false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
/* outside of the outter radius continue 'seeking' */
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(pParent.maximumInnerForce() / myDistanceToArrivalPoint);
|
||||||
|
if (mOverSteer) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.sub(mForce, pParent.velocity());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
mIsArriving = false;
|
||||||
|
mHasArrived = false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(weight());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f force() {
|
||||||
|
return mForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float weight() {
|
||||||
|
return mWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void weight(float pWeight) {
|
||||||
|
mWeight = pWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
111
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Cohesion.java
Executable file
111
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Cohesion.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.IBehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.behavior.Util.ProximityStructure;
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Vector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Cohesion
|
||||||
|
implements IBehavior,
|
||||||
|
Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4953599448151741585L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mProximity;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mWeight;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f mForce;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector<IBehaviorParticle> mNeighbors;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Cohesion() {
|
||||||
|
mProximity = 100.0f;
|
||||||
|
mWeight = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
mForce = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void update(float theDeltaTime, IBehaviorParticle pParent) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
if (mNeighbors != null) {
|
||||||
|
Vector<ProximityStructure> mCloseNeighbors = ProximityStructure.findProximityEntities(pParent, mNeighbors, mProximity);
|
||||||
|
findTowardsVector(mCloseNeighbors, mForce);
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(weight());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static void findTowardsVector(Vector<ProximityStructure> mCloseNeighbors, final Vector3f pForce) {
|
||||||
|
/* find away vector */
|
||||||
|
if (!mCloseNeighbors.isEmpty()) {
|
||||||
|
pForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo the vectors could be weighted according to distance: 1.0 -
|
||||||
|
* distance ( for example )
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
for (ProximityStructure p : mCloseNeighbors) {
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f mTowardsVector = mathematik.Util.scale(p.distanceVec, -1.0f);
|
||||||
|
pForce.add(mTowardsVector);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
pForce.scale(1.0f / mCloseNeighbors.size());
|
||||||
|
pForce.normalize();
|
||||||
|
if (pForce.isNaN()) {
|
||||||
|
pForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
pForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public <E extends IBehaviorParticle> void neighbors(final Vector<E> pNeighbors) {
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo well is this OK?
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
mNeighbors = (Vector<IBehaviorParticle>) pNeighbors;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f force() {
|
||||||
|
return mForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float weight() {
|
||||||
|
return mWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void weight(float pWeight) {
|
||||||
|
mWeight = pWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float proximity() {
|
||||||
|
return mProximity;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void proximity(float thePrivacyRadius) {
|
||||||
|
mProximity = thePrivacyRadius;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
77
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Flee.java
Executable file
77
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Flee.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.IBehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Flee
|
||||||
|
implements IBehavior, Verhalten {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final long serialVersionUID = -6530887943347815188L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector3f mFleePosition;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector3f mForce;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mWeight = 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Flee() {
|
||||||
|
mFleePosition = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mForce = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f position() {
|
||||||
|
return mFleePosition;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setPositionRef(final Vector3f thePoint) {
|
||||||
|
mFleePosition = thePoint;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void update(float theDeltaTime, IBehaviorParticle theParent) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.sub(theParent.position(), mFleePosition);
|
||||||
|
final float myDistanceToPoint = mForce.length();
|
||||||
|
if (myDistanceToPoint > SMALLEST_ACCEPTABLE_DISTANCE) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(theParent.maximumInnerForce() / myDistanceToPoint);
|
||||||
|
mForce.sub(mForce, theParent.velocity());
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(weight());
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f force() {
|
||||||
|
return mForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float weight() {
|
||||||
|
return mWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void weight(float theWeight) {
|
||||||
|
mWeight = theWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
42
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/IBehavior.java
Executable file
42
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/IBehavior.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.IBehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public interface IBehavior
|
||||||
|
extends Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void update(float theDeltaTime, final IBehaviorParticle pParent);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Vector3f force();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float weight();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
void weight(float theWeight);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
127
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Motor.java
Executable file
127
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Motor.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.IBehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Motor
|
||||||
|
implements IBehavior,
|
||||||
|
Verhalten {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final long serialVersionUID = -3781170603537691466L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector3f mDirection;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mStrength;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f mForce;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mWeight;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mAutoNormalizeDirection;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mActive;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mAutoUpdateDirection;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f AUTO_RECOVER_DIRECTION;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Motor() {
|
||||||
|
mDirection = new Vector3f(1, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
mForce = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mActive = true;
|
||||||
|
mStrength = 1;
|
||||||
|
mWeight = 1;
|
||||||
|
mAutoUpdateDirection = false;
|
||||||
|
mAutoNormalizeDirection = true;
|
||||||
|
AUTO_RECOVER_DIRECTION = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
AUTO_RECOVER_DIRECTION.randomize();
|
||||||
|
AUTO_RECOVER_DIRECTION.z = 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean active() {
|
||||||
|
return mActive;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void active(boolean pActive) {
|
||||||
|
mActive = pActive;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float strength() {
|
||||||
|
return mStrength;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void strength(final float theStrength) {
|
||||||
|
mStrength = theStrength;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f direction() {
|
||||||
|
return mDirection;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setDirectionRef(final Vector3f theDirection) {
|
||||||
|
mDirection = theDirection;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void auto_update_direction(boolean pAutoUpdateDirection) {
|
||||||
|
mAutoUpdateDirection = pAutoUpdateDirection;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void auto_normalize_direction(boolean pAutoNormalizeDirection) {
|
||||||
|
mAutoNormalizeDirection = pAutoNormalizeDirection;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void update(float theDeltaTime, IBehaviorParticle pParent) {
|
||||||
|
if (mActive) {
|
||||||
|
if (mAutoUpdateDirection) {
|
||||||
|
if (pParent.velocity().length() > 0.0f) {
|
||||||
|
mDirection.set(pParent.velocity());
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
mDirection.set(AUTO_RECOVER_DIRECTION);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (mAutoNormalizeDirection) {
|
||||||
|
mDirection.normalize();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(mStrength, mDirection);
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(mWeight, mForce);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f force() {
|
||||||
|
return mForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float weight() {
|
||||||
|
return mWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void weight(float theWeight) {
|
||||||
|
mWeight = theWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
96
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Seek.java
Executable file
96
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Seek.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.IBehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Seek
|
||||||
|
implements IBehavior, Verhalten {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final long serialVersionUID = -3781170603537691477L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector3f mSeekPosition;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector3f mForce;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mWeight = 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mDistanceToPoint;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mOverSteer;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Seek() {
|
||||||
|
mSeekPosition = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mForce = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mOverSteer = false;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean oversteer() {
|
||||||
|
return mOverSteer;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void oversteer(boolean pOverSteer) {
|
||||||
|
mOverSteer = pOverSteer;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f position() {
|
||||||
|
return mSeekPosition;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void setPositionRef(final Vector3f thePoint) {
|
||||||
|
mSeekPosition = thePoint;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float distancetopoint() {
|
||||||
|
return mDistanceToPoint;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void update(float theDeltaTime, IBehaviorParticle theParent) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.sub(mSeekPosition, theParent.position());
|
||||||
|
mDistanceToPoint = mForce.length();
|
||||||
|
if (mDistanceToPoint > SMALLEST_ACCEPTABLE_DISTANCE) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(theParent.maximumInnerForce() / mDistanceToPoint);
|
||||||
|
if (mOverSteer) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.sub(mForce, theParent.velocity());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(weight());
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f force() {
|
||||||
|
return mForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float weight() {
|
||||||
|
return mWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void weight(float theWeight) {
|
||||||
|
mWeight = theWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
110
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Separation.java
Executable file
110
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Separation.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.IBehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.behavior.Util.ProximityStructure;
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Vector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Separation
|
||||||
|
implements IBehavior,
|
||||||
|
Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4953599448151741585L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mProximity;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mWeight;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f mForce;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector<IBehaviorParticle> mNeighbors;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Separation() {
|
||||||
|
mProximity = 100.0f;
|
||||||
|
mWeight = 1.0f;
|
||||||
|
mForce = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void update(float theDeltaTime, IBehaviorParticle pParent) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
if (mNeighbors != null) {
|
||||||
|
Vector<ProximityStructure> mCloseNeighbors = ProximityStructure.findProximityEntities(pParent, mNeighbors, mProximity);
|
||||||
|
findAwayVector(mCloseNeighbors, mForce);
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(weight());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private static void findAwayVector(Vector<ProximityStructure> mCloseNeighbors, final Vector3f pForce) {
|
||||||
|
/* find away vector */
|
||||||
|
if (!mCloseNeighbors.isEmpty()) {
|
||||||
|
pForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo the vectors could be weighted according to distance: 1.0 -
|
||||||
|
* distance ( for example )
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
for (ProximityStructure p : mCloseNeighbors) {
|
||||||
|
pForce.add(p.distanceVec);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
pForce.scale(1.0f / mCloseNeighbors.size());
|
||||||
|
pForce.normalize();
|
||||||
|
if (pForce.isNaN()) {
|
||||||
|
pForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
pForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public <E extends IBehaviorParticle> void neighbors(final Vector<E> pNeighbors) {
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @todo well is this OK?
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
mNeighbors = (Vector<IBehaviorParticle>) pNeighbors;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f force() {
|
||||||
|
return mForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float weight() {
|
||||||
|
return mWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void weight(float pWeight) {
|
||||||
|
mWeight = pWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float proximity() {
|
||||||
|
return mProximity;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void proximity(float thePrivacyRadius) {
|
||||||
|
mProximity = thePrivacyRadius;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
91
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Steering.java
Executable file
91
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Steering.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.IBehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Steering implements IBehavior,
|
||||||
|
Verhalten {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f mForce;
|
||||||
|
private final Vector3f mUPVector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mWeight;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mSteering = 0.0f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mActive = true;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Steering() {
|
||||||
|
mForce = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mUPVector = new Vector3f(0, 0, -1);
|
||||||
|
mWeight = 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void update(float theDeltaTime, IBehaviorParticle pParent) {
|
||||||
|
if (mActive) {
|
||||||
|
/* 2D warning -- ignoring z-axis for now */
|
||||||
|
Vector3f mDirection = new Vector3f(pParent.velocity());
|
||||||
|
if (mDirection.lengthSquared() > 0) {
|
||||||
|
mDirection.normalize();
|
||||||
|
mDirection = mathematik.Util.cross(mDirection, mUPVector);
|
||||||
|
mDirection.scale(mSteering);
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(mDirection);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float steering_strength() {
|
||||||
|
return mSteering;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void steering_strength(float pSteering) {
|
||||||
|
mSteering = pSteering;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f force() {
|
||||||
|
return mForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f upvector() {
|
||||||
|
return mUPVector;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float weight() {
|
||||||
|
return mWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void weight(float pWeight) {
|
||||||
|
mWeight = pWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void active(boolean pActive) {
|
||||||
|
mActive = pActive;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
66
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Util.java
Executable file
66
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Util.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.IBehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.util.Vector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Util {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static class ProximityStructure {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Particle particle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final Vector3f distanceVec;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public final float distance;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public ProximityStructure(Particle pP, Vector3f pDistanceVec, float pDistance) {
|
||||||
|
particle = pP;
|
||||||
|
distanceVec = pDistanceVec;
|
||||||
|
distance = pDistance;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public static Vector<ProximityStructure> findProximityEntities(IBehaviorParticle pParentEntity,
|
||||||
|
Vector<IBehaviorParticle> pNeighborsEntity,
|
||||||
|
float pProximity) {
|
||||||
|
/* find neighbors in proximity */
|
||||||
|
Vector<ProximityStructure> mCloseNeighbors = new Vector<ProximityStructure>();
|
||||||
|
for (IBehaviorParticle p : pNeighborsEntity) {
|
||||||
|
if (!p.equals(pParentEntity)) { /* exclude self */
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f mDistanceVec = mathematik.Util.sub(pParentEntity.position(), p.position());
|
||||||
|
final float mDistance = mDistanceVec.length();
|
||||||
|
if (mDistance <= pProximity) {
|
||||||
|
mCloseNeighbors.add(new ProximityStructure(p, mDistanceVec, mDistance));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return mCloseNeighbors;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
33
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Verhalten.java
Executable file
33
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Verhalten.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import java.io.Serializable;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public interface Verhalten
|
||||||
|
extends Serializable {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
float SMALLEST_ACCEPTABLE_DISTANCE = 0.01f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
122
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Wander.java
Executable file
122
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/behavior/Wander.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.behavior;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Random;
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.IBehaviorParticle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class Wander
|
||||||
|
implements IBehavior {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static final long serialVersionUID = 4957162698340669663L;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector3f mForce;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mSteeringStrength;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mSteeringOffset;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mCurrentSteeringStrength;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private Vector3f mUpVector;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mWeight;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Random mRandom;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private boolean mActive;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Wander() {
|
||||||
|
mRandom = new Random();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mForce = new Vector3f();
|
||||||
|
mSteeringStrength = 10f;
|
||||||
|
mSteeringOffset = 5f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mUpVector = new Vector3f(0, 0, 1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
mWeight = 1;
|
||||||
|
mActive = true;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public boolean active() {
|
||||||
|
return mActive;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void active(boolean pActive) {
|
||||||
|
mActive = pActive;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f force() {
|
||||||
|
return mForce;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float weight() {
|
||||||
|
return mWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void weight(float theWeight) {
|
||||||
|
mWeight = theWeight;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void update(float pDeltaTime, IBehaviorParticle pParent) {
|
||||||
|
if (mActive && pParent.velocity().length() > 0) {
|
||||||
|
mCurrentSteeringStrength += mRandom.getFloat(-0.5f, 0.5f) * mSteeringOffset;
|
||||||
|
mCurrentSteeringStrength = Math.max(Math.min(mCurrentSteeringStrength, mSteeringStrength), -mSteeringStrength);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
final Vector3f mWanderTarget = mathematik.Util.cross(mUpVector, pParent.velocity());
|
||||||
|
mWanderTarget.normalize();
|
||||||
|
mWanderTarget.scale(mCurrentSteeringStrength);
|
||||||
|
if (mWanderTarget.isNaN()) {
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
mForce.scale(mWeight, mWanderTarget);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
mForce.set(0, 0, 0);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public Vector3f upvector() {
|
||||||
|
return mUpVector;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float steeringstrength() {
|
||||||
|
return mSteeringStrength;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void steeringstrength(final float theSteeringStrength) {
|
||||||
|
mSteeringStrength = theSteeringStrength;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public float steeringoffset() {
|
||||||
|
return mSteeringOffset;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void steeringoffset(final float theSteeringOffset) {
|
||||||
|
mSteeringOffset = theSteeringOffset;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
79
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/constraint/AngleConstraintStick.java
Executable file
79
day3/libs/teilchen/src/teilchen/constraint/AngleConstraintStick.java
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
|||||||
|
/*
|
||||||
|
* Teilchen
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* Copyright (C) 2013
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||||
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||||
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||||
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||||
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
||||||
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||||
|
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
|
||||||
|
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
|
||||||
|
* {@link http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html}
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
package teilchen.constraint;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import mathematik.Vector3f;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import teilchen.Particle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public class AngleConstraintStick
|
||||||
|
extends Stick {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Particle mParticleA;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Particle mParticleB;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private final Particle mParticleC;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
private float mMinAngle;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* particles are connected like this: A -- B -- C
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param pParticleA
|
||||||
|
* @param pParticleB
|
||||||
|
* @param pParticleC
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
public AngleConstraintStick(Particle pParticleA, Particle pParticleB, Particle pParticleC) {
|
||||||
|
super(pParticleA, pParticleC);
|
||||||
|
mParticleA = pParticleA;
|
||||||
|
mParticleB = pParticleB;
|
||||||
|
mParticleC = pParticleC;
|
||||||
|
mMinAngle = Float.MAX_VALUE;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void min_angle(float pAngle) {
|
||||||
|
mMinAngle = pAngle;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void pre_step() {
|
||||||
|
Vector3f ab = mathematik.Util.sub(mParticleA.position(), mParticleB.position());
|
||||||
|
Vector3f cb = mathematik.Util.sub(mParticleC.position(), mParticleB.position());
|
||||||
|
final float mCurrentAngle = ab.angle(cb);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (mCurrentAngle < mMinAngle) {
|
||||||
|
final float b = ab.length();
|
||||||
|
final float c = cb.length();
|
||||||
|
// a = sqrt ( b*b + c*c - 2bc*cosA )
|
||||||
|
final float mDistance = (float) Math.sqrt(b * b + c * c - 2 * b * c * (float) Math.cos(mMinAngle));
|
||||||
|
restlength(mDistance);
|
||||||
|
active(true);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
public void post_step() {
|
||||||
|
active(false);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user